光学学报, 2020, 40 (12): 1201004, 网络出版: 2020-06-03
紫外双波长激光雷达系统研制与信噪比分析  下载: 1044次
下载: 1044次
Development of Ultraviolet Dual-Wavelength Lidar and Analysis of Its Signal-to-Noise Ratio
摘要
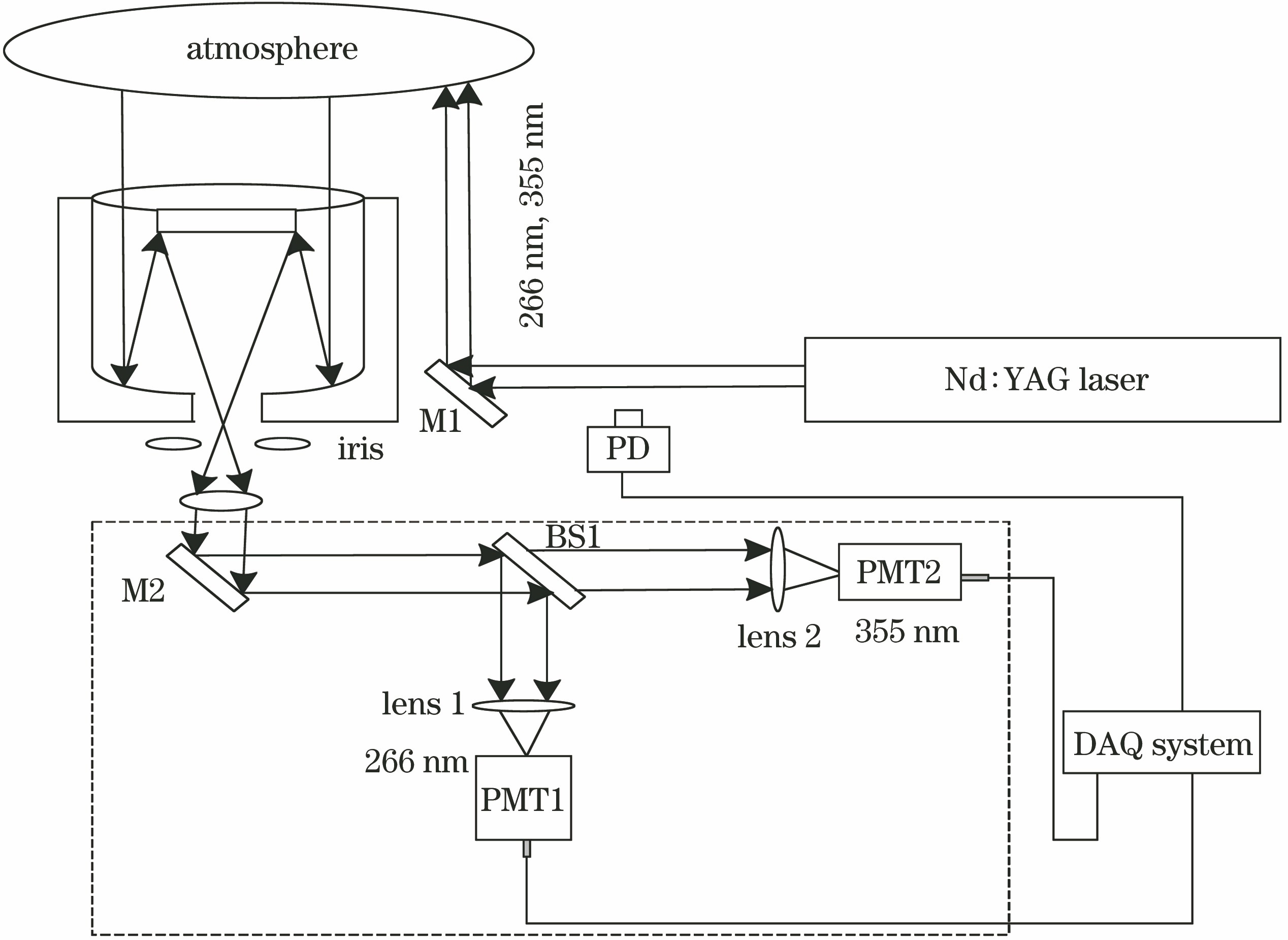
利用Nd∶YAG激光器产生的10 Hz中心波长为355 nm和266 nm的激光束作为光源,研制了用于对流层大气气溶胶探测的紫外双波长激光雷达,实现了气溶胶Mie散射信号在紫外波段的精细分离和提取。利用266 nm信号探测气溶胶光学特性时不受太阳背景光的影响。对双波长Mie散射信号日间和夜间探测信噪比的数值仿真结果和实际探测信噪比作对比分析,得出日间探测时355 nm信号的信噪比较低,夜间探测时266 nm信号的信噪比较低,这与数值仿真结果一致。通过分析实际探测信噪比为10时的数据,得到该系统日间探测时266 nm信号的探测高度可达2 km,夜间探测时355 nm信号的探测高度可达5 km。利用该激光雷达对西安地区的晴天和雾霾天气进行初步探测,研究分析了晴天和雾霾天气的气溶胶光学特性、臭氧浓度和消光系数。分析了臭氧浓度对反演消光系数和Angstrom指数的影响。结果表明,臭氧浓度越大,消光系数的反演误差越大。雾霾天气气溶胶的消光系数大于晴天气溶胶的消光系数。
Abstract
Herein, an ultraviolet dual-wavelength lidar was developed for the detection of atmospheric aerosols in the troposphere. The Nd∶YAG laser emitting beams of 355 and 266 nm at a frequency of 10 Hz were used as a light source by the dual-wavelength lidar. This dual-wavelength lidar achieved fine separation and extraction of the Mie scattering signal at ultraviolet wavelengths. Furthermore, it was not affected by the solar background light when 266-nm signal was used to measure the optical characteristics of the aerosol. The signal-to-noise ratios (SNRs) of the actual detection were compared with the simulation results at two wavelengths. Findings indicate that the SNR of 355-nm signal was lower during daytime detection; however, the SNR of 266-nm signal was lower during night-time detection. These results were consistent with theoretical calculations. The detection height of 266-nm signal can reach 2 km during daytime and that of 355-nm signal can reach 5 km during night-time upon analyzing the data of SNR of 10. Atmospheric observations were conducted using the proposed dual-wavelength lidar. The ozone concentration, aerosol characteristics, and extinction coefficient were studied and analyzed on hazy and sunny days. Moreover, the influence of ozone concentration on the inversion extinction coefficient and Angstrom index was analyzed. Results show that a greater ozone concentration corresponds to a larger inversion error of the extinction coefficient. The extinction coefficient of the aerosol in hazy weather was larger than that in sunny weather.
邵江锋, 华灯鑫, 汪丽, 王东, 潘睿. 紫外双波长激光雷达系统研制与信噪比分析[J]. 光学学报, 2020, 40(12): 1201004. Jiangfeng Shao, Dengxin Hua, Li Wang, Dong Wang, Rui Pan. Development of Ultraviolet Dual-Wavelength Lidar and Analysis of Its Signal-to-Noise Ratio[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2020, 40(12): 1201004.