2015, 13(4) Column
Chinese Optics Letters 第13卷 第4期
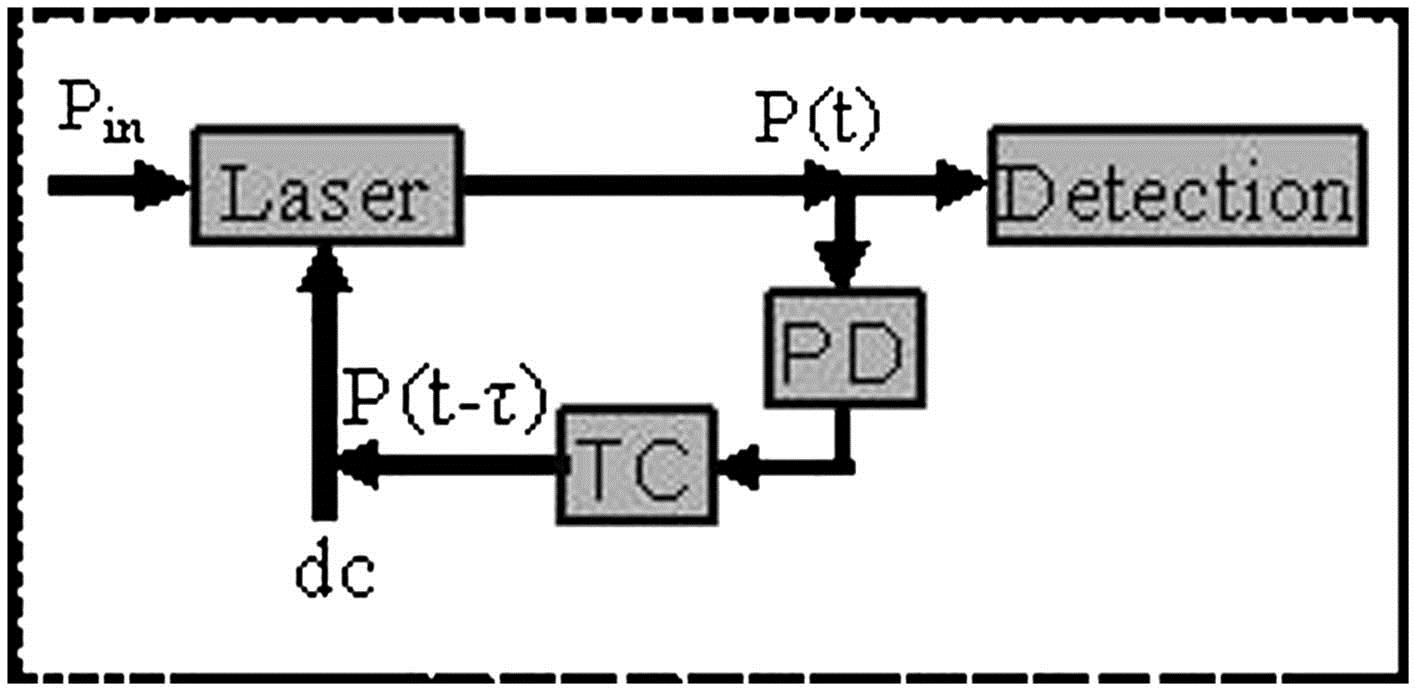
Period-one characteristic in an optoelectronic delayed feedback semiconductor laser and its application in sensing Download:1122次
Download:1122次
 Download:1122次
Download:1122次Nonlinear dynamics in an optoelectronic delayed feedback semiconductor laser and its application in sensing are studied. We analyze the theories of stability and period of the laser. A route to quasi-periodic bifurcation or a stochastic state from stability is numerically analyzed by shifting the feedback level. The induced dynamics are found to be in one of four distributions (stable, periodic pulsed, period-three pulsed, and undamping oscillating). An external injection into the laser results in the process being more or less the opposite with the conventional optical injection cases. Based on this process or the dynamic regimes, we present a modeling of the incoherent detection sensor using the nonlinear period-one characteristic of the laser. The sensor discriminates the injection light variation as a sensing signal via detecting the behaviors from the period-one laser.
