Chinese Optics Letters, 2021, 19 (9): 092501, Published Online: Jul. 8, 2021
Avalanche mechanism analysis of 4H-SiC n-i-p and p-i-n avalanche photodiodes working in Geiger mode
Abstract
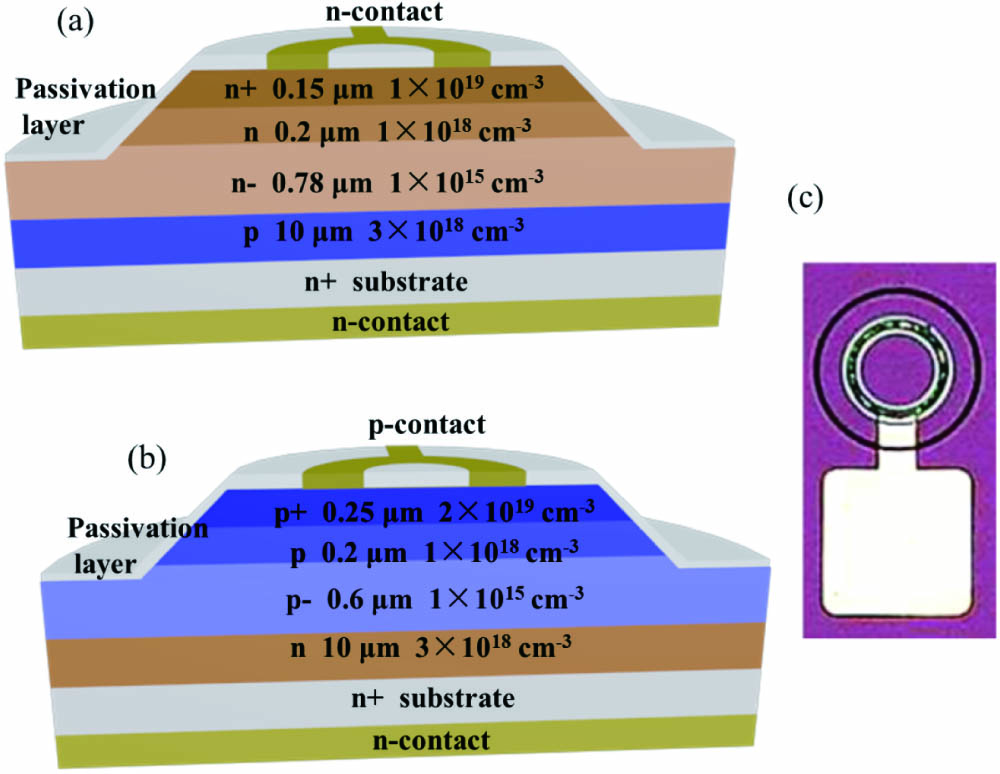
Understanding detailed avalanche mechanisms is critical for design optimization of avalanche photodiodes (APDs). In this work, avalanche characteristics and single photon counting performance of 4H-SiC n-i-p and p-i-n APDs are compared. By studying the evolution of breakdown voltage as a function of incident light wavelength, it is confirmed that at the deep ultraviolet (UV) wavelength region the avalanche events in 4H-SiC n-i-p APDs are mainly induced by hole-initiated ionization, while electron-initiated ionization is the main cause of avalanche breakdown in 4H-SiC p-i-n APDs. Meanwhile, at the same dark count rate, the single photon counting efficiency of n-i-p APDs is considerably higher than that of p-i-n APDs. The higher performance of n-i-p APDs can be explained by the larger impact ionization coefficient of holes in 4H-SiC. In addition, this is the first time, to the best of our knowledge, to report single photon detection performance of vertical 4H-SiC n-i-p-n APDs.
Linlin Su, Weizong Xu, Dong Zhou, Fangfang Ren, Dunjun Chen, Rong Zhang, Youdou Zheng, Hai Lu. Avalanche mechanism analysis of 4H-SiC n-i-p and p-i-n avalanche photodiodes working in Geiger mode[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2021, 19(9): 092501.