激光与光电子学进展, 2020, 57 (24): 242803, 网络出版: 2020-11-16
基于稀疏网络的可见光/近红外反射光谱土壤有机质含量估算  下载: 924次
下载: 924次
Estimation Method of VIS-NIR Spectroscopy for Soil Organic Matter Based on Sparse Networks
遥感 土壤有机质 可见-近红外光谱 稀疏自编码 BP神经网络 remote sensing soil organic matter visible-near infrared spectroscopy sparse self-encoding BP neural network
摘要
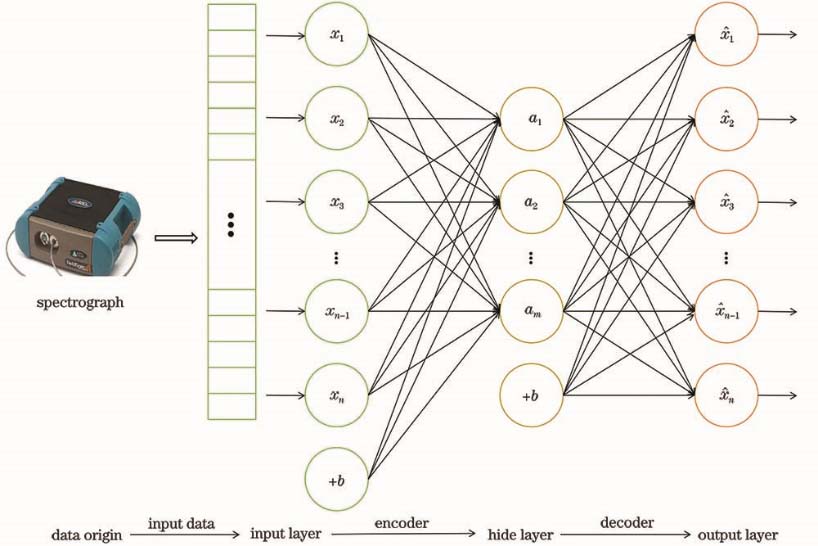
采集艾比湖湿地89个典型样点和土壤实测光谱数据,对所测土壤光谱进行一阶微分变换预处理,采用连续投影算法(SPA)、主成分分析(PCA)和稀疏自编码(SAE)对光谱数据进行特征提取,结合偏最小二乘回归与BP(Back Propagation)神经网络构建SOM估算模型。实验结果表明,SAE方法能够有效对光谱进行压缩;相比于PLSR模型,BP模型能够较好地处理光谱中复杂的非线性信息;SAE-BP方法在估算SOM中取得的精度最高。网络模型的建模方式能够显著提高VIS-NIR光谱反演土壤有机质模型的稳定性和精度,当面对光谱中复杂的非线性问题时,具有很强的解析力和较好的模型稳健性,为使用VIS-NIR数据估算SOM提供一种新思路。
Abstract
This research presents a novel approach for using VIS-NIR spectroscopy for soil organic matter (SOM) estimation. Soil spectrum data is collected from 89 samples retrieved from the Aibi Lake wetland. The samples are measured using a first-order differential transformation achieved through a continuous projection algorithm, a principal component analysis, and a sparse auto-encoder (SAE). The extracted data is then combined with a partial least squares regression (PLSR) and backpropagation (BP) neural network for the purpose of building a SOM estimation model. Experimental results show that the SAE method is able to effectively compress the spectrum. The BP model is shown to handle the complex and nonlinear information of the spectrum better than the PLSR model. Meanwhile, the SAE-BP method has the highest accuracy for estimating SOM. The network model is shown to significantly improve the stability and accuracy of the vis-NIR spectrum inversion of the SOM model. This model shows a robust and strong analytical power when faced with complex nonlinear problems in the spectrum.
冉思, 丁建丽, 葛翔宇, 刘博华, 张钧泳. 基于稀疏网络的可见光/近红外反射光谱土壤有机质含量估算[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2020, 57(24): 242803. Si Ran, Jianli Ding, Xiangyu Ge, Bohua Liu, Junyong Zhang. Estimation Method of VIS-NIR Spectroscopy for Soil Organic Matter Based on Sparse Networks[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2020, 57(24): 242803.