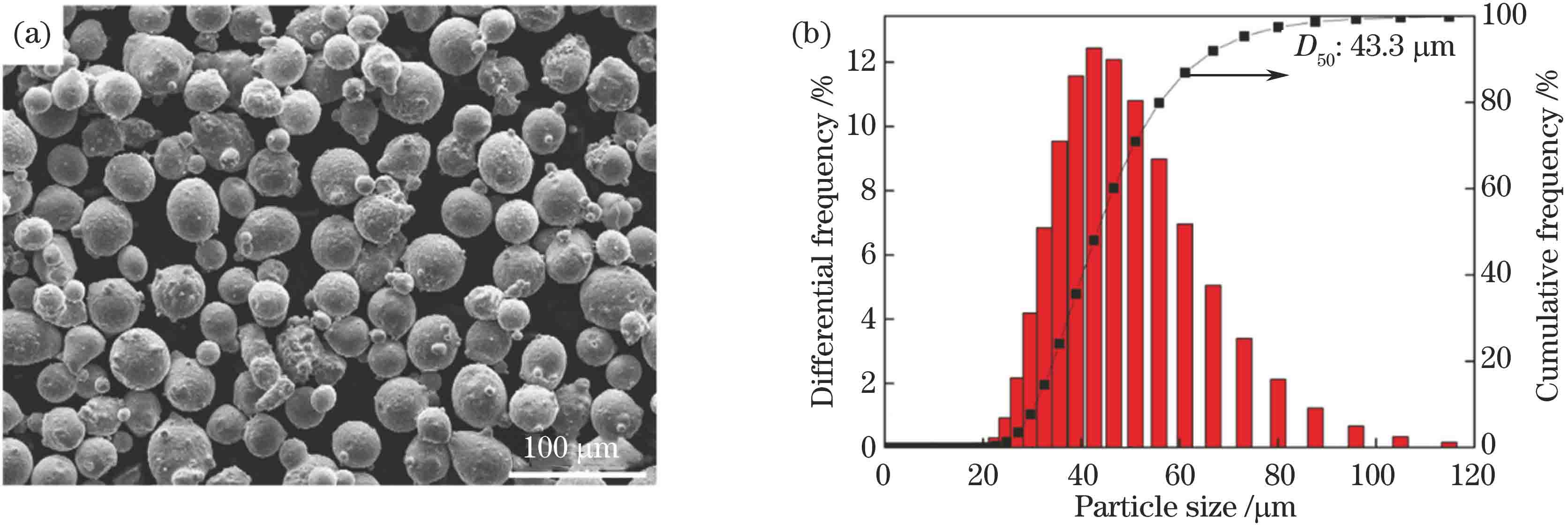
选区激光熔化成形24CrNiMo合金钢的组织结构与力学性能  下载: 1315次
下载: 1315次
杨晨, 董志宏, 迟长泰, 谢玉江, 彭晓. 选区激光熔化成形24CrNiMo合金钢的组织结构与力学性能[J]. 中国激光, 2020, 47(5): 0502008.
Chen Yang, Zhihong Dong, Changtai Chi, Yujiang Xie, Xiao Peng. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 24CrNiMo Alloy Steel Formed by Selective Laser Melting[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2020, 47(5): 0502008.
[1] Wang Y M, Voisin T. McKeown J T, et al.Additively manufactured hierarchical stainless steels with high strength and ductility[J]. Nature Materials, 2018, 17(1): 63-71.
[2] Murr L E, Gaytan S M, Ramirez D A, et al. Metal fabrication by additive manufacturing using laser and electron beam melting technologies[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2012, 28(1): 1-14.
[3] Herzog D, Seyda V, Wycisk E, et al. Additive manufacturing of metals[J]. Acta Materialia, 2016, 117: 371-392.
[4] Gu D D, Hagedorn Y C, Meiners W, et al. Densification behavior, microstructure evolution, and wear performance of selective laser melting processed commercially pure titanium[J]. Acta Materialia, 2012, 60(9): 3849-3860.
[5] Kruth J P, Levy G, Klocke F, et al. Consolidation phenomena in laser and powder-bed based layered manufacturing[J]. CIRP Annals, 2007, 56(2): 730-759.
[6] Sing S L, Wiria F E, Yeong W Y. Selective laser melting of titanium alloy with 50wt% tantalum: effect of laser process parameters on part quality[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2018, 77: 120-127.
[7] 王华明, 张述泉, 王向明. 大型钛合金结构件激光直接制造的进展与挑战(邀请论文)[J]. 中国激光, 2009, 36(12): 3204-3209.
[9] Jia Q B, Gu D D. Selective laser melting additive manufacturing of Inconel 718 superalloy parts: densification, microstructure and properties[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2014, 585: 713-721.
[10] Montero-Sistiaga M L, Godino-Martinez M, Boschmans K, et al. Microstructure evolution of 316L produced by HP-SLM (high power selective laser melting)[J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2018, 23: 402-410.
[11] Nguyen Q B, Zhu Z, Ng F L, et al. High mechanical strengths and ductility of stainless steel 304L fabricated using selective laser melting[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2019, 35(2): 388-394.
[12] 杨永强, 罗子艺, 苏旭彬, 等. 不锈钢薄壁零件选区激光熔化制造及影响因素研究[J]. 中国激光, 2011, 38(1): 0103001.
