High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 2017, 5 (2): 02000e10, Published Online: Jul. 26, 2018
An investigation progress toward Be-based ablator materials for the inertial confinement fusion
Abstract
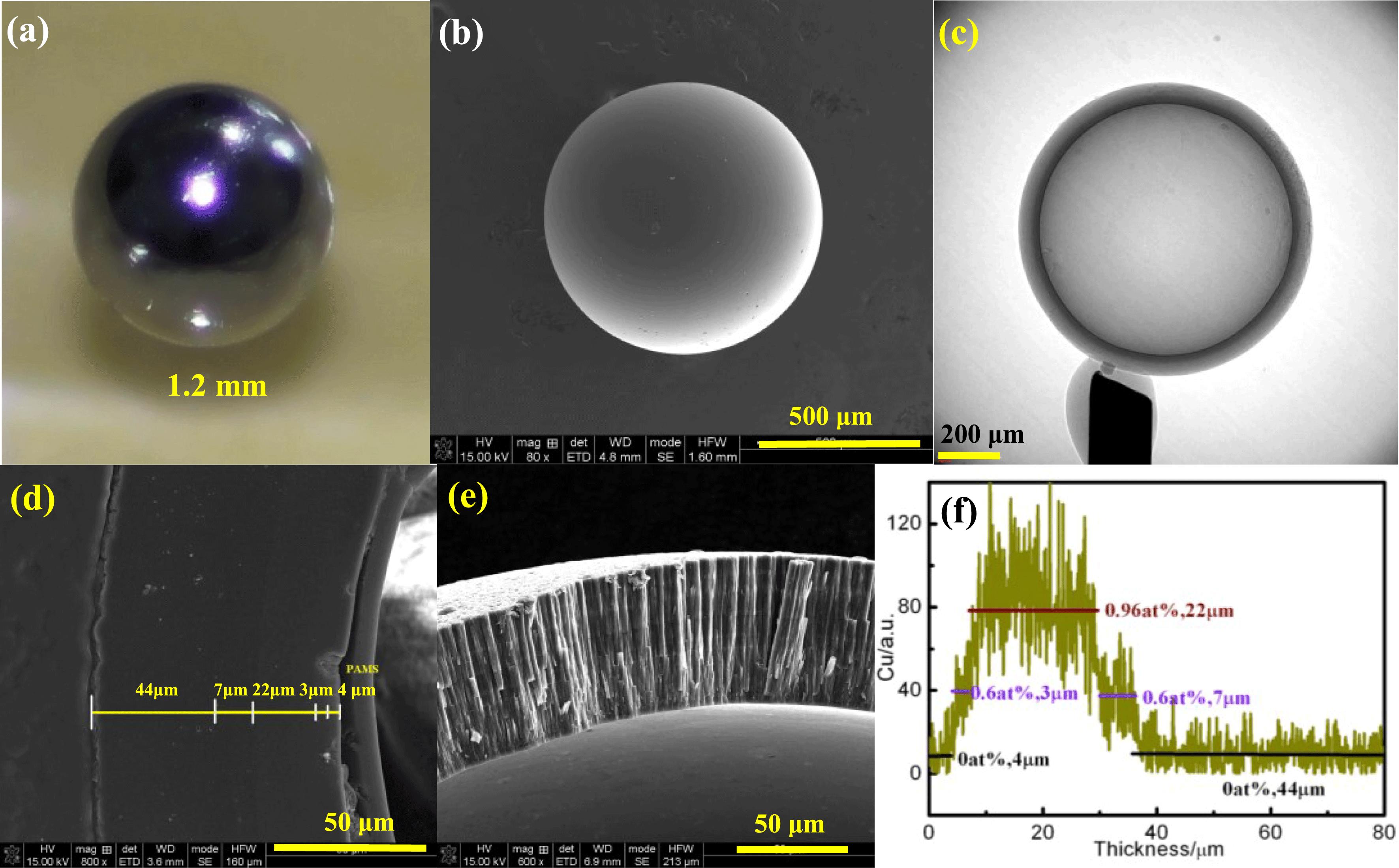
The Be-based materials with many particular properties lead to an important research subject. The investigation progresses in the fabrication technologies are introduced here, including main three kinds of Be-based materials, such as Be–Cu capsule, $\text{Be}_{2}\text{C}$ ablator and high-purity Be material. Compared with the pioneer workgroup on Be-based materials, the differences in Be–Cu target fabrication were described, and a grain refinement technique by an active hydrogen reaction for Be coating was proposed uniquely. $\text{Be}_{2}\text{C}$ coatings were first prepared by the DC reactive magnetron sputtering with a high deposition rate $({\sim}300~\text{nm}/\text{h})$ . Pure polycrystalline $\text{Be}_{2}\text{C}$ films with uniform microstructures, smooth surface, high density $({\sim}2.2~\text{g}\cdot \text{cm}^{3})$ and good optical transparency were fabricated. In addition, the high-purity Be materials with metal impurities in a ppm magnitude were fabricated by the pyrolysis of organometallic Be.
Bingchi Luo, Jiqiang Zhang, Yudan He, Long Chen, Jiangshan Luo, Kai Li, Weidong Wu. An investigation progress toward Be-based ablator materials for the inertial confinement fusion[J]. High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 2017, 5(2): 02000e10.