040.5160 Photodetectors 140.5960 Semiconductor lasers 190.3100 Instabilities and chaos Light source system for high-precision flat-field correction and the calibration of an array detector Download:1193次
Download:1193次
 Download:1193次
Download:1193次Signal distortion due to the non-uniform response of the detector degrades the measurement accuracy of most metrology instruments. In this Letter, we report a newly developed calibration source system for reference-based non-uniformity correction using a laser source, a fiber, and a diffusive module. By applying the Monte Carlo simulation, we show that the transmittance of the system highly depends on the cavity reflection of the diffusive module. We also demonstrate the use of this system to achieve a flat field at a very low non-uniformity (less than 0.2%) with proper illumination intensity, which most costly commercial integrating sphere systems traditionally cannot provide.
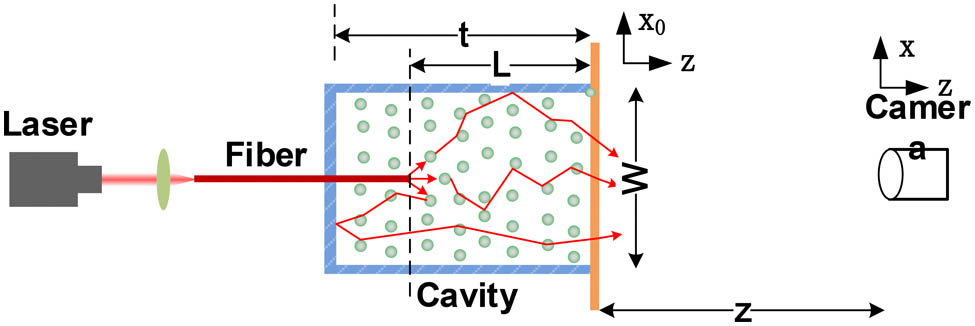
040.1240 Arrays 290.7050 Turbid media 290.0290 Scattering 030.1670 Coherent optical effects 030.6140 Speckle Performance analysis of non-line-of-sight ultraviolet communication through turbulence channel Download:858次
Download:858次
 Download:858次
Download:858次The bit error rate performance of non-line-of-sight ultraviolet communication through atmospheric turbulence is studied. The communication performance degradation under different strengths of turbulence is evaluated. Particularly, under strong turbulence conditions, the communication distance can be shortened by 30%, or at a given distance the communication rate can be reduced by half than the counterpart of no turbulence.
060.2605 Free-space optical communication 060.4510 Optical communications A transfer method is introduced to derive the normalized radiance for CE318 Sun/sky radiometer using viewing solid angles and extraterrestrial calibration constants. The new transfer method has a good consistency at different parts of the sky scanning. Error analysis suggests that the uncertainty of the transferred method is about 2.0%–2.4%. The normalized radiances are used as input of the aerosol inversion to test the performance of the new transfer method. The residuals of the inversion (e.g., difference between fitted and measured radiance) are chosen as the index of the radiance calibration accuracy. Analyses of one year’s measurements in Beijing suggest an average sky residual of 3.3% for almucantar scanning (while 3.7% for the AERONET method), which suggest a better accuracy of the transfer method when used in aerosol retrieval.
010.0280 Remote sensing and sensors 010.1310 Atmospheric scattering 010.3920 Meteorology 120.5630 Radiometry The stochastic parallel gradient descent (SPGD) algorithm is widely used in wavefront sensor-less adaptive optics (WSAO) systems. However, the convergence is relatively slow. Modal-based algorithms usually provide much faster convergence than SPGD; however, the limited actuator stroke of the deformable mirror (DM) often prohibits the sensing of higher-order modes or renders a closed-loop correction inapplicable. Based on a comparative analysis of SPGD and the DM-modal-based algorithm, a hybrid approach involving both algorithms is proposed for extended image-based WSAO, and is demonstrated in this experiment. The hybrid approach can achieve similar correction results to pure SPGD, but with a dramatically decreased iteration number.
