2021, 19(10) Column
Atmospheric, Oceanic, Space, and Environmental Optics Diffraction, Gratings, and Holography Imaging Systems and Image Processing Instrumentation, Measurement, and Optical Sensing Integrated Optics Lasers, Optical Amplifiers, and Laser Optics Optical Design and Fabrication Physical Optics Spectroscopy Ultrafast Optics and Attosecond/High-field Physics Light-matter Interaction Microwave Photonics
Chinese Optics Letters 第19卷 第10期
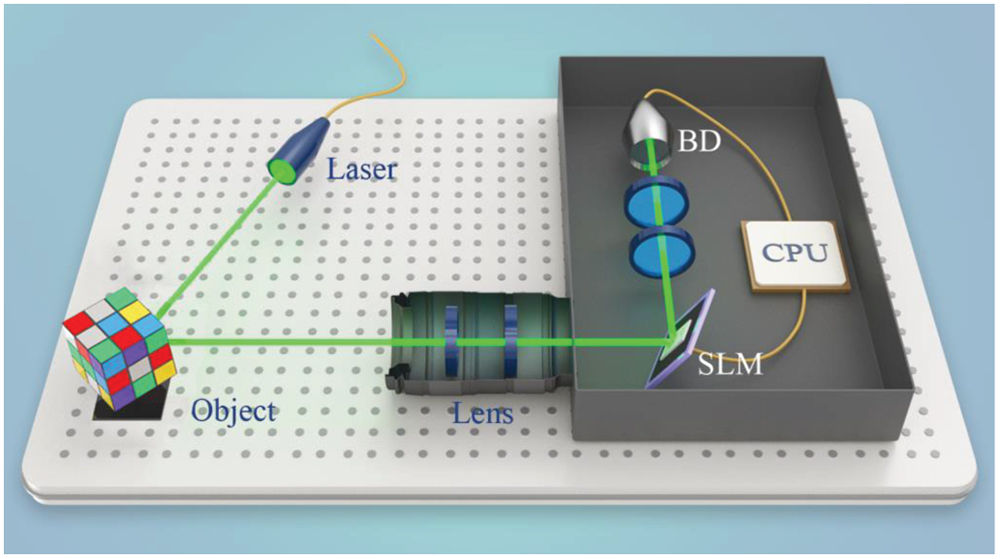
Orbital angular momentum (OAM) is a fundamental physical characteristic to describe laser fields with a spiral phase structure. Vortex beams carrying OAMs have attracted more and more attention in recent years. However, the wavefront of OAM light would be destroyed when it passes through scattering media. Here, based on the feedback-based wavefront shaping method, we reconstitute OAM wavefronts behind strongly scattering media. The intensity of light with desired OAM states is enhanced to 150 times. This study provides a method to manipulate OAMs of scattered light and is of great significance for OAM optical communication and imaging to overcome complex environment interference.
orbital angular momentum scattering wavefront shaping A general method to realize arbitrary dual-band independent phase control is proposed and demonstrated in this paper. A double-layered C-shape reflective meta-atom is designed to realize independent phase control with high efficiency. As a proof of concept, we propose two functional metasurfaces in the microwave region; the first metasurface performs beam steering in different directions, and the second metasurface generates achromatic beam steering at two distinct frequencies. Both simulation and measurement results agree well with the theoretical pre-setting. The maximum measured efficiency is 88.7% and 92.3% at 6.8 GHz and 8.0 GHz, respectively, for one metasurface, and 91.0% and 89.8% at 6.9 GHz and 8.6 GHz, respectively, for the other.
dual-band independent phase control microwave metasurface high efficiency reflection geometric phase Computational ghost imaging with compressed sensing based on a convolutional neural network Download:513次
Download:513次
 Download:513次
Download:513次Computational ghost imaging (CGI) has recently been intensively studied as an indirect imaging technique. However, the image quality of CGI cannot meet the requirements of practical applications. Here, we propose a novel CGI scheme to significantly improve the imaging quality. In our scenario, the conventional CGI data processing algorithm is optimized to a new compressed sensing (CS) algorithm based on a convolutional neural network (CNN). CS is used to process the data collected by a conventional CGI device. Then, the processed data are trained by a CNN to reconstruct the image. The experimental results show that our scheme can produce higher quality images with the same sampling than conventional CGI. Moreover, detailed comparisons between the images reconstructed using the deep learning approach and with conventional CS show that our method outperforms the conventional approach and achieves a ghost image with higher image quality.
