Matter and Radiation at Extremes, 2024, 9 (1): 015603, Published Online: Mar. 27, 2024
Resistive field generation in intense proton beam interaction with solid targets
Abstract
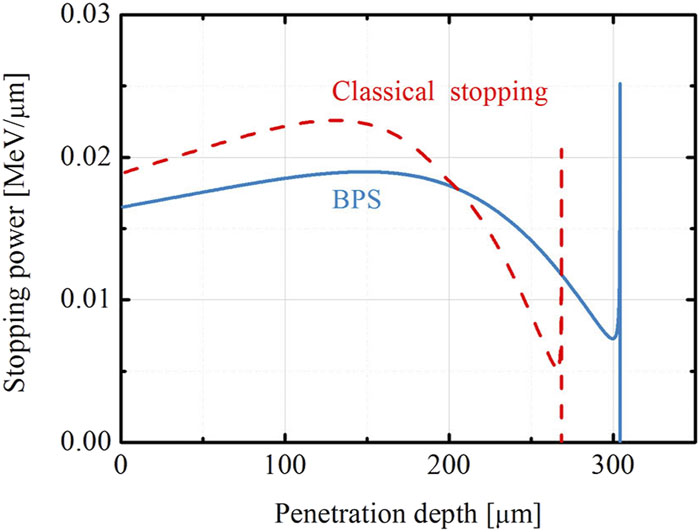
The Brown–Preston–Singleton (BPS) stopping power model is added to our previously developed hybrid code to model ion beam–plasma interaction. Hybrid simulations show that both resistive field and ion scattering effects are important for proton beam transport in a solid target, in which they compete with each other. When the target is not completely ionized, the self-generated resistive field effect dominates over the ion scattering effect. However, when the target is completely ionized, this situation is reversed. Moreover, it is found that Ohmic heating is important for higher current densities and materials with high resistivity. The energy fraction deposited as Ohmic heating can be as high as 20%–30%. Typical ion divergences with half-angles of about 5°–10° will modify the proton energy deposition substantially and should be taken into account.
W. Q. Wang, J. J. Honrubia, Y. Yin, X. H. Yang, F. Q. Shao. Resistive field generation in intense proton beam interaction with solid targets[J]. Matter and Radiation at Extremes, 2024, 9(1): 015603.