2016, 14(10) Column
Chinese Optics Letters 第14卷 第10期
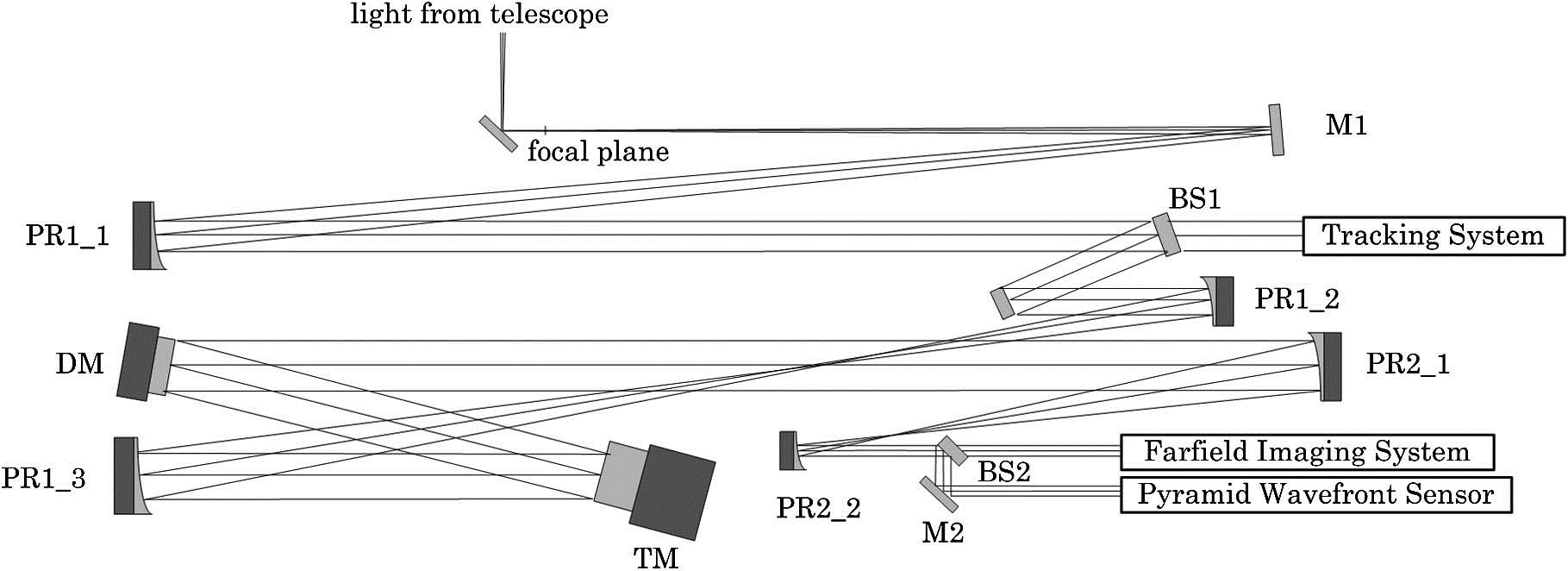
Our adaptive optics system based on a non-modulation pyramid wavefront sensor is integrated into a 1.8 m astronomical telescope installed at the Yunnan Observatory in LiJiang, and the first light with high-resolution imaging of an astronomical star is successfully achieved. In this Letter, the structure and performance of this system are introduced briefly, and then the observation results of star imaging are reported to show that the angular resolution of an adaptive optics system using a non-modulation pyramid wavefront sensor can approach the diffraction limit quality of a 1.8 m telescope.
