2015, 13(6) Column
Chinese Optics Letters 第13卷 第6期
We propose and experimentally demonstrate a novel scheme to realize electrical/optical (E/O) conversion on the receiver side of a wireless fiber integration system at the W band. At the receiver, a directly modulated laser (DML) is used to realize E/O conversion. The received 85 GHz wireless millimeter-wave (mm-wave) signal is first down-converted into a 10 GHz electrical intermediate-frequency (IF) signal to overcome the insufficient bandwidth of the subsequent DML. Then, two cascaded electrical amplifiers (EAs) are employed to boost the electrical IF signal before it is used to drive a DML. By using this scheme, we transmit a 10 Gb/s 16 quadrature amplitude modulation (16QAM) signal over a 10 m wireless link, and then deliver it over a 2 km single-mode fiber-28 (SMF-28) wire link with a bit error ratio (BER) that is less than the hard-decision forward error correction threshold of 3.8 × 10 3
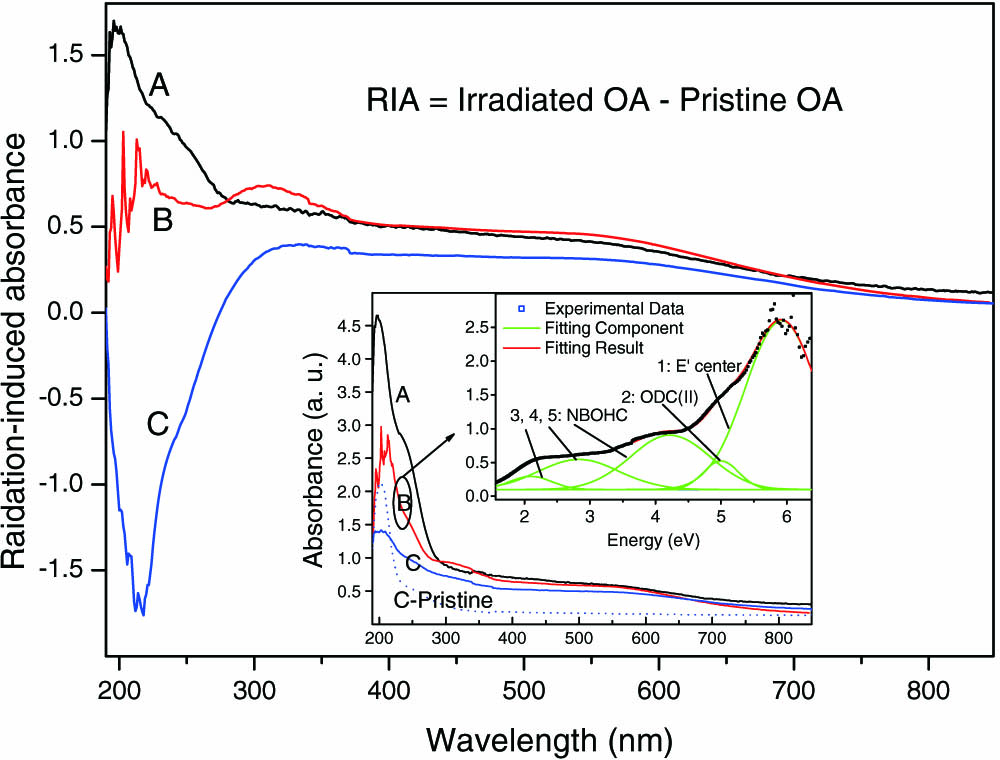
060.0060 Fiber optics and optical communications 060.2840 Heterodyne 060.5625 Radio frequency photonics 060.3510 Lasers, fiber Yb-doped silica glasses containing low, medium, and high content of OH are prepared through nanoporous glass sintering technology. High-OH sample exhibits better X-ray irradiation resistivity than low- and medium-OH samples. After irradiation, OH content of low- and medium-OH samples increases 37.5% and 11%, respectively; in contrast, OH content of high-OH sample decreases dramatically. The different OH content changes among the samples are discussed regarding the proposed inter-conversion reactions involving Si - H Si - OH
060.2290 Fiber materials 160.2750 Glass and other amorphous materials 160.5690 Rare-earth-doped materials 350.5610 Radiation Theoretical study of all-optical RZ-OOK to NRZ-OOK format conversion in uniform FBG for mixed line-rate DWDM systems Download:852次
Download:852次
 Download:852次
Download:852次In this work we study all-optical multi-channel return-to-zero (RZ)–on-off keying (OOK) to nonreturn-to-zero (NRZ)–OOK format conversion in single uniform fiber Bragg grating (FBG) for mixed line-rate dense wavelength-division multiplexing systems using mathematical simulations. Forty and 20 Gbit/s RZ–OOK signals with 33% and 50% duty cycles are converted to NRZ–OOK signals in single uniform FBG with 21% reflectivity. Impact of amplitude noise from FBG contrast profile on modulation format conversion efficiency is also studied.
