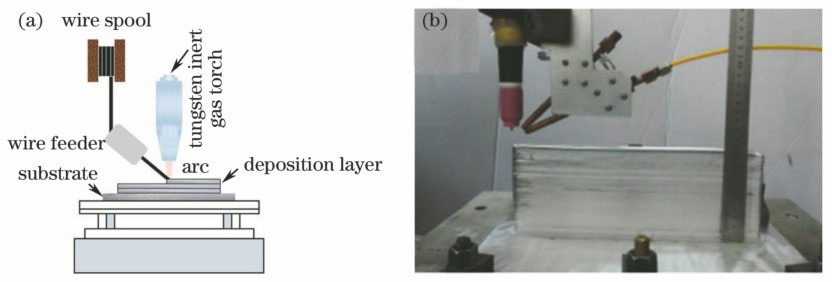
激光与光电子学进展, 2018, 55 (1): 011413, 网络出版: 2018-09-10
激光冲击强化对电弧增材2319铝合金微观组织及残余应力的影响  下载: 1567次
下载: 1567次
Effect of Laser Shock Peening on Microstructure and Residual Stress of Wire-Arc Additive Manufactured 2319 Aluminum Alloy
激光技术 激光冲击强化 电弧增材制造 微观组织 残余应力 laser technique laser shock peening wire arc additive manufacturing microstructure residual stress
摘要
利用激光冲击强化(LSP)与电弧增材制造(WAAM)复合技术,改善增材构件微观组织及应力状态,并研究LSP前后WAAM 2319铝合金的微观组织、显微硬度以及深度方向残余应力分布。研究结果表明,LSP能够减小WAAM 2319铝合金的晶粒尺寸,优化残余应力分布。LSP后,增材构件的平均晶粒直径由冲击前的68.86 μm减小到34.32 μm,显微硬度由冲击前的67.8 HV增大到100.6 HV;残余压应力的最大值约为90 MPa,影响深度为0.65 mm。
Abstract
The microstructure and stress state of the additive parts are improved by the combination of laser shock peening (LSP) and wire-arc additive manufacturing (WAAM) technologies. The microstructures, microhardness and residual stress distributions in the depth direction of 2319 aluminum alloys fabricated by WAAM before and after LSP are investigated. The research results show that LSP can significantly refine the grain size and improve the residual stress distribution of 2319 aluminum alloys fabricated by WAAM. After LSP, the average grain diameter of additive parts decreases from 68.86 μm before LSP to 34.32 μm, and the microhardness increases from 67.8 HV before LSP to 100.6 HV. The maximum residual compressive stress is about 90 MPa and the influence depth is 0.65 mm.
孙汝剑, 朱颖, 李刘合, 郭伟, 彭鹏. 激光冲击强化对电弧增材2319铝合金微观组织及残余应力的影响[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2018, 55(1): 011413. Sun Rujian, Zhu Ying, Li Liuhe, Guo Wei, Peng Peng. Effect of Laser Shock Peening on Microstructure and Residual Stress of Wire-Arc Additive Manufactured 2319 Aluminum Alloy[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2018, 55(1): 011413.