[13] Gong H J, Rafi K, Gu H F, et al. Influence of defects on mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V components produced by selective laser melting and electron beam melting[J]. Materials & Design, 2015, 86: 545-554.
[14] Moussaoui K, Rubio W, Mousseigne M, et al. Effects of selective laser melting additive manufacturing parameters of Inconel 718 on porosity, microstructure and mechanical properties[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2018, 735: 182-190.
[15] Guan K, Wang Z M, Gao M, et al. Effects of processing parameters on tensile properties of selective laser melted 304 stainless steel[J]. Materials & Design, 2013, 50: 581-586.
[17] Mertens R, Vrancken B, Holmstock N, et al. Influence of powder bed preheating on microstructure and mechanical properties of H13 tool steel SLM parts[J]. Physics Procedia, 2016, 83: 882-890.
[18] Liu F G, Lin X, Yang H O, et al. Effect of microstructure on the fatigue crack growth behavior of laser solid formed 300M steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2017, 695: 258-264.
[19] Wei M W, Chen S Y, Xi L Y, et al. Selective laser melting of 24CrNiMo steel for brake disc: fabrication efficiency, microstructure evolution, and properties[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2018, 107: 99-109.
[20] 袁梅彦, 陈勇, 王森, 等. 24CrNiMo合金钢的激光选区熔化成形工艺研究[J]. 工程与试验, 2019, 59(2): 18-21.
Yuan M Y, Chen Y, Wang S, et al. Study on selective laser melting process of 24CrNiMo alloy steel[J]. Engineering & Test, 2019, 59(2): 18-21.
[21] Tucho W M, Lysne V H, Austbø H, et al. Investigation of effects of process parameters on microstructure and hardness of SLM manufactured SS316L[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 740: 910-925.
[22] Casati R, Coduri M, Lecis N, et al. Microstructure and mechanical behavior of hot-work tool steels processed by selective laser melting[J]. Materials Characterization, 2018, 137: 50-57.
[23] Krell J, Röttger A, Geenen K, et al. General investigations on processing tool steel X40CrMoV5-1 with selective laser melting[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2018, 255: 679-688.
[24] Geenen K, Röttger A, Feld F, et al. Microstructure, mechanical, and tribological properties of M3:2 high-speed steel processed by selective laser melting, hot-isostatic pressing, and casting[J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2019, 28: 585-599.
[25] 李铷寅, 宋崇智. 基于冒口的250 km/h高铁制动盘铸造工艺研究[J]. 机械工程师, 2017( 2): 44- 45.
Li RY, Song CZ. Research on casting process of 250 km/h high speed rail brake disc based on riser[J]. Mechanical Engineer, 2017( 2): 44- 45.
[26] Futás P, Pribulová A, Fedorko G, et al. Failure analysis of a railway brake disc with the use of casting process simulation[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2019, 95: 226-238.
[27] 耿靖贺, 焦建强, 朱平, 等. 24CrNiMo激光沉积技术在高铁动车组制动盘制造中的应用[J]. 铁道机车与动车, 2018( 12): 12- 13.
Geng JH, Jiao JQ, ZhuP, et al. Application of 24CrNiMo laser deposition technology in the manufacture of brake discs for high-speed railway[J]. Railway Locomotive and Motor Car, 2018( 12): 12- 13.
[28] 陶宇, 付传锋. 中国高速铁路几个重要零件的精锻成形[J]. 兵器装备工程学报, 2016, 37(6): 119-123.
Tao H Y, Fu C F. Precision forging and shaping of several important parts of Chinese high-speed railway[J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2016, 37(6): 119-123.
[29] Girault E, Jacques P. HarletP, et al. Metallographic methods for revealing the multiphase microstructure of TRIP-assisted steels[J]. Materials Characterization, 1998, 40(2): 111-118.
[30] Vandijk N, Butt A, Zhao L, et al. Thermal stability of retained austenite in TRIP steels studied by synchrotron X-ray diffraction during cooling[J]. Acta Materialia, 2005, 53(20): 5439-5447.
[31] Khairallah S A, Anderson A T, Rubenchik A, et al. Laser powder-bed fusion additive manufacturing: physics of complex melt flow and formation mechanisms of pores, spatter, and denudation zones[J]. Acta Materialia, 2016, 108: 36-45.
[32] Luo X, Chen X H, Wang T, et al. Effect of morphologies of martensite-austenite constituents on impact toughness in intercritically reheated coarse-grained heat-affected zone of HSLA steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2018, 710: 192-199.
[33] Qiu C L, Panwisawas C, Ward M, et al. On the role of melt flow into the surface structure and porosity development during selective laser melting[J]. Acta Materialia, 2015, 96: 72-79.
[34] Zhang K, Zhang M H, Guo Z H, et al. A new effect of retained austenite on ductility enhancement in high-strength quenching-partitioning-tempering martensitic steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2011, 528(29/30): 8486-8491.
杨晨, 董志宏, 迟长泰, 谢玉江, 彭晓. 选区激光熔化成形24CrNiMo合金钢的组织结构与力学性能[J]. 中国激光, 2020, 47(5): 0502008. Chen Yang, Zhihong Dong, Changtai Chi, Yujiang Xie, Xiao Peng. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of 24CrNiMo Alloy Steel Formed by Selective Laser Melting[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2020, 47(5): 0502008.