computational ghost imaging compressed sensing convolutional neural network In this Letter, the periodical errors, which are caused by the nonlinear effect of the commercial projector and camera, are analyzed as a more generic single-coefficient model. The probability density function of the wrapped phase distributions is used as a tool to find the compensation coefficient. When the compensation coefficient is detected, on the premise of ensuring accuracy, a correlation algorithm process is used to replace the traditional iterative process. Therefore, the proposed algorithm improves the efficiency of coefficient detection dramatically. Both computer simulation and experiment show the effectiveness of this method.
nonlinear response phase error probability density function three-dimensional sensing A broadband instantaneous multi-frequency measurement system based on chirped pulse compression, which potentially has a sub-megahertz (MHz) accuracy and a hundred-gigahertz (GHz) measurement range, is demonstrated. A signal-under-test (SUT) is converted into a carrier-suppressed double-sideband (CS-DSB) signal, which is then combined with an optical linearly frequency-modulated signal having the sweeping range covering the +1st-order sideband of the CS-DSB signal. With photodetection, low-pass filtering, and pulse compression, accurate frequencies of the SUT are obtained via locating the correlation peaks. In the experiment, single- and multi-frequency measurements with a measurement range from 3 to 18 GHz and a measurement accuracy of <±100 MHz are achieved.
instantaneous frequency measurement chirped pulse compression frequency-to-time mapping microwave photonics A micro stereo sensor system is proposed for human sensors, where eyes, ears, tongue, nose, body, and brain are applied by six panda rings embedded in a Mach–Zehnder interferometer (MZI). The input power is applied to the upper branch of MZI and propagates within the system. The six antennas (sensors) are formed by the whispering gallery modes of the panda rings. The space–time modulation signal is applied to the MZI lower branch. The modulated stereo signals can be configured as the plasmon (electron) spin orientations, which can be identified and applied for quantum codes and quantum consciousness.
micro-optical devices electro-optical devices integrated optics devices We demonstrate a polarization-insensitive silicon
optical switch polarization control silicon photonics optical routing We design a 645 nm laser diode (LD) with a narrow vertical beam divergence angle based on the mode expansion layer. The vertical beam divergence of 10.94° at full width at half-maximum is realized under 1.5 A continuous-wave operation, which is the smallest vertical beam divergence for such an LD based on the mode expansion layer, to the best of our knowledge. The threshold current and output power are 1.07 A and 0.94 W, limited by the thermal rollover for the 100 µm wide and 1500 µm long broad area laser, and the slope efficiency is 0.71 W/A. The low coherence device is fabricated with the speckle contrast of 3.6% and good directional emission. Such 645 nm LDs have promising applications in laser display.
