激光与光电子学进展, 2019, 56 (24): 241003, 网络出版: 2019-11-26
基于循环卷积神经网络的甲状腺恶性结节检测  下载: 972次
下载: 972次
Malignant Thyroid Nodule Detection Based on Circular Convolutional Neural Network
图像处理 神经网络 超声图像 甲状腺 图像分类预测 image processing neural network ultrasound image thyroid image classification prediction
摘要
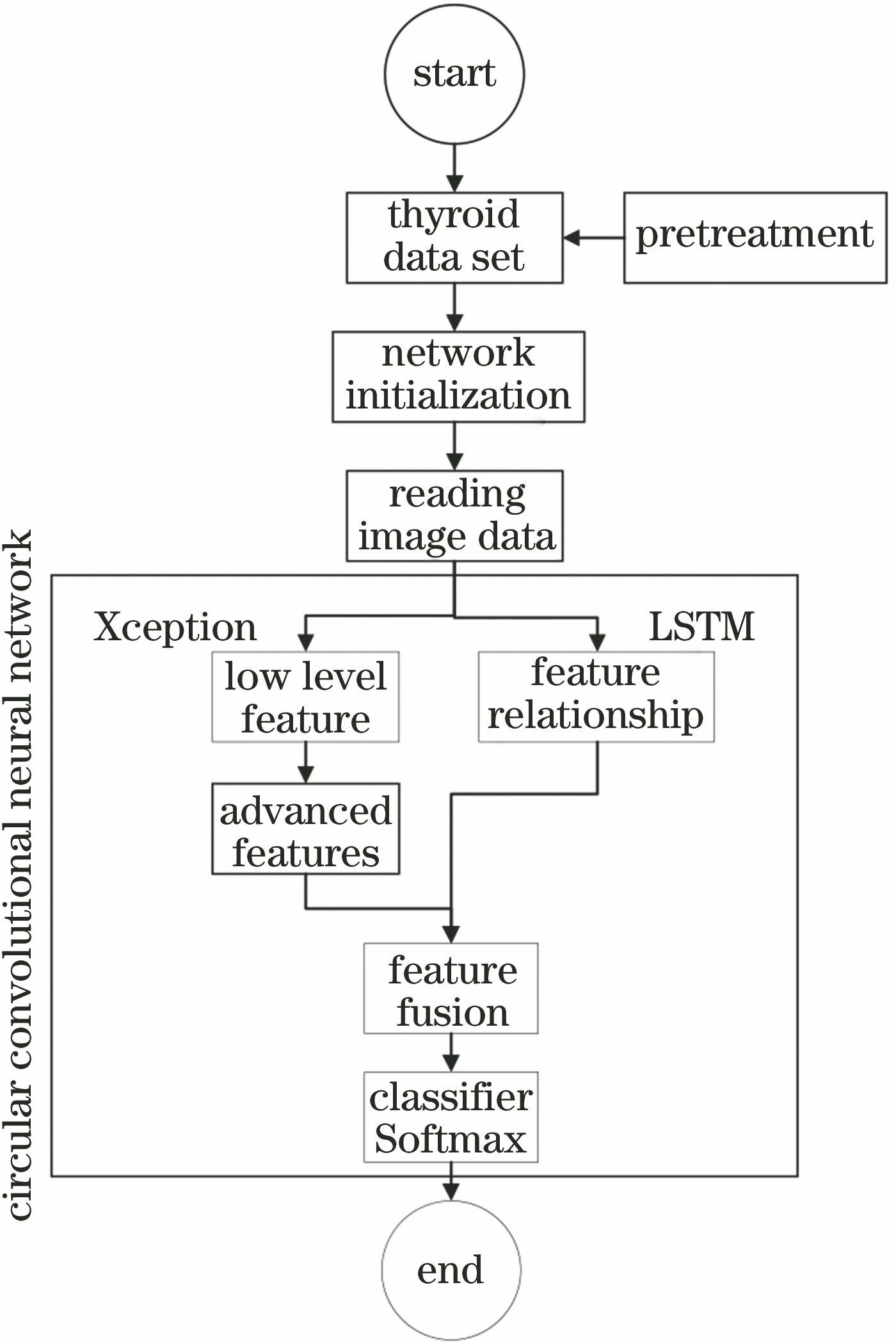
针对过拟合及甲状腺恶性结节细粒度分类(恶性分为恶性与高度恶化)的问题,提出一种基于循环卷积神经网络的分类方法。将Xception网络与长短时记忆网络(LSTM)作为互不干扰的两部分,分别对甲状腺结节样本进行特征提取得到两个权重矩阵;通过Merge算法融合为单个权重矩阵,将单个权重矩阵导入卷积神经网络(CNN)进行特征提取与池化;采用L2正则化的Softmax函数作为分类器,完成循环卷积神经网络的训练与测试。实验结果表明,甲状腺恶性结节细粒度分类的准确率为87.00%,并有较好的特征提取能力。
Abstract
In this study, a classification method is proposed based on a circular convolutional neural network (CNN) to deal with the issues of over-fitting and fine-grained classification of the malignant and highly deteriorated thyroid nodules. First, the Xception network and long short-term memory network (LSTM) are used as two non-interference parts. Next, the features of thyroid nodule samples are separately extracted to obtain two weight matrices, which are subsequently merged into a single weight matrix using the Merge algorithm. Further, the single weight matrix is imported into the CNN for feature extraction and pooling. Finally, the Softmax function of L2 regularization is used as a classifier to complete the training and testing of the circular CNN. Our experimental results denote that the accuracy of the fine-grained classification of malignant thyroid nodules is 87.00%, denoting a good feature-extraction capability.
郑斌, 杨晨, 马小萍, 刘立波. 基于循环卷积神经网络的甲状腺恶性结节检测[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2019, 56(24): 241003. Bin Zheng, Chen Yang, Xiaoping Ma, Libo Liu. Malignant Thyroid Nodule Detection Based on Circular Convolutional Neural Network[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2019, 56(24): 241003.