Chinese Optics Letters, 2015, 13 (10): 103101, Published Online: Sep. 13, 2018
Role of oxygen defects in inducing the blue photoluminescence of zinc oxide films deposited by magnetron sputtering  Download: 987次
Download: 987次
310.6860 Thin films, optical properties 310.1860 Deposition and fabrication 300.6280 Spectroscopy, fluorescence and luminescence 260.3800 Luminescence
Abstract
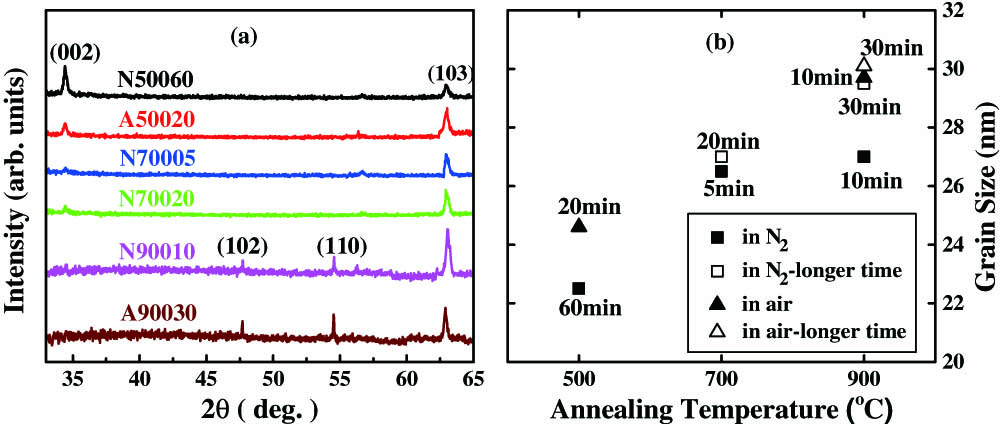
A number of zinc oxide (ZnO) films are deposited on silicon substrates using the magnetron sputtering method. After undergoing thermal treatment under different conditions, those films exhibit hexagonal wurtzite structures and different photoluminescent characteristics. Besides the notable ultraviolet emission, which is related to the free exciton effect, a distinct blue fluorescence around 475 nm is found in some special samples. The blue photoluminescence emission of the ZnO film is believed to be caused by oxygen vacancies.
Kun Chen, Huanfeng Zhu, Xinyu Yi, Shuai Cheng, Jing Li, Songyou Wang, Ming Lu, Min Xu, Li Ma, Lei Lü. Role of oxygen defects in inducing the blue photoluminescence of zinc oxide films deposited by magnetron sputtering[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2015, 13(10): 103101.