110.1080 Active or adoptive optics 110.3010 Image reconstruction techniques Alignment methods for micron-scale surface defects automatic evaluation of large-aperture fine optics Download:929次
Download:929次
 Download:929次
Download:929次A surface defect evaluation system can combine microscopic scattering dark-field imaging with sub-aperture scanning and stitching. Thousands of sub-apertures are involved; mechanical errors will cause stitching dislocation, leading to defect cracks. In this Letter, we propose standard line coordinate error adjustment dealing with consistency error between coordinates of the scanning and imaging system, and defocus depth estimation leveling method dealing with high-cleanliness fine optics defocuing caused by the surface which is not perpendicular to microscope’s optical axis. Experiments show defect cracks are effectively solved and the defocus of 420 mm × 420 mm
110.2970 Image detection systems 150.1835 Defect understanding 330.1880 Detection We propose a sub-aperture stitching algorithm based on a frequency domain that can be denoted as a power spectral density (PSD). Our algorithm is verified by the experimental data obtained from measuring a Φ1.23 m mirror at the Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics. Then, we apply it to the Great Steering Science Mirror (GSSM) of the Thirty Meter Telescope (TMT) with the simulated data before the preliminary design phase, and obtain a more objective result on the frequency domain aberrations. Therefore, the sub-aperture stitching-based PSD is expected to be useful for specifying a large aperture mirror surface for mirror vendors.
