
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Energy Photon-Technology in Western China, International Collaborative Center on Photoelectric Technology and Nano Functional Materials, Institute of Photonics & Photon-Technology, Northwest University, Xi’an 710127, China
2 Shaanxi Engineering Technology Research Center for Solid State Lasers and Application, Shaanxi Provincial Key Laboratory of Photo-electronic Technology, Northwest University, Xi’an 710127, China
We demonstrate a stable narrow linewidth single-frequency erbium-doped fiber laser (EDFL) operating at 1.6 µm. A Fabry–Perot fiber Bragg grating and two cascaded subrings are incorporated in the main ring cavity to achieve single-frequency operation. The experimentally measured optical signal-to-noise ratio is greater than 73 dB. Furthermore, the linewidth of the EDFL is measured to be about 480 Hz by the self-built short-delayed self-heterodyne interferometry device. The laser shows superior stability, with no mode-hopping during the 60-min observation period. The proposed EDFL provides a new experimental idea for realizing a single-frequency fiber laser in the L-band.
erbium-doped fiber laser two cascaded subrings single frequency Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(4): 041406
香港大学物理系新基石科学实验室,香港 999077
耦合等离激元体系在光场调控、光学传感、光学成像及光电器件等领域中有着广泛应用。目前,阻碍耦合等离激元进一步实用化发展的关键问题是金属材料具有较大的损耗。结合数值仿真方法,从理论上研究了耦合等离激元的损耗机理,并进一步分析复频率光源激励对耦合等离激元体系的作用,提出了通过合成复频率波的方法来补偿损耗,从而恢复被削弱的耦合共振信号。所提优化手段具有泛用性高且无需额外成本的优势,研究结果对耦合等离激元体系在各个领域中的研究发展具有借鉴意义,有利于挖掘该体系的潜在应用价值。
物理光学 纳米光学 等离激元 复频率波 光学传感 光学学报
2024, 44(10): 1026019
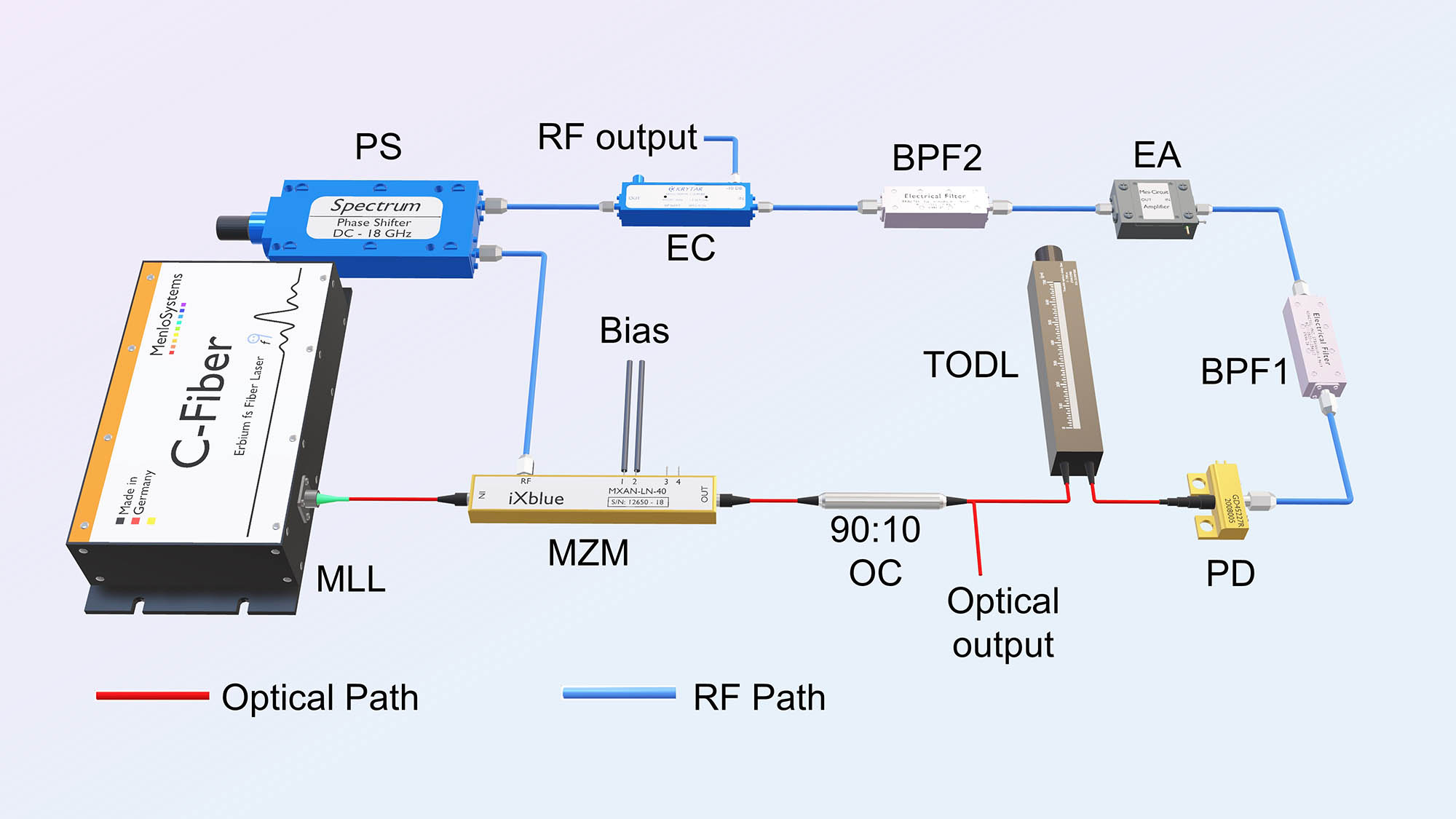
Author Affiliations
Abstract
National Key Laboratory of Microwave Photonics, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing 210016, China
An approach for frequency division of an optical pulse train (OPT) based on an optoelectronic oscillator (OEO) is proposed and experimentally demonstrated. When the OPT is injected into the OEO, a microwave signal with a frequency equaling fractional multiples of the repetition rate of the OPT is generated. This signal is then fed back to the OEO, maintaining its oscillation, while simultaneously serving as the control signal of a Mach–Zehnder modulator (MZM) in the OEO. The MZM acts as an optical switch, permitting specific pulses to pass through while blocking others. As a result, the repetition rate of the OPT is manipulated. A proof-of-concept experiment is carried out. Frequency division factors of 2 and 3 are successfully achieved. The phase noises of the OPT before and after the frequency division are investigated. Compared to previously reported systems, no external microwave source and sophisticated synchronization structure are needed.
frequency division optoelectronic oscillator mode-locked laser microwave photonics Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(4): 043902

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Center of Ultra-precision Optoelectronic Instrument, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin 150080, China