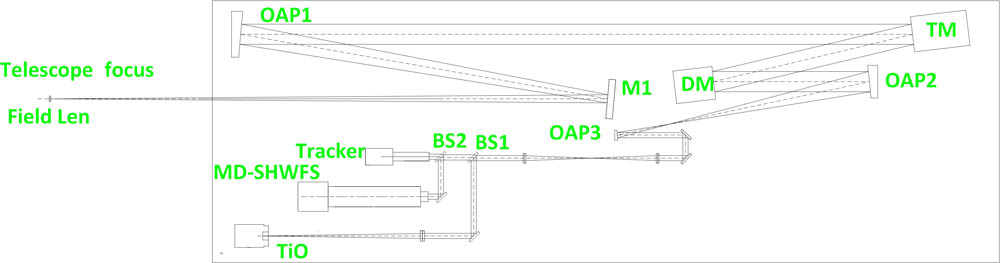
010.1080 Active or adoptive optics 010.7350 Wave-front sensing A prototype of a solar ground-layer adaptive optics (GLAO) system, which consists of a multi-direction correlating Shack–Hartmann wavefront sensor with 30 effective subapertures and about a 1 arcmin field of view (FoV) in each subaperture, a deformable mirror with 151 actuators conjugated to the telescope entrance pupil, and a custom-built real-time controller based on field-programmable gate array and multi-core digital signal processor (DSP), is implemented at the 1 m New Vacuum Solar Telescope at Fuxian Solar Observatory and saw its first light on January 12th, 2016. The on-sky observational results show that the solar image is apparently improved in the whole FoV over 1 arcmin with the GLAO correction.
010.1080 Active or adoptive optics 110.1080 Active or adoptive optics To reduce the cost and achieve high diffraction efficiency, a modified moiré technique for fabricating a large-aperture multi-level Fresnel membrane optic by a novel design of alignment marks is proposed. The modified moiré fringes vary more sensitively with the actual misalignment. Hence, the alignment accuracy is significantly improved. Using the proposed method, a 20 μm thick, four-level Fresnel diffractive polyimide membrane optic with a 200 mm diameter is made, which exhibits over 62% diffraction efficiency into the + 1
220.1140 Alignment 050.1380 Binary optics 310.6845 Thin film devices and applications Carrier phase estimation scheme for faster-than-Nyquist optical coherent communication systems Download:1157次
Download:1157次
 Download:1157次
Download:1157次We propose a modified-Viterbi and Viterbi phase estimation (VVPE) carrier phase recovery scheme that shows an effective capability of reducing the frequent and accumulated cycle slips induced by inter-symbol interference (ISI) in a faster-than-Nyquist (FTN) optical coherent communications system. In a 28-Gbaud FTN polarization-division multiplexed quadrature phase-shift keying optical communication system, the comparison of the proposed modified-VVPE scheme and the conventional VVPE scheme is carried out. It is proved that the proposed modified-VVPE scheme can effectively overcome the challenge of ISI induced error carrier phase estimation, which leads to a better bit error ratio performance.
