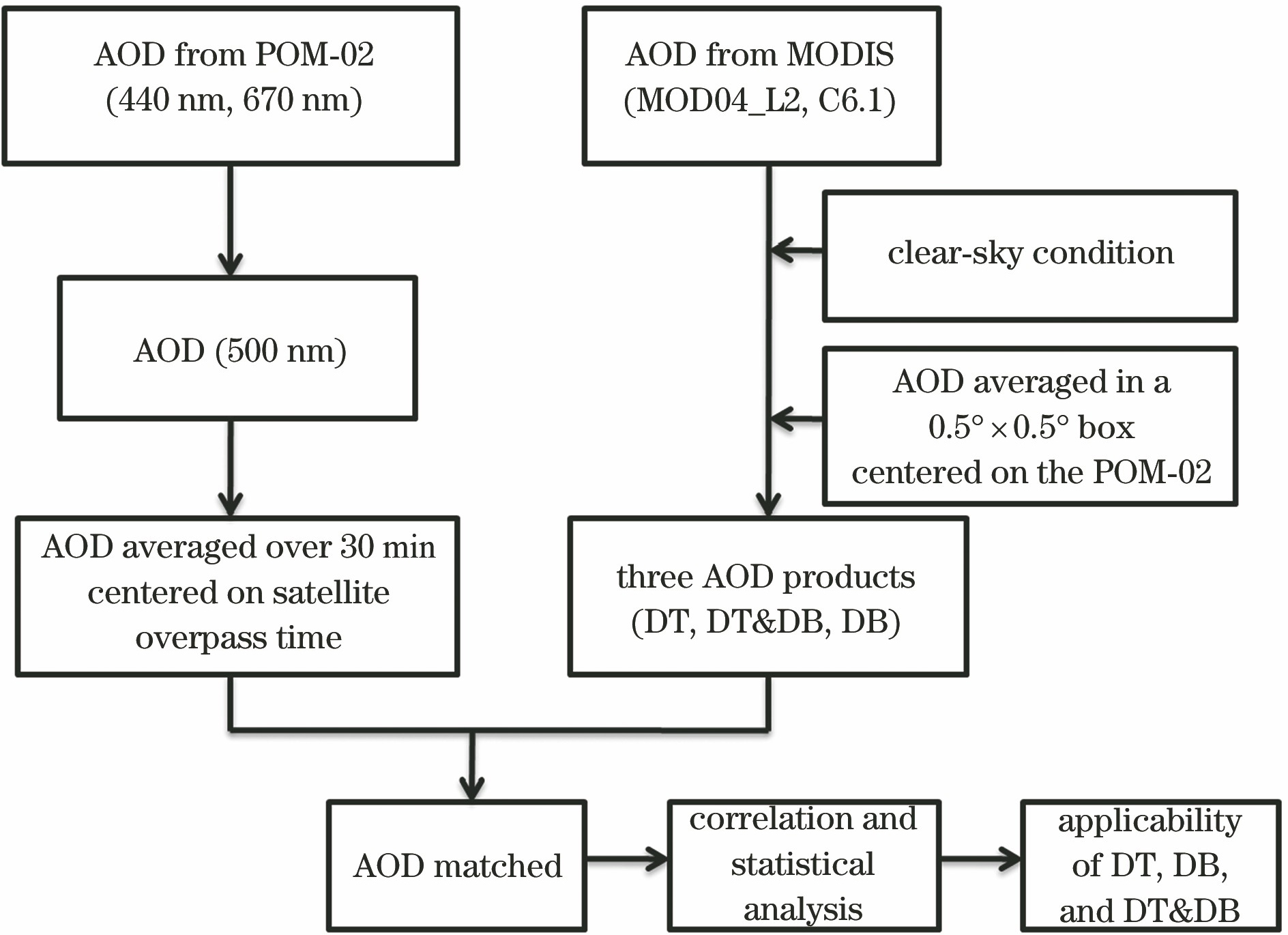
MODIS C061气溶胶光学厚度产品在西安地区的适用性研究  下载: 1006次
下载: 1006次
刘晶晶, 刘芸, 王国英, 华灯鑫, 王骏, 闫庆, 何廷尧, 高飞. MODIS C061气溶胶光学厚度产品在西安地区的适用性研究[J]. 光学学报, 2019, 39(10): 1001004.