060.1155 All-optical networks 060.2340 Fiber optics components 060.3735 Fiber Bragg gratings Generation of ultra-flat optical frequency comb using a balanced driven dual parallel Mach–Zehnder modulator Download:926次
Download:926次
 Download:926次
Download:926次We propose and experimentally demonstrate an ultra-flat optical frequency comb (OFC) generator by a balanced driven dual parallel Mach–Zehnder modulator. Five- and seven-tone OFC with exactly equal intensity can be generated theoretically. Experimentally obtained five- and seven-tone OFC with flatness of 0.6 and 1.26 dB are demonstrated, respectively, which agrees well with the theoretical results.
060.1660 Coherent communications 060.2330 Fiber optics communications 060.2380 Fiber optics sources and detectors In order to select a suitable spatial filter for the spatial filtering velocimeter, the filtering characteristics of the spatial filters with a rectangular window and rectangular transmittance are investigated by the power spectrum of transmittance function method. The filtering characteristics of differential filters are investigated and compared with that of common ones. The influences of the number of spatial periods on the spectral bandwidth, deviation to central frequency, and peak transmittance are deeply analyzed. The results show that the influence is due to the form of superposition of the signal components and other components, the pedestal and higher-order components, and the superposition results from the finite size of the spatial filter. According to the results, a method is proposed to compensate for the deviation to central frequency.
070.6110 Spatial filtering 110.4850 Optical transfer functions 050.2770 Gratings Past research has demonstrated that if the intensity image of an object is uniformly down-sampled and converted into a Fresnel hologram, the phase component alone will be sufficient to reconstruct the source image. However, due to down-sampling, the edge and line patterns are degraded heavily. In this Letter, we propose an enhancement on the parent method by incorporating an adaptive down-sampling lattice. A hologram generated with our proposed method, which is referred to as the edge-enhanced sampled phase-only hologram, preserves favorable visual quality on both the shaded regions as well as the edge patterns of the object image.
090.1995 Digital holography 090.1760 Computer holography 090.0090 Holography The energy of light exposed on human skin is compulsively limited for safety reasons which affects the power of photoacoustic (PA) signal and its signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) level. Thus, the final reconstructed PA image quality is degraded. This Letter proposes an adaptive multi-sample-based approach to enhance the SNR of PA signals and in addition, detailed information in rebuilt PA images that used to be buried in the noise can be distinguished. Both ex vivo and in vivo experiments are conducted to validate the effectiveness of our proposed method which provides its potential value in clinical trials.
100.2980 Image enhancement 170.1065 Acousto-optics 170.5120 Photoacoustic imaging Fiber-based radio frequency dissemination for branching networks with passive phase-noise cancelation Download:913次
Download:913次
 Download:913次
Download:913次We demonstrate a new fiber-based radio frequency (RF) dissemination scheme suitable for a star-shaped branching network. Without any phase controls on the RF signals or the use of active feedback-locking components, the highly stable reference frequency signal can be delivered to several remote sites simultaneously and independently. The relative frequency stabilities of 6 × 10 15 / s 7 × 10 17 / 10 4 s
120.3930 Metrological instrumentation 120.3940 Metrology 060.2360 Fiber optics links and subsystems We report a compact 2 × 2 22 dB π / 2
130.4815 Optical switching devices 130.3120 Integrated optics devices 200.4650 Optical interconnects A laser-diode-pumped high-pulse-energy Nd:LiYF4 master oscillator power amplifier 1053 nm laser system is demonstrated. We design a home-made pump module to homogenize the pump intensity through the ray tracing method. To increase the extraction efficiency, the pre-amplifier adopts a double-pass amplification structure. At a repetition rate of 50 Hz, 655 mJ pulse energy and 12.9 ns pulse width of 1053 nm laser is obtained from the master oscillator power amplifier system. The corresponding peak power is 51 MW. The optical-to-optical efficiency of the system is about 9.7%.
