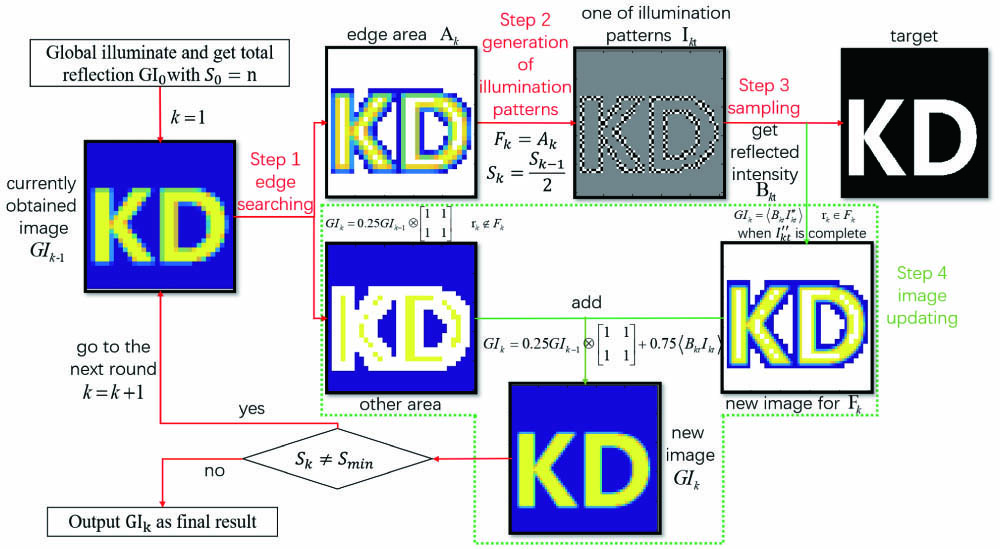
Feedback ghost imaging by gradually distinguishing and concentrating onto the edge area  Download: 588次
Download: 588次
Junhao Gu, Shuai Sun, Yaokun Xu, Huizu Lin, Weitao Liu. Feedback ghost imaging by gradually distinguishing and concentrating onto the edge area[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2021, 19(4): 041102.
[10] D. Z. Cao, J. Xiong, S. H. Zhang, L. F. Lin, L. Gao, K. Wang. Enhancing visibility and resolution in Nth-order intensity correlation of thermal light. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2008, 92: 013802.
[12] J. H. Shapiro. Computational ghost imaging. Phys. Rev. A, 2008, 78: R061802.
[31] M. Amann, M. Bayer. Compressive adaptive computational ghost imaging. Sci. Rep., 2013, 3: 1545.
Junhao Gu, Shuai Sun, Yaokun Xu, Huizu Lin, Weitao Liu. Feedback ghost imaging by gradually distinguishing and concentrating onto the edge area[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2021, 19(4): 041102.