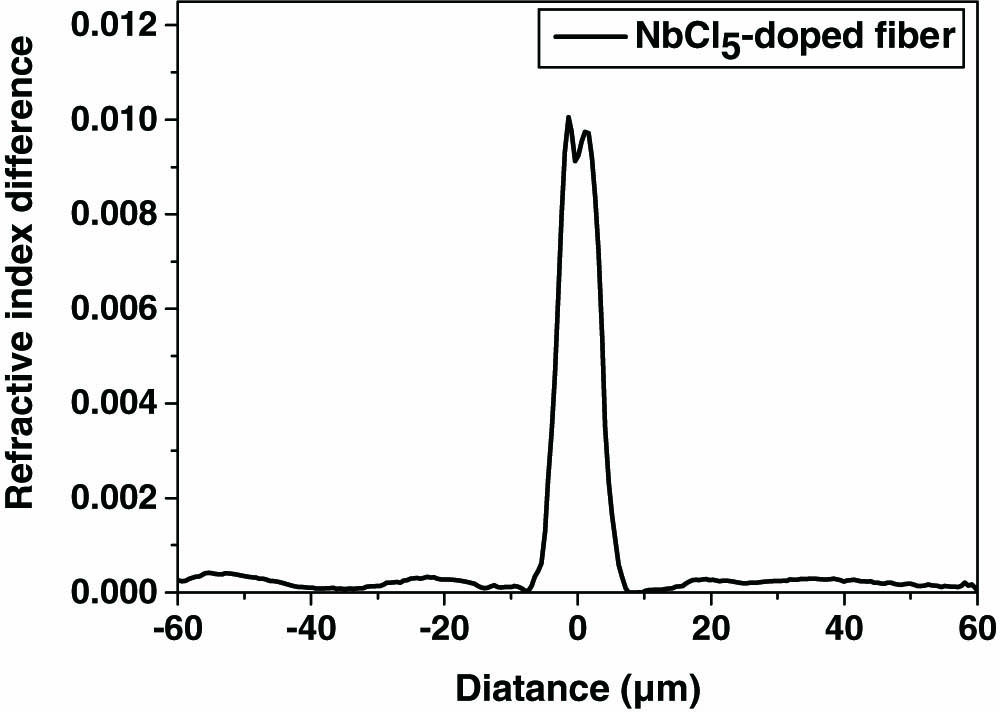
060.1660 Coherent communications 060.2330 Fiber optics communications 060.4510 Optical communications Two kinds of Nb-doped silica fibers, an NbCl 5 Nb 2 O 5 GeO 2 Nb 2 O 5
060.2270 Fiber characterization 290.5860 Scattering, Raman 060.2400 Fiber properties 060.2290 Fiber materials In a D-shaped twin-core fiber (DTCF), the central core is insensitive to the variation of the external environment, while the other core is highly sensitive. As an electro-optic polymer coated on a DTCF, the coupling between the two cores varies with voltages applied to the polymer. Based on this, a superior all-fiber modulator is proposed that bears little coupling loss, prohibits mode mismatch, and provides a more stable working circumstance. A half-wave driving voltage (V π
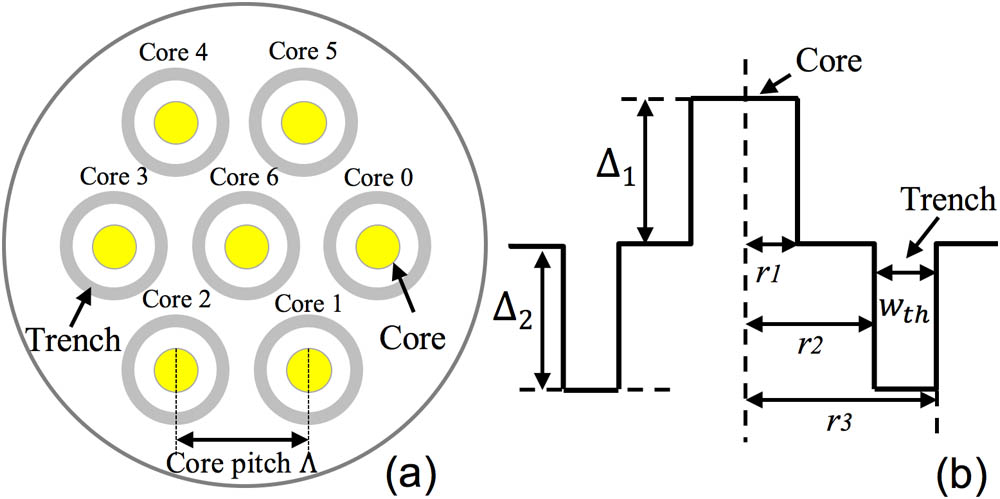
060.2310 Fiber optics 060.4080 Modulation Crosstalk-aware RCSA for spatial division multiplexing enabled elastic optical networks with multi-core fibers Download:1089次
Download:1089次
 Download:1089次
Download:1089次In this Letter, we propose two crosstalk-aware routing, core, and spectrum assignment (CA-RCSA) algorithms for spatial division multiplexing enabled elastic optical networks (SDM-EONs) with multi-core fibers. First, the RCSA problem is modeled, and then a metric, i.e., CA spectrum compactness (CASC), is designed to measure the spectrum status in SDM-EONs. Based on CASC, we propose two CA-RCSA algorithms, the first-fit (FF) CASC algorithm and the random-fit (RF) CASC algorithm. Simulation results show that our proposed algorithms can achieve better performance than the baseline algorithm in terms of blocking probability and spectrum utilization, with FF-CASC providing the best performance.
