激光与光电子学进展, 2019, 56 (13): 130101, 网络出版: 2019-07-11
基于激光雷达与铁塔风场数据的浙江北部地区一次污染过程及其特征研究  下载: 914次
下载: 914次
Characteristics of Pollution Process in Northern Zhejiang Province Based on Lidar and Tower Wind Field Data
大气光学 激光雷达 后向散射系数 气溶胶 污染传输 atmospheric optics lidar backscattering coefficient aerosols pollution transport
摘要
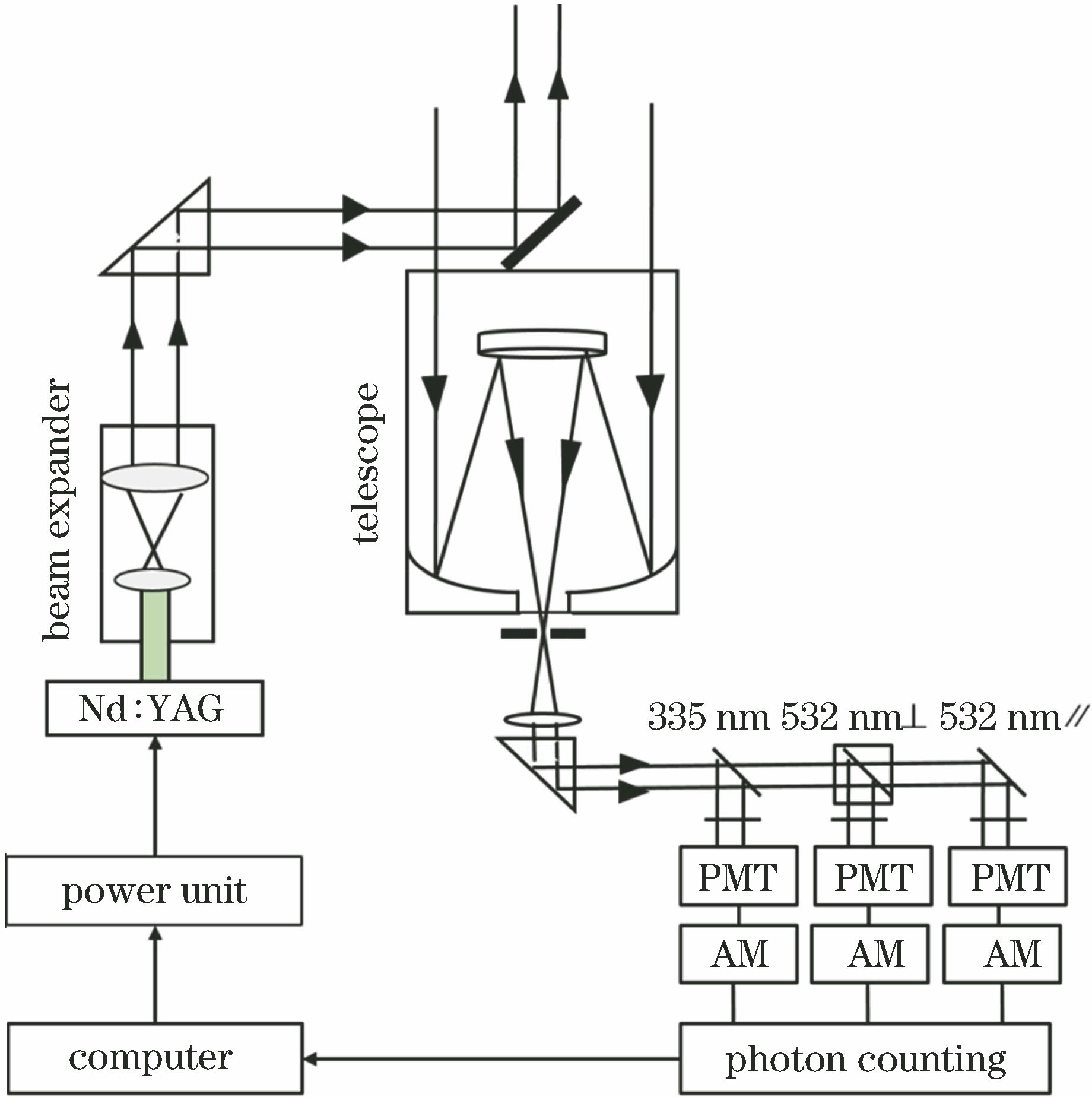
利用大气颗粒物激光雷达观测数据、地面监测站数据和铁塔上搭载的超声波风速仪测量得到的风场数据(简称“铁塔风场数据”),对2018年1月16日至1月18日浙江北部地区的一次污染过程及特征进行了分析。本次污染过程主要受区域污染物传输影响。激光雷达观测结果表明:受西北风影响,16日12时开始,西北方向城市的污染物开始向宁波传输,颗粒物浓度迅速升高,17日18时之后风向转为较弱南风,污染开始消散;532 nm通道的距离平方校正信号与近地面污染物浓度的变化趋势一致;退偏振比、波长指数的结果显示,0.5~1 km高度处的污染物与近地面污染物为两种不同的类型。HYSPLIT后向轨迹模式结果表明,该污染气团来自宁波的西北方向城市,且气团输送速度较快,HYSPLIT模式结果与铁塔风场数据分析结果一致。可见激光雷达的探测结果能够有效地表征颗粒物浓度的空间分布以及演变,并为大气污染的监测和预警提供理论依据。
Abstract
Based on lidar observational data of atmospheric particulate matter, ground monitoring station data, and wind field data measured by an ultrasonic anemometer on a tower (later referred to as tower wind field data), a pollution process that occurred from January 16 to 18, 2018 in the northern Zhejiang Province and its characteristics were comprehensively analyzed. The results show that the pollution process is primarily caused by regional pollutant transport. The lidar results show that pollutants in northwest cities begin to be transported to Ningbo via a northwest wind at 12:00 on January 16, causing the concentration of particulate matter to increase rapidly. The wind direction switches to a weaker southern wind at 18:00 on January 17, resulting in the dissipation of the pollutants. The 532 nm range-square-corrected signal is in agreement with the variation trend of the near-ground pollutant concentration; the depolarization ratio and wavelength dependence show that the pollutants at a height of 0.5-1 km and those near the ground are of two different types. The results of the HYSPLIT backward trajectory model show that the polluted air mass comes from the northwest city of Ningbo and is transported at a high speed, consistent with results analyzed from the tower wind field data. Therefore, the lidar observational results can effectively characterize the spatial distribution and evolution of the particulate matter concentration and provide a theoretical basis for air pollution monitoring and early warning systems.
吴彬, 李艳芳, 蒋璐璐, 胡景波, 周之栩, 张喜亮. 基于激光雷达与铁塔风场数据的浙江北部地区一次污染过程及其特征研究[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2019, 56(13): 130101. Bin Wu, Yanfang Li, Lulu Jiang, Jingbo Hu, Zhixu Zhou, Xiliang Zhang. Characteristics of Pollution Process in Northern Zhejiang Province Based on Lidar and Tower Wind Field Data[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2019, 56(13): 130101.