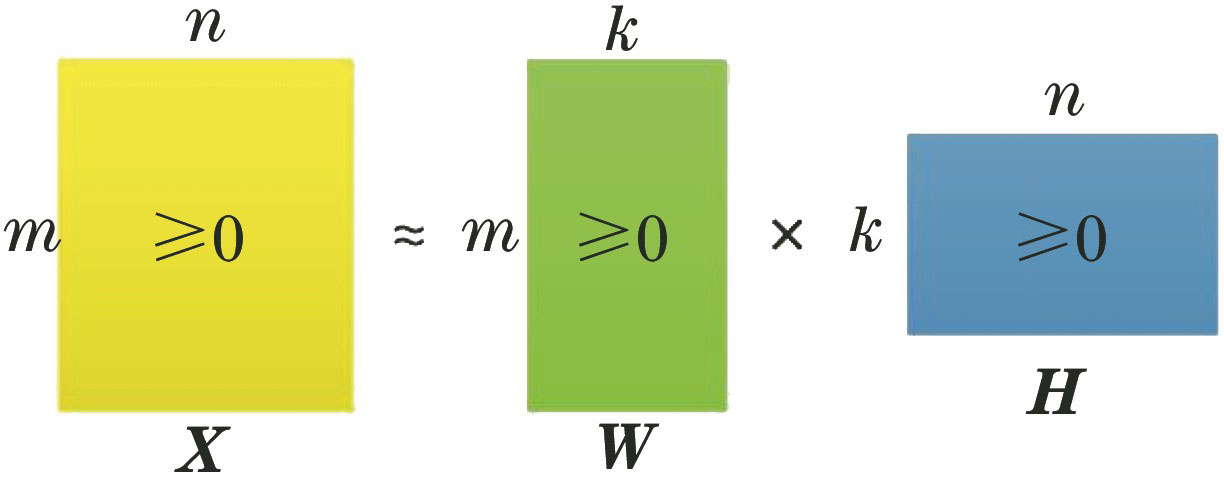激光与光电子学进展, 2019, 56 (10): 101007, 网络出版: 2019-07-04
非负矩阵分解在空间目标图像识别中的应用  下载: 1192次
下载: 1192次
Application of Non-Negative Matrix Factorization in Space Object Recognition
图像处理 图像识别 非负矩阵分解 空间目标图像 最小距离分类器 image processing image recognition non-negative matrix factorization space object image minimum distance classifier
摘要
将非负矩阵分解(NMF)算法应用到空间目标图像识别中,对两种传统NMF算法的迭代规则进行了改进,得到了稀疏NMF算法,并分别在二维(2D)和(2D)
2维度应用了这3种算法。在实验室模拟了空间光学环境,获得了多组空间目标缩比模型图像,图像预处理后建立了训练样本库和测试样本库,运用不同NMF算法对训练样本进行了特征基提取,采用最小距离分类器进行了测试样本的分类,各种NMF算法识别率均在78%以上,最高可达90%。实验结果验证了所提算法的有效性,与其他已有的目标图像识别方法相比,具有准确率较高、速度快、资源开销少的优点。
Abstract
In this study, we applies the non-negative matrix factorization (NMF) algorithm to space object image recognition. First, we obtain the sparse NMF algorithm by improving the iterative rules of two traditional NMF algorithms and separately apply the three algorithms to the two-dimension (2D) and (2D)
2 dimensions. Then, we simulate the space optical environment and acquire multiple sets of space-object-scaling model images in the laboratory. After image preprocessing, we establish the training and the testing sample databases, and extract the features of the training samples using different NMF algorithms. Finally, the minimum distance classifier is used to classify the testing samples. The results show that the recognition rates of various NMF algorithms are all above 78%, and the maximum is up to 90%. The experimental results confirm the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm. Compared with the existing methods for space object image recognition, the NMF algorithm is advantageous owing to its high accuracy, fast speed and low resource cost.
孙静静, 赵飞. 非负矩阵分解在空间目标图像识别中的应用[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2019, 56(10): 101007. Jingjing Sun, Fei Zhao. Application of Non-Negative Matrix Factorization in Space Object Recognition[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2019, 56(10): 101007.