140.3280 Laser amplifiers 140.3480 Lasers, diode-pumped 140.3580 Lasers, solid-state One-step formation of multifunctional nano- and microscale structures on metal surface by femtosecond laser Download:898次
Download:898次
 Download:898次
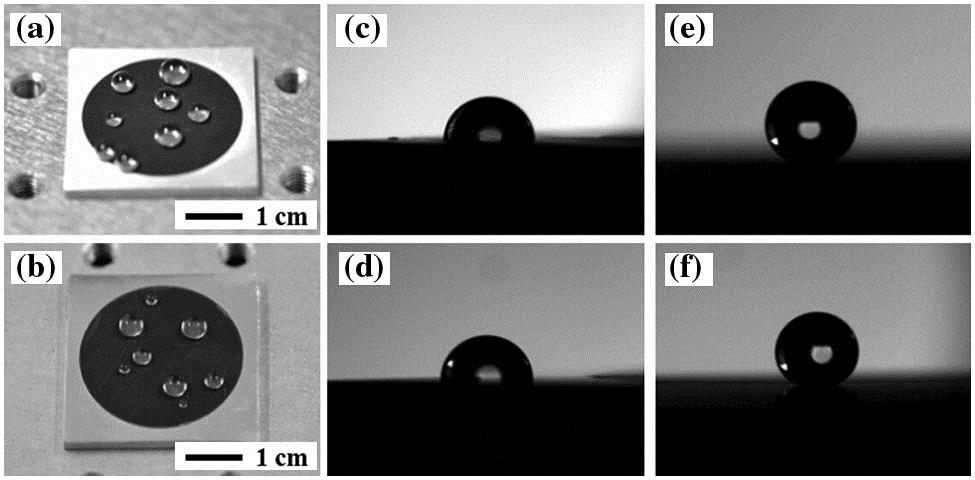
Download:898次Metals in nature exhibit a mediocre wettability and a high optical reflectance from the visible region to the infrared. This Letter reports that, by formation of nano- and microscale structures via a simple raster scanning of a focused femtosecond laser pulse without any further treatment, structured aluminum and nickel surfaces exhibit combined features of superhydrophobicity with a contact angle of 155.5°, and a high optical absorption with a reflectivity of several percent over a broad spectral range (0.2–2.5 μm). Thus, a multifunctional structured metal surface that integrates superhydrophobicity and a high broadband absorptivity has been easily realized by one-step femtosecond laser processing.
140.3390 Laser materials processing 160.4236 Nanomaterials 240.6700 Surfaces Spectral characteristics of arc plasma during laser-arc double-sided welding for aluminum alloy Download:661次
Download:661次
 Download:661次
Download:661次In laser-arc double-sided welding, the spectral characteristics of the arc plasma are calculated and analyzed by spectroscopic diagnosis. The results show that, compared with conventional tungsten inert gas (TIG) welding, the introduction of a laser changes the physical characteristics of the arc plasma regardless of whether laser plasma penetration takes place, and that the influence of the laser mainly affects the near-anode region of the arc. When the laser power is relatively low, the arc column tends to compress, and the arc spectral characteristics show no significant difference. When the arc root constricts, compared with pure TIG arc, the electron density increases by ~ 2.7 ~ 3000 K
140.3390 Laser materials processing 350.3390 Laser materials processing 300.6170 Spectra We report on a widely tunable, narrow linewidth operation of a Tm:YAG ceramic laser. A volume Bragg grating is used in the cavity as a folding mirror for wavelength selection. The wavelength is tuned from 1956.2 to 1995 nm, leading to a total tuning range of 38.7 nm. The linewidth is around 0.1 nm over the whole tuning range. A maximum output power of 1.51 W at 1990.5 nm is achieved at 37.8 W absorbed pump power. Different saturation behaviors are observed in the laser performances at different wavelengths.