Jingjing Liu, Yun Liu, Guoying Wang, Dengxin Hua, Jun Wang, Qing Yan, Tingyao He, Fei Gao. Applicability of MODIS C061 Aerosol Optical Depth Products in Xi'an Region[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2019, 39(10): 1001004.
[1] 毛节泰, 张军华, 王美华. 中国大气气溶胶研究综述[J]. 气象学报, 2002, 60(5): 625-634.
[2] 石广玉, 王标, 张华, 等. 大气气溶胶的辐射与气候效应[J]. 大气科学, 2008, 32(4): 826-840.
[3] 张华, 黄建平. 对IPCC第五次评估报告关于人为和自然辐射强迫的解读[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2014, 10(1): 40-44.
[4] 张小曳, 廖宏, 王芬娟. 对IPCC第五次评估报告气溶胶-云对气候变化影响与响应结论的解读[J]. 气候变化研究进展, 2014, 10(1): 37-39.
[5] 姚玉璧, 王毅荣, 李耀辉, 等. 中国黄土高原气候暖干化及其对生态环境的影响[J]. 资源科学, 2005, 27(5): 146-152.
[6] 夏祥鳌, 王普才, 陈洪滨, 等. 中国北方地区春季气溶胶光学特性地基遥感研究[J]. 遥感学报, 2005, 9(4): 429-437.
[7] Takamura T, Sugimoto N, Shimizu A, et al. Journal of Geophysical Research: Atmospheres, 2007, 112(D22): D22S36[J]. Korea, during the atmospheric Brown cloud east Asian regional experiment, 2005.
[8] Che H, Shi G, Uchiyama A, et al. Intercomparison between aerosol optical properties by a PREDE skyradiometer and CIMEL sunphotometer over Beijing, China[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics, 2008, 8(12): 3199-3214.
[9] 毛节泰, 李成才, 张军华, 等. MODIS卫星遥感北京地区气溶胶光学厚度及与地面光度计遥感的对比[J]. 应用气象学报, 2002, 13(s1): 127-135.
[10] 李成才, 毛节泰, 刘启汉, 等. 利用MODIS研究中国东部地区气溶胶光学厚度的分布和季节变化特征[J]. 科学通报, 2003, 48(19): 2094-2100.
[11] 谭浩波, 吴兑, 邓雪娇, 等. 珠江三角洲气溶胶光学厚度的观测研究[J]. 环境科学学报, 2009, 29(6): 1146-1155.
[12] 胡蝶, 张镭, 沙莎, 等. 西北地区MODIS气溶胶产品的对比应用分析[J]. 干旱气象, 2013, 31(4): 677-683.
[15] 周春艳, 柳钦火, 唐勇, 等. MODIS气溶胶C004、C005产品的对比分析及其在中国北方地区的适用性评价[J]. 遥感学报, 2009, 13(5): 854-872.
[17] Che H Z, Qi B, Zhao H J, et al. Aerosol optical properties and instantaneous radiative forcing based on high temporospatial resolution CARSNET ground-based measurements over eastern China[J]. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics Discussions, 2017: 1-42.
[20] Nakajima T. Overview of SKYNET and its activities[J]. Óptica Pura Y Aplicada, 2004, 37(3): 3303-3308.
[21] Khatri P, Takamura T, Yamazaki A, et al. Use of 315 nm channel data of the sky radiometer to estimate the columnar ozone concentration: a preliminary study[J]. Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan Ser II, 2014, 92A: 185-194.
[23] Uchiyama A, Yamazaki A, Kudo R, et al. Continuous ground-based observation of aerosol optical properties at Tsukuba, Japan: trend and climatology[J]. Journal of the Meteorological Society of Japan Ser II, 2014, 92A: 93-108.
[26] Justice C O. Townshend J R G, Vermote E F, et al. An overview of MODIS land data processing and product status[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2002, 83(1/2): 3-15.
[27] 王钊, 彭艳, 车慧正, 等. 近10年关中盆地MODIS气溶胶的时空变化特征[J]. 高原气象, 2013, 32(1): 234-242.
刘晶晶, 刘芸, 王国英, 华灯鑫, 王骏, 闫庆, 何廷尧, 高飞. MODIS C061气溶胶光学厚度产品在西安地区的适用性研究[J]. 光学学报, 2019, 39(10): 1001004. Jingjing Liu, Yun Liu, Guoying Wang, Dengxin Hua, Jun Wang, Qing Yan, Tingyao He, Fei Gao. Applicability of MODIS C061 Aerosol Optical Depth Products in Xi'an Region[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2019, 39(10): 1001004.