激光与光电子学进展, 2020, 57 (16): 160003, 网络出版: 2020-08-05
深度学习行人再识别研究综述  下载: 1471次
下载: 1471次
Person Re-Identification Research via Deep Learning
机器视觉 深度学习 行人再识别 特征表达 局部特征 生成对抗网络 machine vision deep learning person re-identification feature expression local features generative adversarial networks
摘要
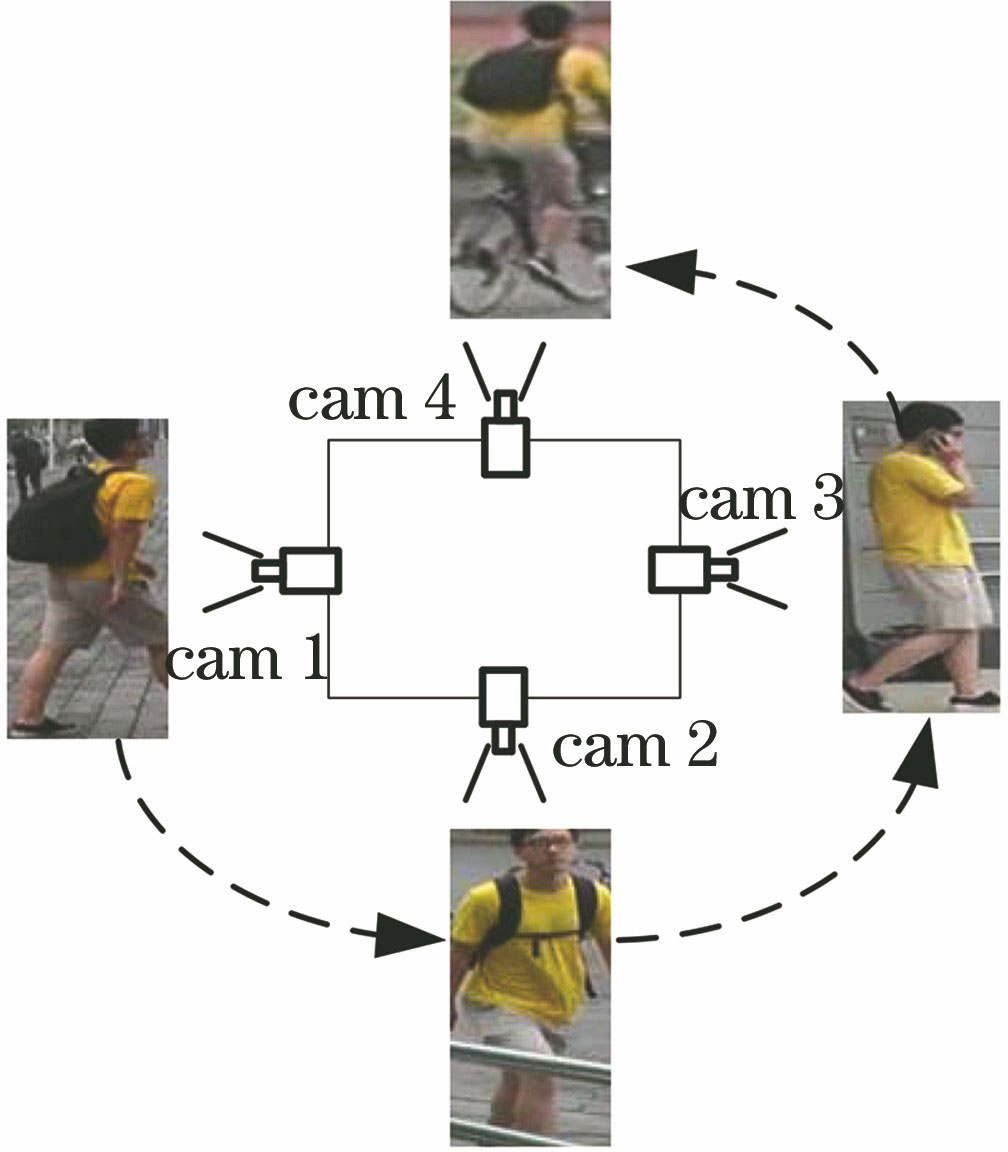
行人再识别的主要任务是利用计算机视觉对特定行人进行跨视域匹配和检索。相比于传统算法,由数据驱动的深度学习方法所提取的特征更能表征行人之间的区分性。对行人再识别的背景及研究历史、主要面临的挑战、主要方法、数据集及评价指标进行了梳理和总结。主要从特征表达、局部特征、生成对抗网络三个方面对行人再识别的算法进行分析,列举了行人再识别9个常用数据集、3个评价标准和14种典型方法在Market1501数据集上取得的准确率,最后对行人再识别的未来研究方向进行展望。
Abstract
The main task of person re-identification is to use computer vision to match and retrieve specific person across view fields. Compared with the traditional algorithm, deep learning is a more appropriate representative method for the discrimination between persons using data-driven extraction features. This study summarized the background and research history, main challenges, main methods, datasets, and evaluation index of person re-identification. The algorithms of person re-identification were mainly analyzed based on three aspects: feature expression, local features, and generative adversarial networks. The accuracy of 9 common datasets, 3 evaluation criteria, and 14 typical methods of person re-identification on the Market1501 dataset was listed. Finally, the prospects for the future research direction of person re-identification were established.
卢健, 陈旭, 罗毛欣, 王航英. 深度学习行人再识别研究综述[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2020, 57(16): 160003. Jian Lu, Xu Chen, Maoxin Luo, Hangying Wang. Person Re-Identification Research via Deep Learning[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2020, 57(16): 160003.