beam divergence laser diode speckle laser display An improved self-mixing grating interferometer based on the Littrow structure has been proposed in this Letter to measure displacement. The grating is integrated inside the interferometer to reduce the impact on the vibration parameters of the object caused by the grating attached to the vibrating object. The
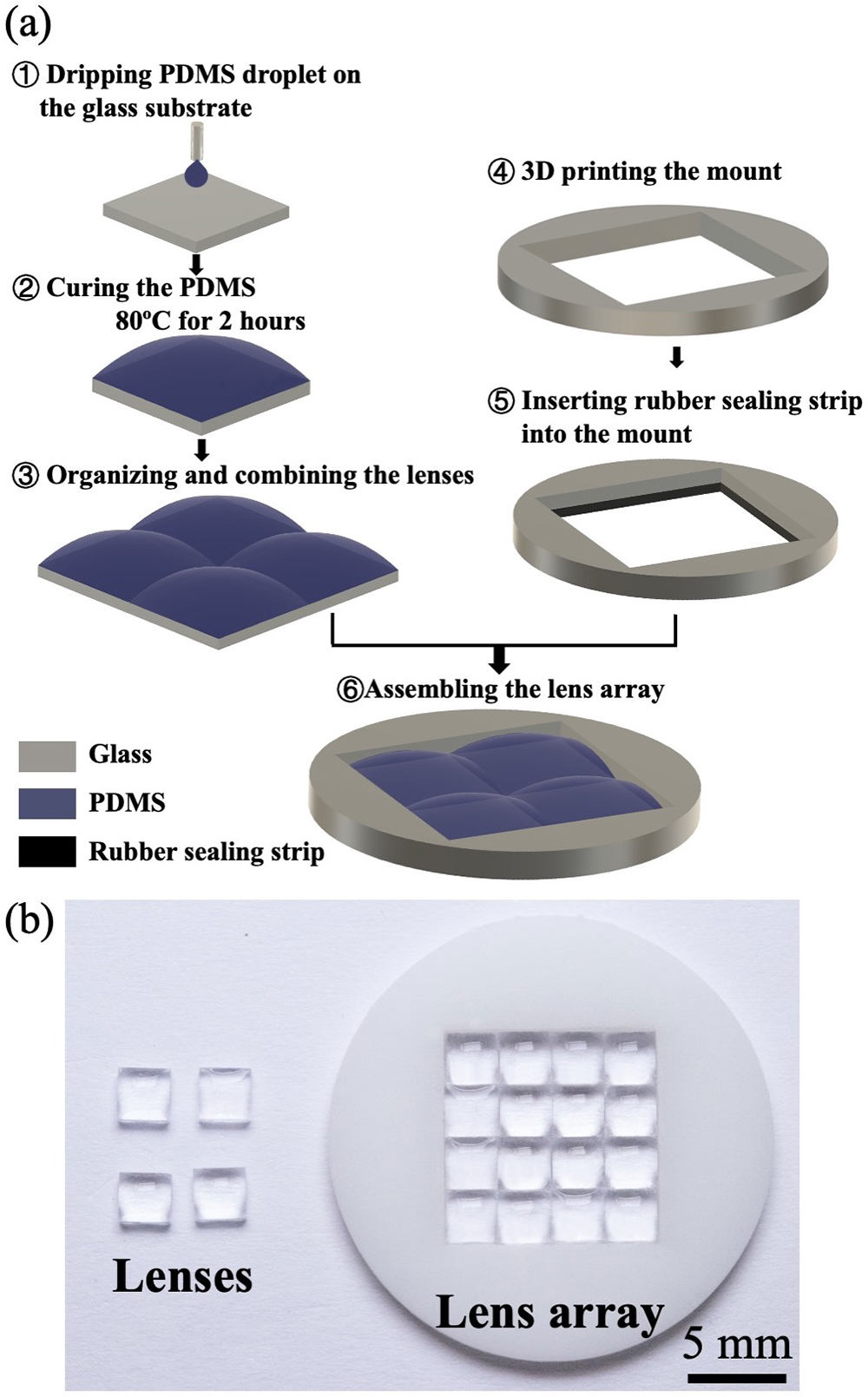
displacement sensor self-mixing interferometer diffraction grating A straightforward, cost-effective scheme for fabricating multi-focus droplet lens arrays is proposed. Mini lenses can be rapidly produced by dripping liquid-state polydimethylsiloxane droplets on the square glass substrate. The focal length of the lenses can be precisely controlled by adjusting the mass of the droplet. A group of prepared mini lenses can be flexibly assembled in a three-dimensional printed mount. The lenses are tightly packed together, ensuring a high filling factor of the lens array. The lens array consisting of the mini lenses with a proper combination of focal length can capture images of interests at different depth.
optical design and fabrication lenses Optical fibers have been widely applied to telecommunication, imaging, lasers, and sensing. Among the different types of fibers, photonic crystal fibers (PCFs), also called microstructured optical fibers, characterized by air holes arranged along the length of fibers have experienced tremendous advance due to their unique advantages. They are regarded as a desirable platform to excite surface plasmon resonance (SPR) because of easy realization of phase matching conditions between the fundamental core mode and the plasmonic mode, which plays a critical role in miniaturization and integration of SPR sensors. In this mini-review, the current status of PCF sensors based on SPR is summarized. The theory of SPR is discussed, and simulation methods for PCF-SPR sensors are described. The important parameters including the refractive index detection range, resonance wavelength, and spectral sensitivity responsible for the sensing properties of PCF-SPR sensors are reviewed. The fabrication and the comparison of performances are also illustrated, and, finally, the challenges and future perspectives are outlined.
