Chinese Optics Letters, 2021, 19 (4): 041402, Published Online: Jan. 8, 2021
Combined studies of surface evolution and crack healing for the suppression of negative factors during CO2 laser repairing of fused silica  Download: 854次
Download: 854次
Abstract
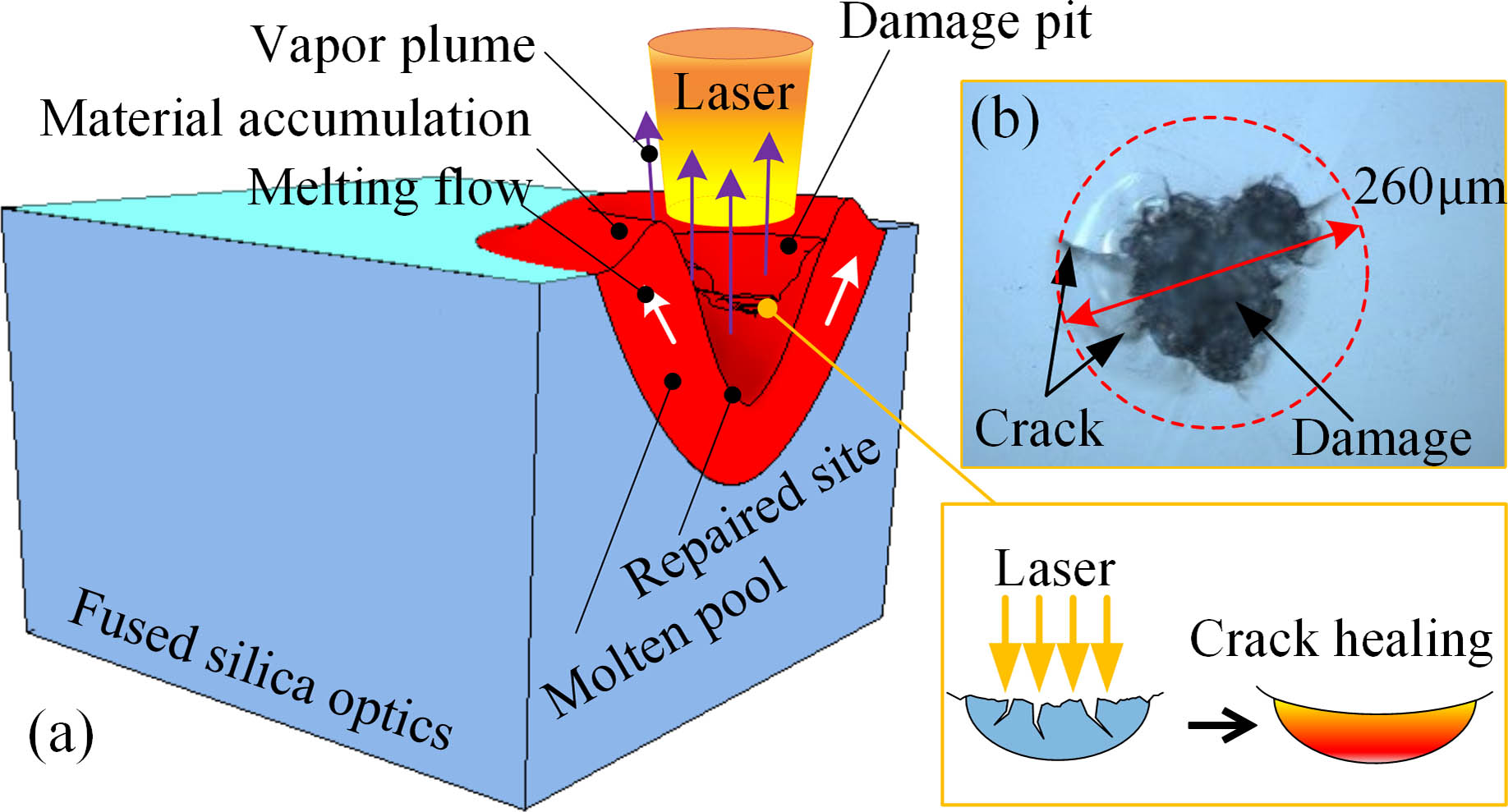
In order to reveal the evolution mechanism of repaired morphology and the material’s migration mechanism on the crack surface in the process of
Chao Tan, Linjie Zhao, Mingjun Chen, Jian Cheng, Zhaoyang Yin, Qi Liu, Hao Yang, Wei Liao. Combined studies of surface evolution and crack healing for the suppression of negative factors during CO2 laser repairing of fused silica[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2021, 19(4): 041402.