2 Key Laboratory of Ultra-precision Intelligent Instrumentation (Harbin Institute of Technology), Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, Harbin 150080, China
To ensure the frequency accuracy of a heterodyne laser source in the ambient temperature range of -20°C to 40°C, a dual-longitudinal-mode thermally stabilized He–Ne laser based on non-equilibrium power locking was designed. The ambient adaptive preheating temperature setting scheme ensured the laser could operate normally in the range of -20°C to 40°C. The non-equilibrium power-locked frequency stabilization scheme compensated for the frequency drift caused by different stabilization temperatures. The experimental results indicated that the frequency accuracy of the laser designed in this study could reach 5.2 × 10-9 in the range of -20°C to 40°C.
He–Ne laser frequency accuracy ambient adaptability non-equilibrium power locking Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(4): 041407

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Dynamic Measurement Technology, North University of China, Taiyuan 030051, China
2 School of Information & Communication Engineering, North University of China, Taiyuan 030051, China
3 School of Instrument & Electronics, North University of China, Taiyuan 030051, China
Sensors based on optical resonators often have their measurement range limited by their cavity linewidth, particularly in the measurement of time-varying signals. This paper introduces a method for optical frequency shift detection using multiple harmonics to expand the dynamic range of sensors based on optical resonators. The proposed method expands the measurement range of optical frequency shift beyond the cavity linewidth while maintaining measurement accuracy. The theoretical derivation of this method is carried out based on the equation of motion for an optical resonator and the recursive relationship of the Bessel function. Experimental results show that the dynamic range is expanded to 4 times greater than the conventional first harmonic method while still maintaining accuracy. Furthermore, we present an objective analysis of the correlation between the expansion factor of the method and the linewidth and free spectrum of the optical resonator.
optical resonator optical frequency shift multiple harmonics dynamic range expansion Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(4): 041201
1 中国科学院上海高等研究院上海 201204
2 上海科技大学上海 201210
利用高精度磁电式速度传感器可以测量超导腔在低温环境下的振动。定量描述低温环境对超导腔位移振动特性的影响,是实现超导直线加速器亚微米级束流稳定性要求并抑制机械振动导致腔频偏移的基础,这对模组机械和低温系统设计具有重要意义。上海光源机械团队以目前承建的“硬X射线自由电子激光装置(Shanghai HIgh repetitioN rate XFEL and Extreme light facility,SHINE)”1.3 GHz超导加速模组为研究对象,在超导腔常温振动测试基础上,采用频谱分析方法研究了超导腔在300.0 K、125.0 K、2.0 K三种温度下的位移功率谱密度、位移均方根和频响函数。测试结果表明:在上海光源地面本底振动下,2.0 K低温环境引起的超导腔垂向振动影响为本底的9.4%,横向振动影响为本底的4.5%。低温环境下新增振源为冷质流动,流体工质的状态对超导腔垂向和横向振动具有不同的影响。研究成果可用于指导模组测试以及结构设计优化。
超导加速模组 2.0 K低温 振动测量 频响函数 硬X自由电子激光 Superconducting cryomodule 2.0 K Vibration measurement Frequency-response function Hard X-ray free-electron laser
强激光与粒子束
2024, 36(4): 043019
强激光与粒子束
2024, 36(4): 043001
强激光与粒子束
2024, 36(4): 043009
强激光与粒子束
2024, 36(4): 043007





