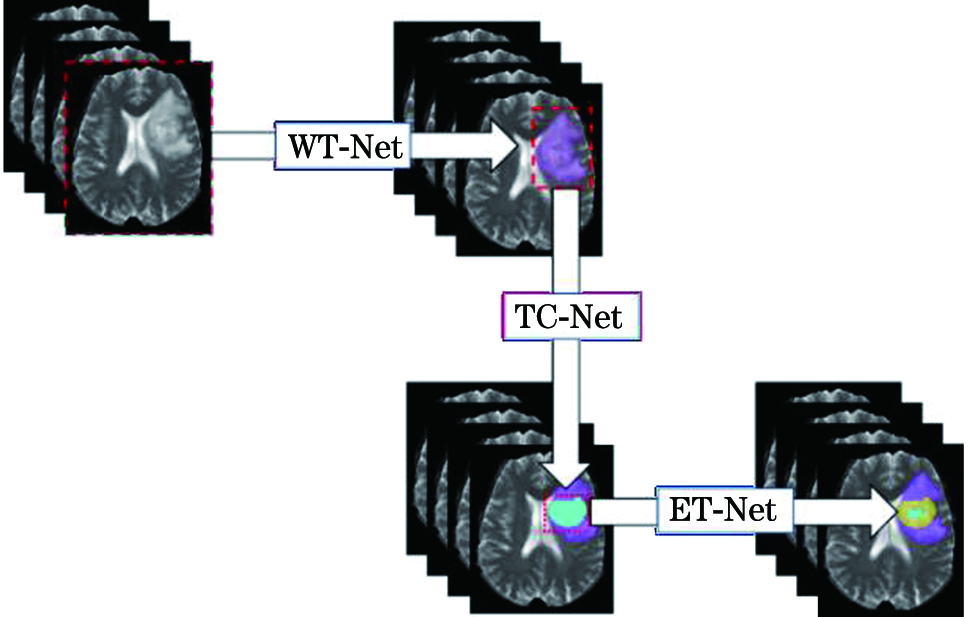
一种级联改进U-Net网络的脑肿瘤分割方法  下载: 1278次
下载: 1278次
褚晶辉, 黄凯隆, 吕卫. 一种级联改进U-Net网络的脑肿瘤分割方法[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2021, 58(8): 0810020.
Jinghui Chu, Kailong Huang, Wei Lü. A Method for Brain Tumor Segmentation Using Cascaded Modified U-Net[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2021, 58(8): 0810020.
[1] 任璐, 李锵, 关欣, 等. 改进的连续型最大流算法脑肿瘤磁核共振成像三维分割[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2018, 55(11): 111011.
[2] 张祥甫, 刘健, 石章松, 等. 基于深度学习的语义分割问题研究综述[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2019, 56(15): 150003.
[3] ShelhamerE, LongJ, DarrellT. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[C] //IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,New York: IEEE Press, 2015: 640- 651.
[4] RonnebergerO, FischerP, BroxT. U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[M] //Navab N, Hornegger J, Wells W, et al. Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention Cham: Springer, 2015, 9351: 234- 241.
[5] MilletariF, NavabN, Ahmadi SA. V-net: fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation[C] //2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), October 25-28, 2016, Stanford, CA, USA. New York: IEEE Press, 2016: 565- 571.
[10] Chen LC, Zhu YK, PapandreouG, et al. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation[C] //Ferrari V, Hebert M, Sminchisescu C, et al. Computer Vision-ECCV 2018. Cham: Springer, 2018, 11211: 833- 851.
[12] MyronenkoA. 3D MRI brain tumor segmentation using autoencoder regularization[C] // Crimi A, Bakas S, Kuijf H, et al. Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries. Cham: Springer, 2018, 11384: 311- 320.
[13] MalmiE, ParambathS, Peyrat JM, et al. CaBS: a cascaded brain tumor segmentation approach[C] //Proceedings MICCAI Brain, Tumor Segmentation (BRATS). [S.l.: s.n.], 2015: 42- 47.
[14] 褚晶辉, 李晓川, 张佳祺, 等. 一种基于级联卷积网络的三维脑肿瘤精细分割[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2019, 56(10): 101001.
[15] LaffertyJ, MccallumA, PereiraF, et al. Conditional random fields: probabilistic models for segmenting and labeling sequence data[C] // Proceedings of 18th International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, June 28-July 1, 2001, Williamstown, MA, USA. [S. l.]: International Machine Learning Society, 2001: 282- 289.
[16] ZhengS, JayasumanaS, Romera-ParedesB, et al.Conditional random fields as recurrent neural networks[C] //2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), December 7-13, 2015, Santiago, Chile.New York: IEEE Press, 2015: 1529- 1537.
[18] He KM, Zhang XY, Ren SQ, et al.Delving deep into rectifiers: surpassing human-level performance on ImageNet classification[C] //2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), December 7-13, 2015, Santiago, Chile. New York: IEEE Press, 2015: 1026- 1034.
[22] Gibson E, Li W Q, Sudre C, et al. NiftyNet: a deep-learning platform for medical imaging[J]. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 2018, 158: 113-122.
[26] McKinleyR, MeierR, WiestR. Ensembles of densely-connected CNNs with label-uncertainty for brain tumor segmentation[C] // Crimi A, Bakas S, Kuijf H, et al. Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries. Cham: Springer, 2018, 11384: 456- 465.
[28] MehtaR, ArbelT. 3D U-net for brain tumour segmentation[C] //Crimi A, Bakas S, Kuijf H, et al. Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries. Cham: Springer, 2018, 11384: 254- 266.
[29] HuaR, HuoQ, Gao YZ, et al. Multimodal brain tumor segmentation using cascaded V-nets[M] //Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries. Cham: Springer, 2019: 49- 60.
褚晶辉, 黄凯隆, 吕卫. 一种级联改进U-Net网络的脑肿瘤分割方法[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2021, 58(8): 0810020. Jinghui Chu, Kailong Huang, Wei Lü. A Method for Brain Tumor Segmentation Using Cascaded Modified U-Net[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2021, 58(8): 0810020.