Chinese Optics Letters, 2020, 18 (7): 071101, Published Online: May. 25, 2020
Performance comparison of ghost imaging versus conventional imaging in photon shot noise cases  Download: 842次
Download: 842次
Abstract
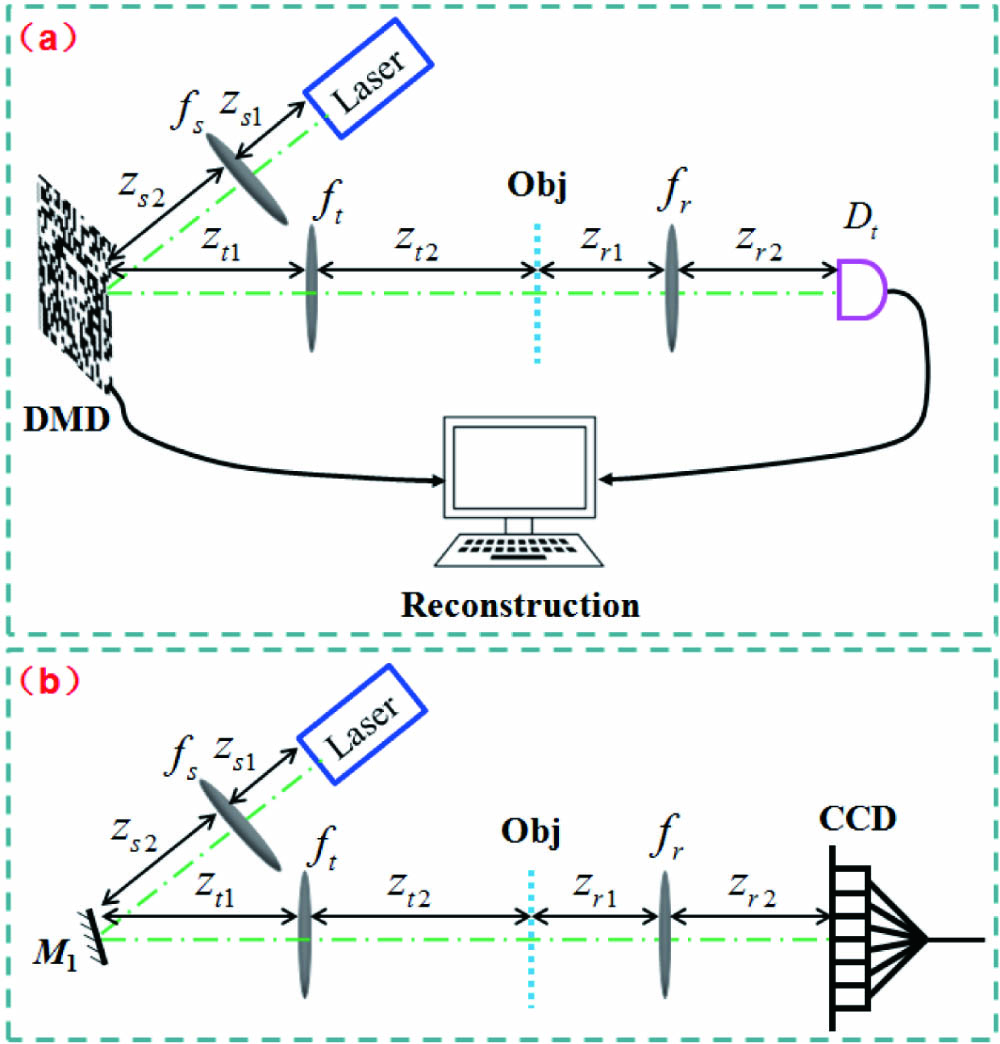
The performances of ghost imaging and conventional imaging in photon shot noise cases are investigated. We define an imaging signal-to-noise ratio called SNRtran where only the object’s transmission region is used to evaluate the imaging quality and it can be applied to ghost imaging (GI) with any random pattern. Both the values
Zijie Li, Qing Zhao, Wenlin Gong. Performance comparison of ghost imaging versus conventional imaging in photon shot noise cases[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2020, 18(7): 071101.