140.3600 Lasers, tunable 140.3580 Lasers, solid-state 050.7330 Volume gratings In this Letter, we describe an optical assembly that is designed for the engineering application of the atomic laser cooling techniques. Using a folded optical path scheme, we have built a miniaturized, compact magneto-optical trap (CMOT) for an Rb 87
140.3320 Laser cooling 130.0130 Integrated optics All-fiber signal combiner is a key component for augmenting the fiber laser power. Presently the reported 7 × 1 7 × 1 M 2
140.3510 Lasers, fiber 140.3298 Laser beam combining 060.2310 Fiber optics 060.2340 Fiber optics components 230.2285 Fiber devices and optical amplifiers Self-Q Yb : KGd ( WO 4 ) 2 Yb 3 + Yb : KGd ( WO 4 ) 2
140.3580 Lasers, solid-state 140.3480 Lasers, diode-pumped 140.3615 Lasers, ytterbium 140.3538 Lasers, pulsed The characteristics of stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) in perfluorinated amine media and the experimental structure used in hundreds of picoseconds pulse compression at 532 nm are demonstrated. A two-stage SBS pulse compression structure is adopted for this work. The compact double-cell SBS compression structure and the scattering media FC-70 are chosen to compress the incident light from 9.5 to about 1 ns in the first stage. Then, the light is used as the pumping source for the second pulse compression. In the second stage, using a single-cell SBS structure in a pulse compression system, perfluorinated amine media with different phonon lifetimes, such as FC-3283, FC-40, FC-43, and FC-70, are chosen to run the comparative experimental study. The narrowest compressed pulse times obtained are 294, 274, 277, and 194 ps; they respectively correspond to the above listed media. The average width of the compressed pulse width is 320 ps for FC-3283, with a fluctuation range of 87 ps. For FC-40, the average pulse width is 320 ps, with a fluctuation range of 72 ps. And for FC-43, the average pulse width is 335 ps, with a fluctuation range of 88 ps. However, the average pulse width is only 280 ps for FC-70, with a fluctuation range of 57 ps. The highest energy reflectivity is more than 80% for all of the media. The experimental results show that a two-stage SBS pulse compression system has lower pump energy requirements, thus making it easier to achieve a compressed pulse waveform. The results also show that the shorter the phonon lifetime of the medium, the narrower the obtained compressed pulse width.
190.0190 Nonlinear optics 140.0140 Lasers and laser optics Morphology control of laser-induced periodic surface structure on the surface of nickel by femtosecond laser Download:866次
Download:866次
 Download:866次
Download:866次An interesting transition between low spatial frequency laser-induced periodic surface structure (LIPSS) and high spatial frequency LIPSS (HSFL) on the surface of nickel is revealed by changing the scanning speed and the laser fluence. The experimental results show the proportion of HSFL area in the overall LIPSS (i.e., K ) presents a quasi-parabola function trend with the polarization orientation under a femtosecond (fs) laser single-pulse train. Moreover, an obvious fluctuation dependence of K on the pulse delay is observed under a fs laser dual-pulse train. The peak value of the fluctuation is found to be determined by the polarization orientation of the dual-pulse train.
220.4241 Nanostructure fabrication 320.2250 Femtosecond phenomena 260.5430 Polarization 320.5540 Pulse shaping A portable infrared spectral radiance measurement apparatus without the cooling based on PbSe detectors is designed to measure the spectral radiance of the object in the wavelength range from 2.1 to 4.1 μm. Cores Luxell 256 module is applied which integrates 256 pixel line array PbSe detectors, amplifiers, analog-to-digital convertors, and Universal Serial Bus output interface. Electric aperture is applied to eliminate the effect of temperature drift. Wavelength and response function of the apparatus is calibrated with the blackbody. Results show that the wavelength resolution is 10 nm. The relative error of measured spectral radiance is below 2.3%.