120.3940 Metrology 110.6770 Telescopes 110.3925 Metrics We report a 1.8 μm two-section distributed Bragg reflector laser using butt-jointed InGaAsP bulk material as the waveguide core layer. The threshold current is 17 mA and the output power is 8 mW on average. The threshold current, output power, and emitting wavelength dependences on temperature are measured. The obtained wavelength tuning range is 10 nm. This device has potential applications in simultaneous multiple-gas detection.
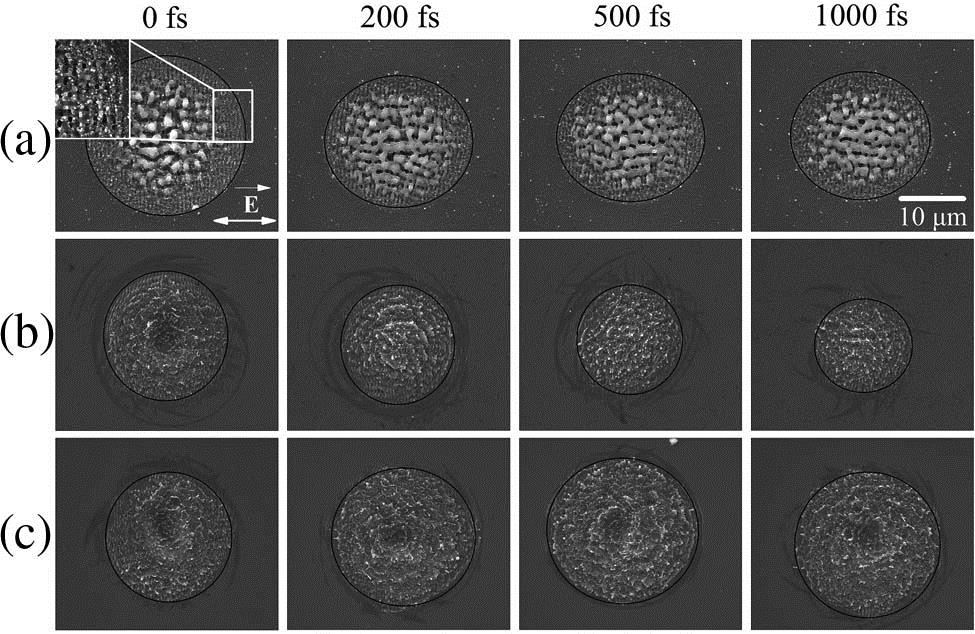
140.0140 Lasers and laser optics 140.5960 Semiconductor lasers 140.3600 Lasers, tunable 140.3570 Lasers, single-mode Ethanol-assisted ablation of silicon and germanium by temporally shaped femtosecond pulses Download:964次
Download:964次
 Download:964次
Download:964次A surprising phenomenon can be discovered by using femtosecond double-pulse ablation of silicon and germanium in ethanol. The ablation areas present an oscillation increase phenomenon when the pulse delay increases from 200 fs to 1 ps in the fluence range of 0.5 – 0.6 J / cm 2 F < 0.5 J / cm 2
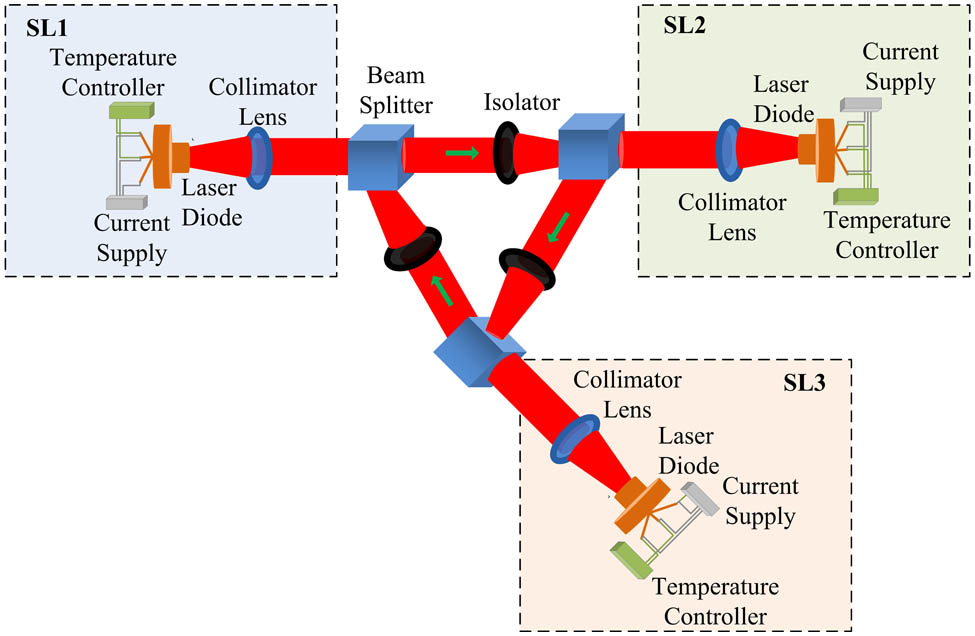
140.3390 Laser materials processing 320.5540 Pulse shaping 320.2250 Femtosecond phenomena Loss of time-delay signature in a ring of three unidirectionally coupled semiconductor lasers Download:844次
Download:844次
 Download:844次
Download:844次A ring of three unidirectionally coupled semiconductor lasers (RTUC-SLs) is used to generate broadband chaos with no pronounced time-delay (TD) signature. Using the autocorrelation function and permutation entropy as the TD measures, we demonstrate that under suitable coupling strength, the loss of the TD signature of the lasers in the RTUC-SL configuration is achieved both for the intensity and the phase. These findings should prove valuable for developing high-quality optical chaos for potential applications, such as chaos-based communications and random number generation.
