Chinese Optics Letters, 2016, 14 (4): 040301, Published Online: Aug. 6, 2018
Thermal light subwavelength diffraction using positive and negative correlations  Download: 909次
Download: 909次
030.0030 Coherence and statistical optics 030.4280 Noise in imaging systems 050.0050 Diffraction and gratings 110.1650 Coherence imaging 110.6150 Speckle imaging
Abstract
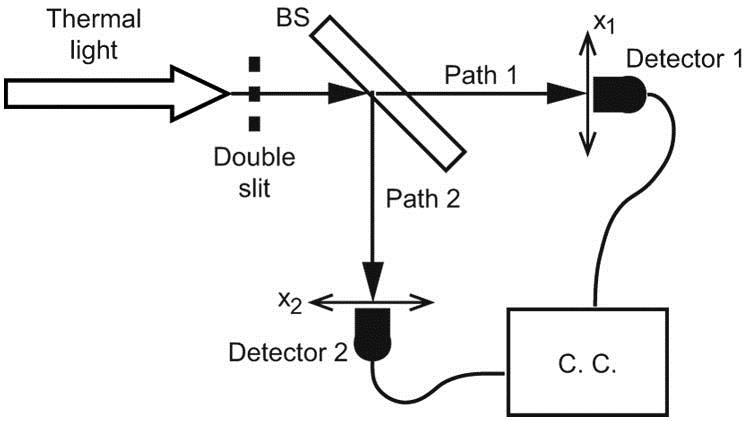
Ghost imaging and diffraction, inspired by the Hanbury Brown and Twiss effect, have potential in both classical and quantum optics regimes on account of their nonlocal characteristics and subwavelength resolution capability, and therefore have aroused particular interest. By extending the correspondence imaging scheme, we utilize the positive and negative intensity correlations in diffraction and perform subwavelength diffraction with pseudo-thermal light. In the experiment, a subwavelength (λ / 2
Mingjie Sun, Xingdan He, Mingfei Li, Ling'an Wu. Thermal light subwavelength diffraction using positive and negative correlations[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2016, 14(4): 040301.