photonic crystal fibers surface plasmon resonance refractive index sensors A new phase unwrapping method based on dual-frequency fringe is proposed to improve both high accuracy and large measurement range of three-dimensional shape measurement by synthesizing the projected dual-frequency fringes obtaining higher and lower frequencies. The lower-frequency one is their phase difference, which can help unwrap the wrapped phase of the higher-frequency one from their phase sum. In addition, the relationship between the measuring accuracy and the frequencies of the projected fringes is studied to guide the frequency selection in actual measurement. It is found that the closer the two frequencies are, the higher the measurement accuracy will be. The computer simulation and experiment results show the viability of this method.
fringe projection 3D shape measurement dual frequency phase shifting phase sum Photonic nanojets (PNJs) are subwavelength jet-like propagating waves generated by illuminating a dielectric microstructure with an electromagnetic wave, conventionally a linearly polarized plane wave. Here, we study the donut-like PNJ produced when a circularly polarized vortex beam is used instead. This novel PNJ also has a reverse energy flow at the donut-like focal plane depending on both the optical vortex topological charge and microsphere size. Our tunable PNJ, which we investigate numerically and analytically, can find applications in optical micromanipulation and trapping.
photonic nanojet optical vortex reverse energy flow Two-dimensional (2D) perovskites exhibit broadband emission due to strong exciton–phonon coupling-induced self-trapped excitons and thus would find important applications in the field of white-light emitting devices. However, the available identifying methods for self-trapped excitons are currently rather limited and complex. Here, we identify the existence of self-trapped excitons by Raman spectroscopy in both excited and non-excited states. Under excited states, the shifting of the Raman peak indicates the presence of the lattice distortion, which together with the extra Raman scattering peak reveals the presence of self-trapped excitons. Our work provides an alternative simple method to study self-trapped excitons in 2D perovskites.
self-trapped excitons 2D perovskite Raman spectrum excited states Laser polarization and its intensity inside a filament core play an important role in filament-based applications. However, polarization dependent clamping intensity inside filaments has been overlooked to interpret the polarization-related filamentation phenomena. Here, we report on experimental and numerical investigations of polarization dependent clamping intensity inside a femtosecond filament in air. By adjusting the initial polarization from linear to circular, the clamping intensity is increased by 1.36 times when using a 30 cm focal length lens for filamentation. The results indicate that clamping intensity inside the filament is sensitive to laser polarization, which has to be considered to fully understand polarization-related phenomena.
femtosecond laser filamentation clamping intensity polarization We present the perfect light absorption of monolayer molybdenum disulfide (
optical Tamm states molybdenum disulfide light absorption An approach to generate high-speed and wideband frequency shift keying (FSK) signals based on carrier phase-shifted double sideband (CPS-DSB) modulation is proposed and experimentally validated. The core part of the scheme is a pair of cascaded polarization-sensitive LiNbO3 Mach–Zehnder modulators and phase modulators, whose polarization directions of the principal axes are mutually orthogonal to each other. A proof-of-concept experiment is carried out, where a 0.5 Gb/s FSK signal with the carrier frequencies of 4 and 8 GHz and a 1 Gb/s FSK signal with the carrier frequencies of 8 and 16 GHz are generated successfully.
microwave photonics frequency shift keying polarization-sensitive modulator microwave signals generation carrier phase-shifted double sideband modulation 动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 | 经典导波与拓扑单向波间的高效转换动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 主编推荐 | 单片集成硅基灵活栅格MWSS为突破“容量危机”提供新策略动态信息 丨 2024-04-10
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 封面 |构造任意自相似类贝塞尔光束构造新方法动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 |声光调制的干涉增强效应,助力光学量子信息技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 基于时空耦合效应的超宽带频率转换技术激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