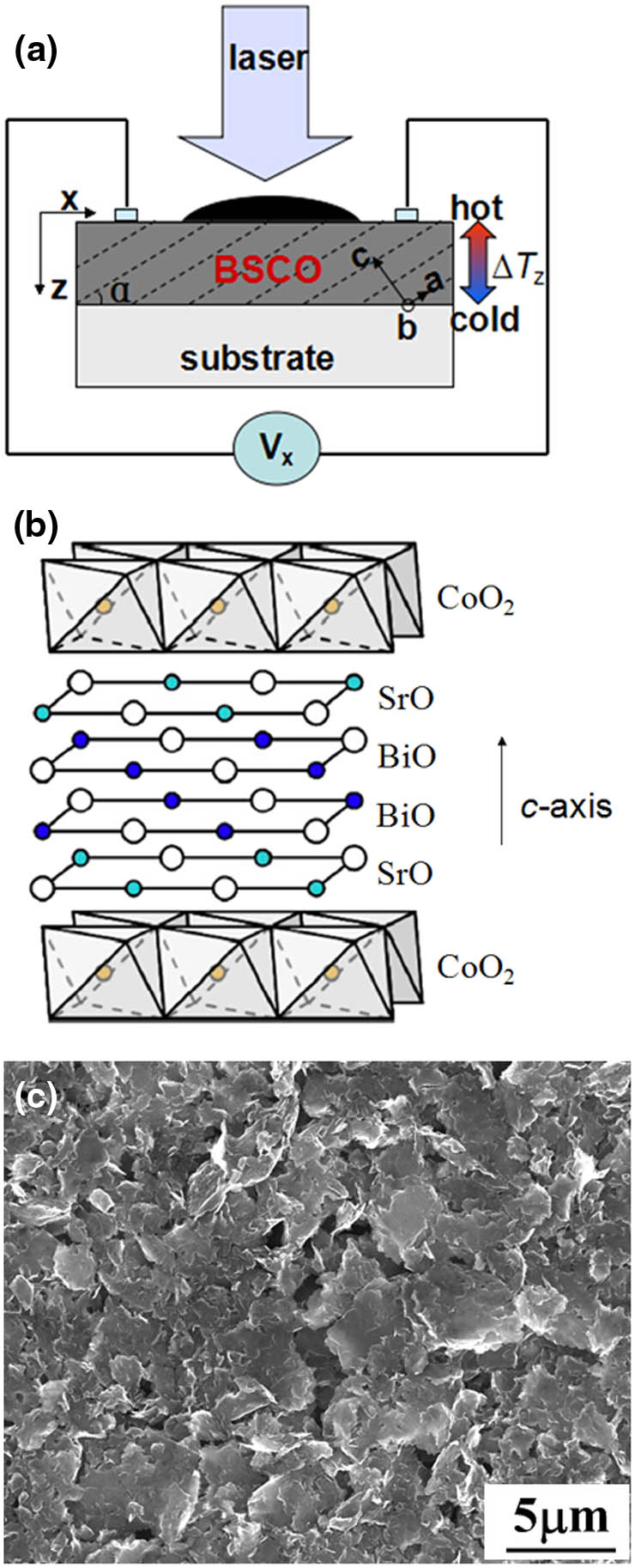
300.6340 Spectroscopy, infrared 040.3060 Infrared 120.4570 Optical design of instruments Light-induced transverse thermoelectric effect is investigated in incline-oriented Bi 2 Sr 2 Co 2 O y
310.6845 Thin film devices and applications 040.5160 Photodetectors 230.4170 Multilayers 动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 | 经典导波与拓扑单向波间的高效转换动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 主编推荐 | 单片集成硅基灵活栅格MWSS为突破“容量危机”提供新策略动态信息 丨 2024-04-10
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 封面 |构造任意自相似类贝塞尔光束构造新方法动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 |声光调制的干涉增强效应,助力光学量子信息技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 基于时空耦合效应的超宽带频率转换技术激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