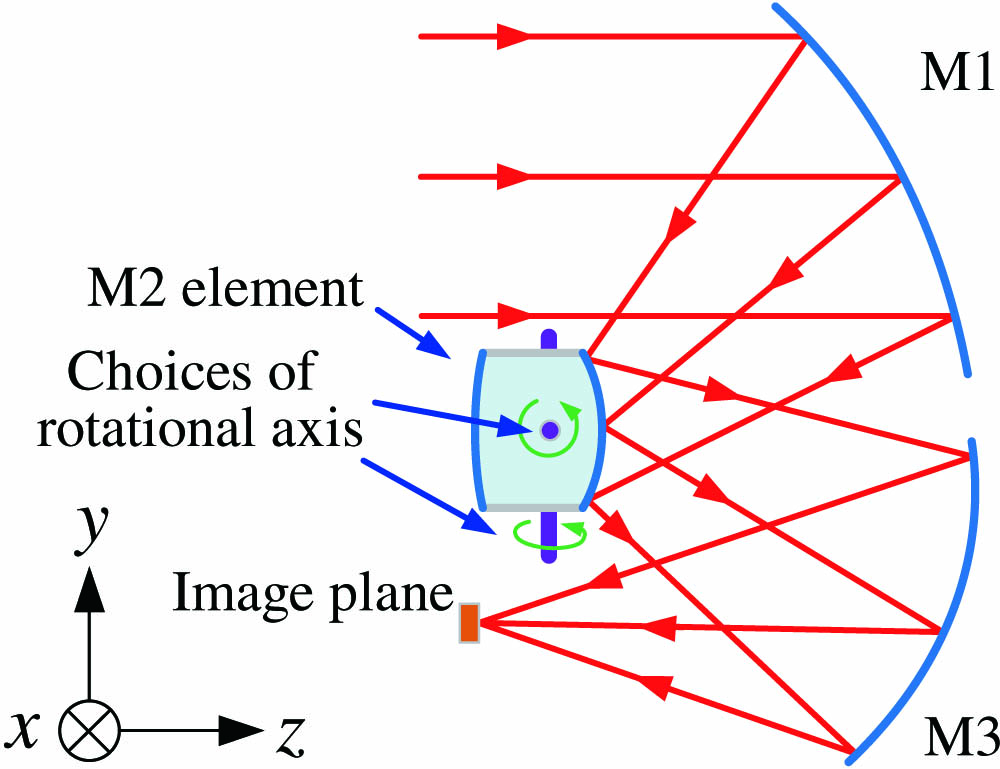
060.1155 All-optical networks 060.4250 Networks 060.4251 Networks, assignment and routing algorithms In this Letter, we propose a novel configuration and design method of freeform, dual fields-of-view (FOVs), dual focal lengths, off-axis three-mirror zoom imaging systems. The switch of the two zooms is achieved by rotating a single mirror element. The design of a freeform, dual focal lengths zoom system is realized by a point-by-point design approach for the first time to our knowledge. This method enables the direct design of freeform surfaces from initial planes using given system specifications and configuration, and the designed system can be taken as a good starting point for further optimization. A freeform, dual FOVs, dual focal lengths, off-axis three-mirror zoom system is demonstrated. The F-numbers of the two zooms are 2 and 2.4. The dual FOVs are 3 ° × 3 ° 2.5 ° × 2.5 °
080.4228 Nonspherical mirror surfaces 080.4035 Mirror system design 220.2740 Geometric optical design Noise addition is a simple but effective method for generating a phase-only hologram (POH) of an object. Briefly, the intensity image of an object is added with random phase noise and converted into a digital Fresnel hologram. Subsequently, the phase component of the hologram is retained as the POH. Although the method is fast and the visual quality of the reconstructed image is acceptable, the edges and lines patterns are heavily fragmented. In this Letter, we propose a method to overcome this problem. An experimental evaluation based on numerical and optical reconstructions reveals that a hologram generated by our proposed method is capable of preserving line patterns with favorable quality.