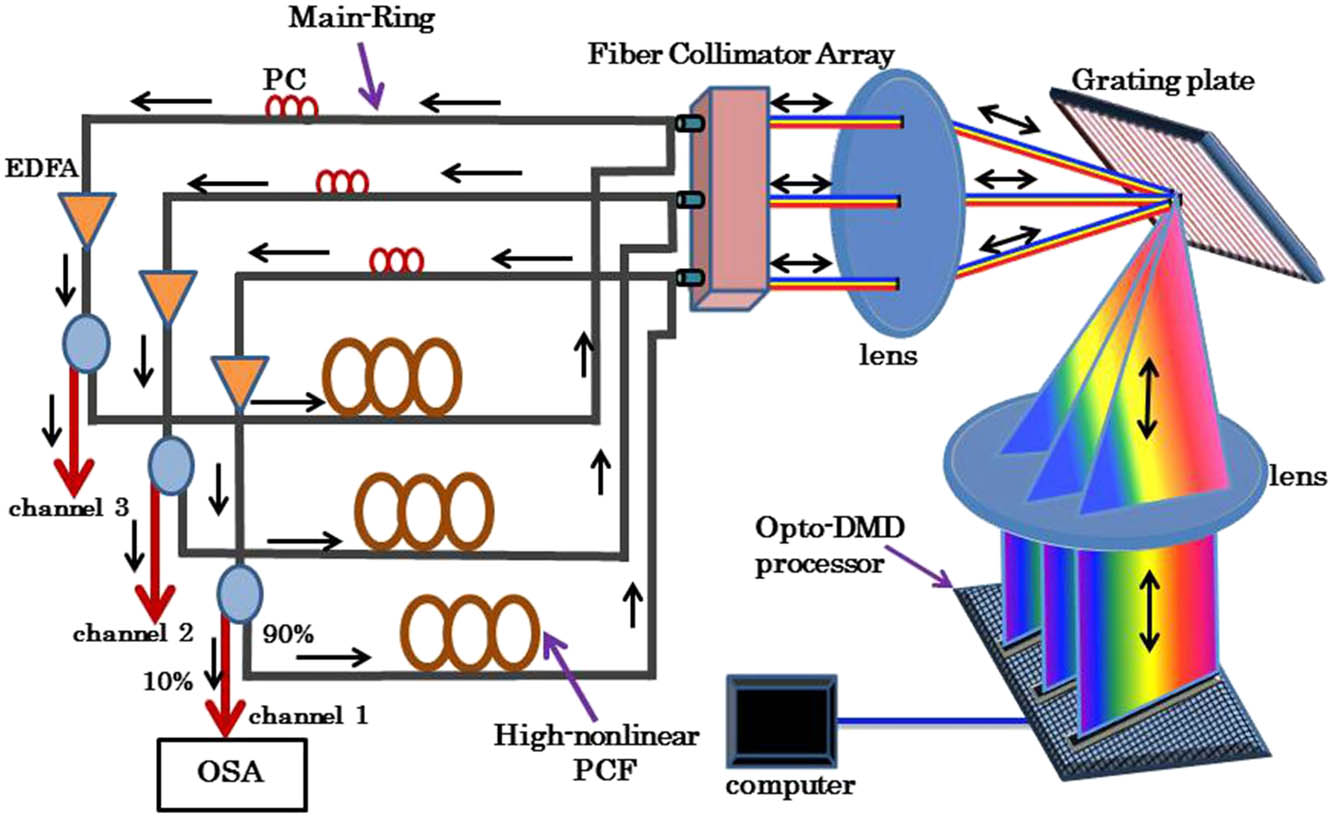
140.5960 Semiconductor lasers 190.3100 Instabilities and chaos Three-channel dual-wavelength fiber laser based on a digital micromirror-device processor and photonic crystal fiber Download:937次
Download:937次
 Download:937次
Download:937次A stable three-channel dual-wavelength fiber ring laser is proposed and experimentally demonstrated. The digital micromirror-device (DMD) processor can select and recirculate any dual waveband from the gain spectrum of the erbium-doped fiber at each channel. The uniform and stable dual-wavelength oscillation is obtained by a highly nonlinear photonic crystal fiber, which causes two degenerate the four-wave-mixing processes. By loading different reproducibility diffraction gratings on the optoelectronic DMD processor, the laser can be operated stably in a three-channel dual-wavelength scheme at room temperature. The power fluctuation of each laser channel is less than ~ 0.02 dB
140.3500 Lasers, erbium 140.3510 Lasers, fiber 140.3515 Lasers, frequency doubled Femtosecond Bessel-beam-assisted high-aspect-ratio microgroove fabrication in fused silica Download:1149次
Download:1149次
 Download:1149次
Download:1149次A simple and repeatable method to fabricate high-aspect-ratio (HAR) and high-quality microgrooves in silica is reported. The method consists of two steps: (1) formation of laser-modified regions by femtosecond Bessel beam irradiation, and (2) removing laser-modified regions through HF etching. Uniform, straight microgrooves can be fabricated and the highest aspect ratio that can be reached is ~ 52
140.3390 Laser materials processing 230.4000 Microstructure fabrication 320.5540 Pulse shaping The generation and measurement of complex ultraviolet laser pulse shapes is demonstrated in the SG-III laser facility. Relatively high contrast ratio of 300 ∶ 1
140.3300 Laser beam shaping 350.2660 Fusion 350.4600 Optical engineering The combination of deep wet etching and a magneto-rheological finishing (MRF) process is investigated to simultaneously improve laser damage resistance of a fused-silica surface at 355 nm. The subsequently deposited SiO 2 SiO 2
140.3330 Laser damage 140.3440 Laser-induced breakdown 140.3380 Laser materials Refractive indices for crystals ammonium dihydrogen phosphate (ADP), 30% deuterated ADP (DADP), 50% DADP, and 70% DADP are measured from 253 to 1529 nm with 5 × 10 6
160.4760 Optical properties 160.4330 Nonlinear optical materials 260.1180 Crystal optics 190.4400 Nonlinear optics, materials We report on the rich dynamics of two-dimensional fundamental solitons coupled and interacting on the top of an elliptical shaped potential in a two-dimensional Ginzburg–Landau model. Under the elliptical shaped potential, the solitons display unique and dynamic properties, such as the generation of straight-line arrays, emission of either one elliptical shaped soliton or several elliptical ring soliton arrays, and soliton decay. When changing the depth and sharpness of the external potential and fixing other parameters of the potential, various scenarios of soliton dynamics are also revealed. These results suggest some possible applications for all-optical data-processing schemes, such as the routing of light signals in optical communication devices.
