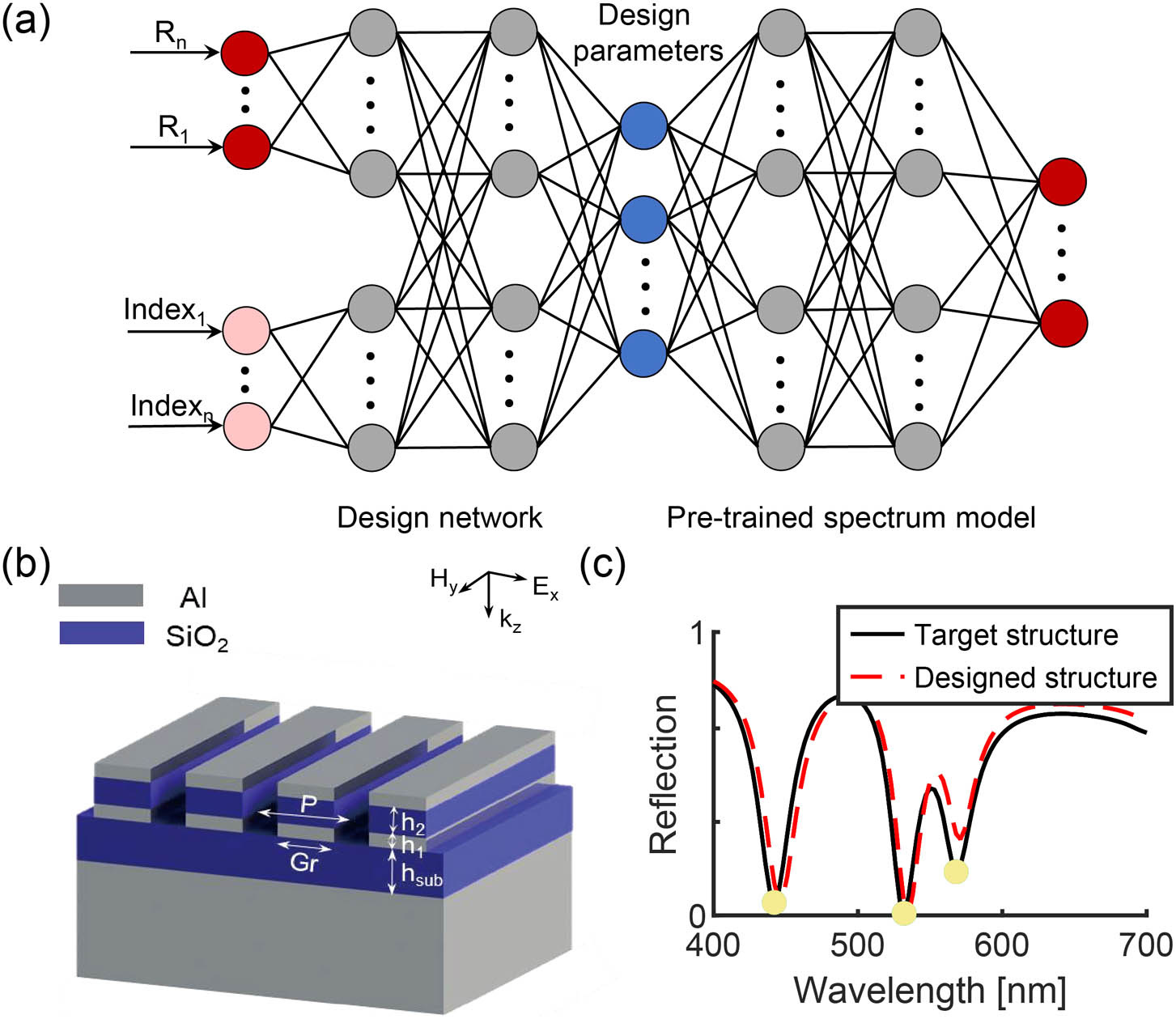
On-demand design of spectrally sensitive multiband absorbers using an artificial neural network
Sunae So, Younghwan Yang, Taejun Lee, Junsuk Rho. On-demand design of spectrally sensitive multiband absorbers using an artificial neural network[J]. Photonics Research, 2021, 9(4): 0400B153.
[2] N. I. Landy, S. Sajuyigbe, J. J. Mock, D. R. Smith, W. J. Padilla. Perfect metamaterial absorber. Phys. Rev. Lett., 2008, 100: 207402.
[3] M. Diem, T. Koschny, C. M. Soukoulis. Wide-angle perfect absorber/thermal emitter in the terahertz regime. Phys. Rev. B, 2009, 79: 033101.
[4] A. Vora, J. Gwamuri, N. Pala, A. Kulkarni, J. M. Pearce, D. Ö. Güney. Exchanging ohmic losses in metamaterial absorbers with useful optical absorption for photovoltaics. Sci. Rep., 2014, 4: 4901.
