Chinese Optics Letters, 2016, 14 (4): 043101, Published Online: Aug. 6, 2018
Molybdenum thin films fabricated by rf and dc sputtering for Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cell applications
Abstract
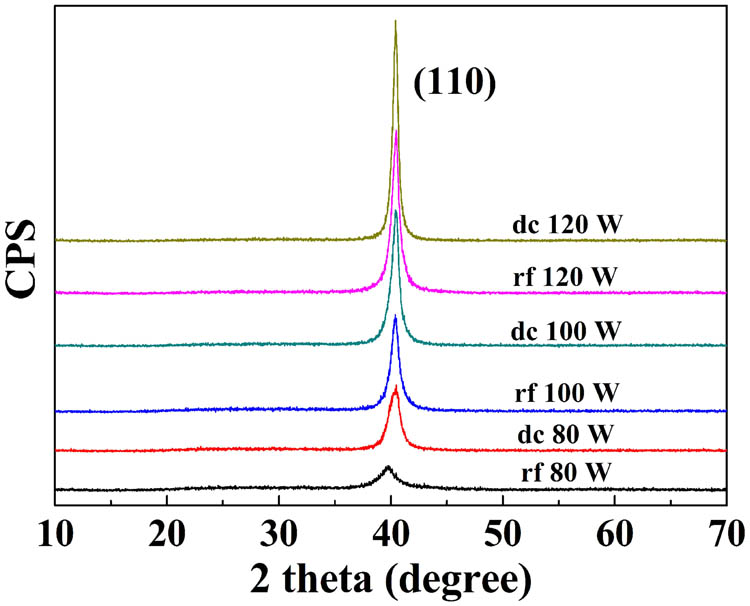
Molybdenum (Mo) thin films, most commonly used as electrical back contacts in Cu ( In , Ga ) Se 2
Beibei Guo, Yaoming Wang, Xiaolong Zhu, Mingsheng Qin, Dongyun Wan, Fuqiang Huang. Molybdenum thin films fabricated by rf and dc sputtering for Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cell applications[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2016, 14(4): 043101.