190.0190 Nonlinear optics 190.6135 Spatial solitons Closed-loop correction and ocular wavefronts compensation of a 62-element silicon unimorph deformable mirror Download:817次
Download:817次
 Download:817次
Download:817次Adaptive optics (AO) systems greatly improve the resolution of retinal imaging instruments by actively correcting ocular aberrations. In this Letter, closed-loop correction as well as ocular aberration compensation of a 62-element silicon unimorph deformable mirror (DM) driven by only positive voltage is performed. The experimental results show that the root-mean square (RMS) wavefront of the initial mirror surface is reduced to 0.011 μm in a closed-loop AO system. The DM reproduces Zernike shapes from the third to 35th mode accurately. The simulated compensation of 200 ocular wavefronts shows that the average RMS value after correction is reduced to 0.017 μm.
220.1080 Active or adoptive optics 170.4470 Ophthalmology 220.1000 Aberration compensation Synthesis and properties of novel blue-emitting materials: anthracene-based derivatives Download:902次
Download:902次
 Download:902次
Download:902次Two kinds of novel blue-emitting materials, anthracene-based derivatives, are synthesized by the Suzuki coupling reaction. It is worth noting that the maximum emission wavelengths of the two materials are 441 and 444 nm in tetrahydrofuran and 456 and 454 nm in film states, which are the typical blue fluorescence and the fluorescence quantum yields of them are 0.87 and 1.12 by using 9,10-diphenylanthracene ( Φ f = 0.90 )
230.3670 Light-emitting diodes 160.2540 Fluorescent and luminescent materials 160.4890 Organic materials In this Letter, we present a possible methodology to directly “read” the force on an atom via the photons emitted from the atom. In this methodology, the mean radiative force on an atom exerted by external fields can be expressed as a function of the average number of emitted photons N
270.5290 Photon statistics 030.5260 Photon counting 020.3320 Laser cooling A static-mode synthetic aperture imaging ladar (SAIL) in which the target and carrying platform are kept still during the collection process is proposed and demonstrated. A target point of 0.5 mm × 0.5 mm
280.6730 Synthetic aperture radar 280.3640 Lidar 100.2000 Digital image processing 100.3010 Image reconstruction techniques 110.0110 Imaging systems 动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-10
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 封面 |构造任意自相似类贝塞尔光束构造新方法动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 |声光调制的干涉增强效应,助力光学量子信息技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 基于时空耦合效应的超宽带频率转换技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 21, Iss. 11): 综述:太赫兹偏振光谱和手性光谱传感检测技术新应用动态信息 丨 2024-03-21
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 全光学的相位目标边缘提取,助力高分辨生物医学成像激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