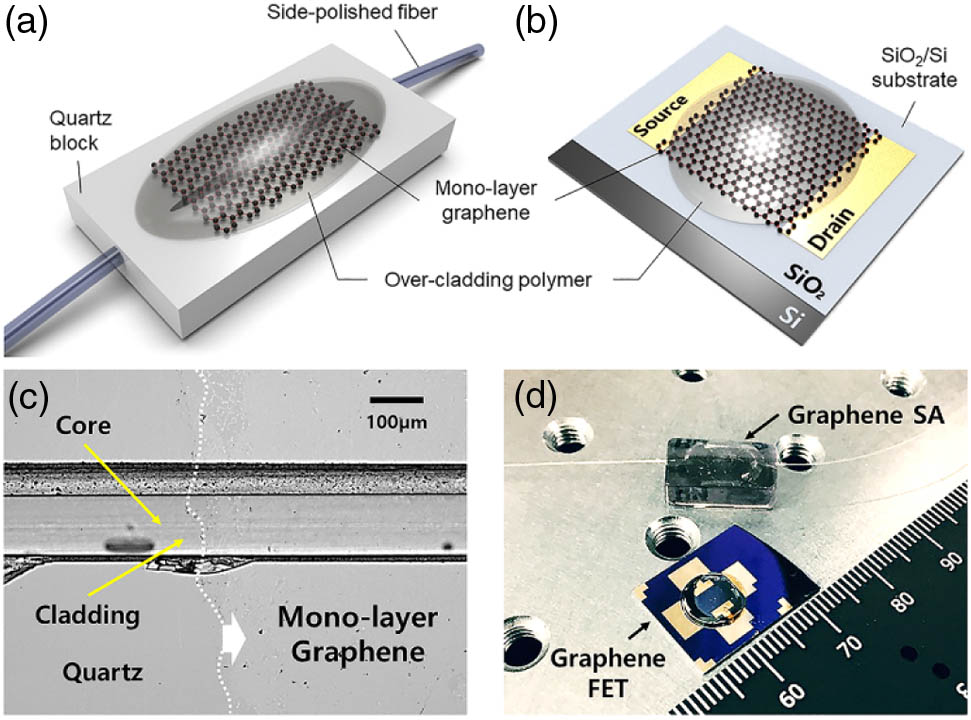
Graphene-based saturable absorber and mode-locked laser behaviors under gamma-ray radiation  Download: 584次
Download: 584次
Dohyun Kim, Nam Hun Park, Hyunju Lee, Jaegoan Lee, Dong-Il Yeom, Jungwon Kim. Graphene-based saturable absorber and mode-locked laser behaviors under gamma-ray radiation[J]. Photonics Research, 2019, 7(7): 07000742.
[3] T. Udem, R. Holzwarth, T. W. Hänsch. Optical frequency metrology. Nature, 2002, 416: 233-237.
[14] A. K. Geim, K. S. Novoselov. The rise of graphene. Nat. Mater., 2007, 6: 183-191.
[21] E. J. Siochi. Graphene in the sky and beyond. Nat. Nanotechnol., 2014, 9: 745-747.
[33]
Dohyun Kim, Nam Hun Park, Hyunju Lee, Jaegoan Lee, Dong-Il Yeom, Jungwon Kim. Graphene-based saturable absorber and mode-locked laser behaviors under gamma-ray radiation[J]. Photonics Research, 2019, 7(7): 07000742.