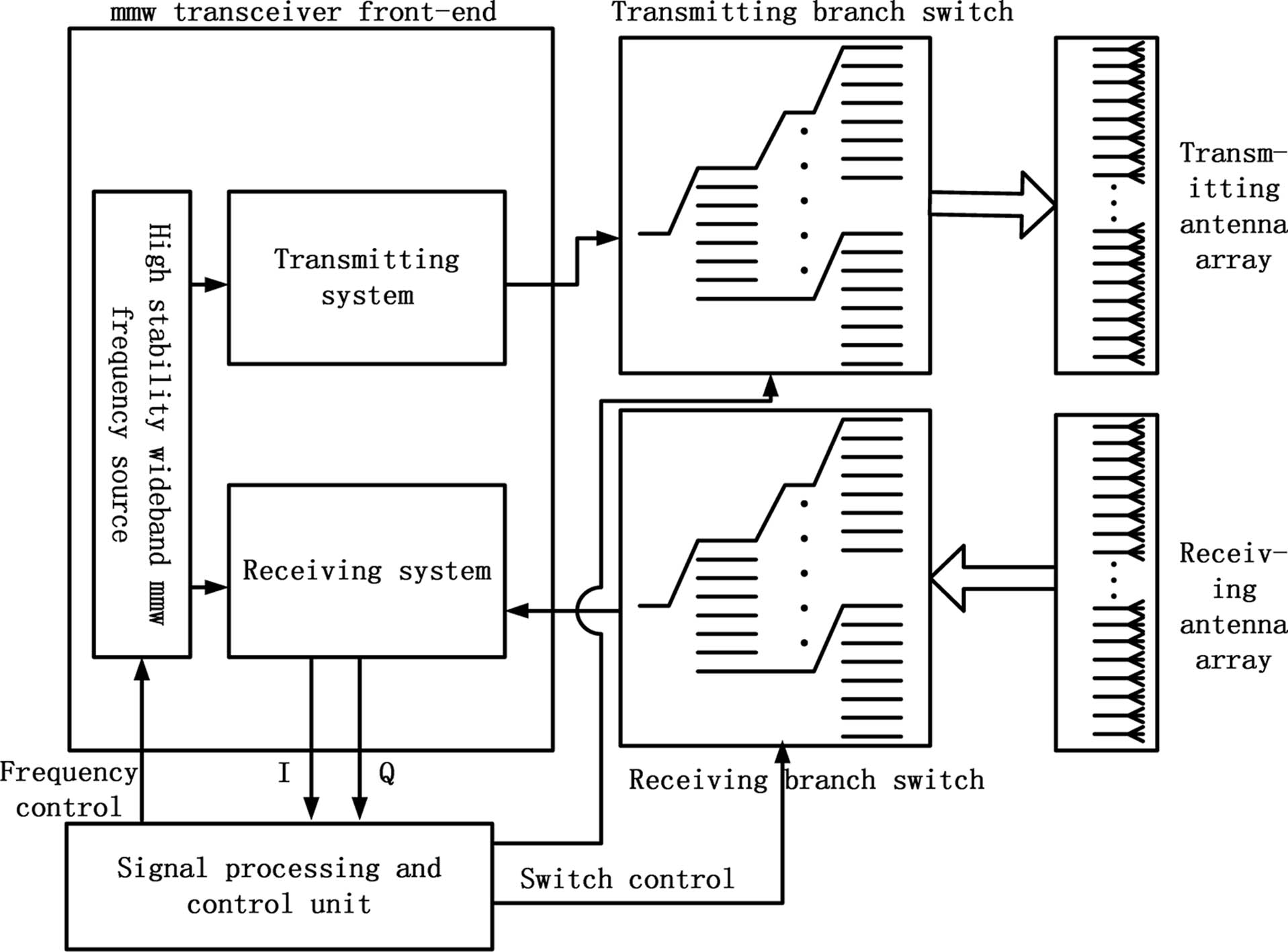
090.0090 Holography 090.1995 Digital holography 090.1760 Computer holography A practical millimeter-wave (MMW) holographic imaging system with good robustness is developed for the detection of concealed weapons at security checkpoints, especially at the airport. The system is used to scan the passenger and detect any weapons hidden in their clothes. To reconstruct the three dimensional image, a holographic MMW imaging algorithm based on aperture synthesis and backscattering is presented. The system is active and works at 28–33 GHz. As a practical imaging system, the robustness is analyzed in detail in terms of the peak signal-to-noise ratio.