[5] F. B. Barho, F. Gonzalez-Posada, M. Bomers, A. Mezy, L. Cerutti, T. Taliercio. Surface-enhanced thermal emission spectroscopy with perfect absorber metasurfaces. ACS Photon., 2019, 6: 1506-1514.
[6] N. Liu, M. Mesch, T. Weiss, M. Hentschel, H. Giessen. Infrared perfect absorber and its application as plasmonic sensor. Nano Lett., 2010, 10: 2342-2348.
[7] H. Tao, C. Bingham, D. Pilon, K. Fan, A. Strikwerda, D. Shrekenhamer, W. Padilla, X. Zhang, R. Averitt. A dual band terahertz metamaterial absorber. J. Phys. D, 2010, 43: 225102.
[8] J. Hao, J. Wang, X. Liu, W. J. Padilla, L. Zhou, M. Qiu. High performance optical absorber based on a plasmonic metamaterial. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2010, 96: 251104.
[9] P. Bouchon, C. Koechlin, F. Pardo, R. Hadar, J.-L. Pelouard. Wideband omnidirectional infrared absorber with a patchwork of plasmonic nanoantennas. Opt. Lett., 2012, 37: 1038-1040.
[10] K. Chen, R. Adato, H. Altug. Dual-band perfect absorber for multispectral plasmon-enhanced infrared spectroscopy. ACS Nano, 2012, 6: 7998-8006.
[11] J. Xu, Z. Zhao, H. Yu, L. Yang, P. Gou, J. Cao, Y. Zou, J. Qian, T. Shi, Q. Ren, Z. An. Design of triple-band metamaterial absorbers with refractive index sensitivity at infrared frequencies. Opt. Express, 2016, 24: 25742-25751.
[12] J. W. Park, P. Van Tuong, J. Y. Rhee, K. W. Kim, W. H. Jang, E. H. Choi, L. Y. Chen, Y. Lee. Multi-band metamaterial absorber based on the arrangement of donut-type resonators. Opt. Express, 2013, 21: 9691-9702.
[13] Y. Ma, Q. Chen, J. Grant, S. C. Saha, A. Khalid, D. R. Cumming. A terahertz polarization insensitive dual band metamaterial absorber. Opt. Lett., 2011, 36: 945-947.
[14] S. Liu, H. Chen, T. J. Cui. A broadband terahertz absorber using multi-layer stacked bars. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2015, 106: 151601.
[15] Z. Zhang, Z. Yu, Y. Liang, T. Xu. Dual-band nearly perfect absorber at visible frequencies. Opt. Mater. Express, 2018, 8: 463-468.
[16] G. Dayal, S. A. Ramakrishna. Design of multi-band metamaterial perfect absorbers with stacked metal–dielectric disks. J. Opt., 2013, 15: 055106.
[17] W. Ma, Z. Liu, Z. A. Kudyshev, A. Boltasseva, W. Cai, Y. Liu. Deep learning for the design of photonic structures. Nat. Photonics, 2021, 15: 77-90.
[18] K. Yao, R. Unni, Y. Zheng. Intelligent nanophotonics: merging photonics and artificial intelligence at the nanoscale. Nanophotonics, 2019, 8: 339-366.
[19] S. So, T. Badloe, J. Noh, J. Rho, J. Bravo-Abad. Deep learning enabled inverse design in nanophotonics. Nanophotonics, 2020, 9: 1041-1057.
[20] J. Peurifoy, Y. Shen, L. Jing, Y. Yang, F. Cano-Renteria, B. G. DeLacy, J. D. Joannopoulos, M. Tegmark, M. Soljačić. Nanophotonic particle simulation and inverse design using artificial neural networks. Sci. Adv., 2018, 4: eaar4206.
[21] D. Liu, Y. Tan, E. Khoram, Z. Yu. Training deep neural networks for the inverse design of nanophotonic structures. ACS Photon., 2018, 5: 1365-1369.
[22] S. So, J. Mun, J. Rho. Simultaneous inverse design of materials and structures via deep learning: demonstration of dipole resonance engineering using core–shell nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2019, 11: 24264-24268.
[23] Z. Liu, D. Zhu, S. P. Rodrigues, K.-T. Lee, W. Cai. Generative model for the inverse design of metasurfaces. Nano Lett., 2018, 18: 6570-6576.
[24] S. So, J. Rho. Designing nanophotonic structures using conditional deep convolutional generative adversarial networks. Nanophotonics, 2019, 8: 1255-1261.
[25] Y. Kiarashinejad, M. Zandehshahvar, S. Abdollahramezani, O. Hemmatyar, R. Pourabolghasem, A. Adibi. Knowledge discovery in nanophotonics using geometric deep learning. Adv. Intell. Syst., 2020, 2: 1900132.
[26] W. Ma, F. Cheng, Y. Liu. Deep-learning-enabled on-demand design of chiral metamaterials. ACS Nano, 2018, 12: 6326-6334.
Sunae So, Younghwan Yang, Taejun Lee, Junsuk Rho. On-demand design of spectrally sensitive multiband absorbers using an artificial neural network[J]. Photonics Research, 2021, 9(4): 0400B153.