110.3010 Image reconstruction techniques 110.6880 Three-dimensional image acquisition Optical readout method based on time-discrete modulation for micro-cantilever array sensing Download:887次
Download:887次
 Download:887次
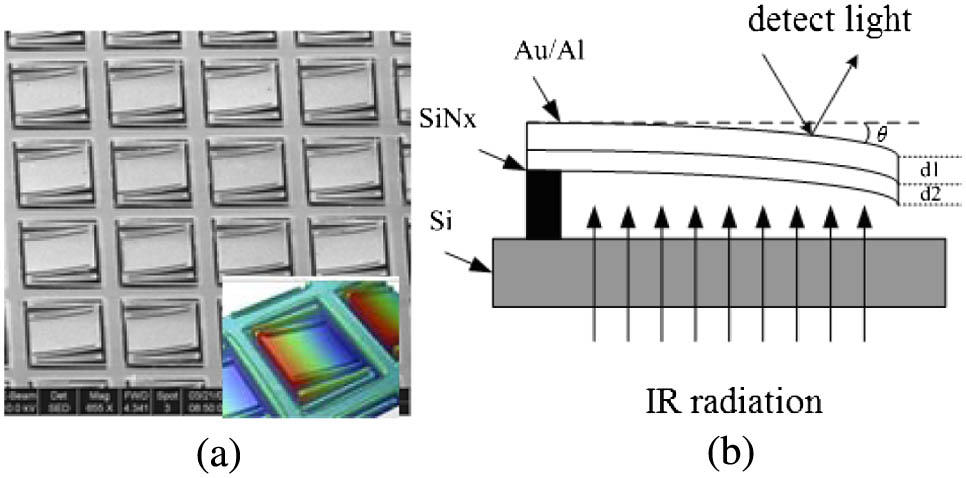
Download:887次Noise and the resonance characteristics of the focal plane array (FPA) are the most important factors that affect the performance of the optical readout infrared (IR) FPA imaging system. This Letter presents a time-discrete modulation technology that eliminates the background and restrain noise, which effectively improves the image quality of the optical readout IR FPA imaging system. The comparative experiments show that this technology can reduce the noise equivalent temperature difference greatly and make the images sharper. Moreover, when the imaging system is influenced by the environment vibration, the images obtained from the imaging system with time-discrete modulation restore twice as fast as without time-discrete modulation.
110.3080 Infrared imaging 110.2970 Image detection systems 040.6808 Thermal (uncooled) IR detectors, arrays and imaging 100.2550 Focal-plane-array image processors Power efficiency of time-stretch imaging system by using parallel interleaving detection Download:798次
Download:798次
 Download:798次
Download:798次A 38.88 MHz time-stretch line-scan imaging system with parallel interleaving detection is experimentally demonstrated. Since only half-chromatic dispersion is used to stretch optical pulses for wavelength-to-time mapping, the power efficiency is significantly improved by 6.5 dB. Furthermore, the theoretical analysis indicates that the power loss can be efficiently reduced for scan rates less than 100 MHz. In addition, a mathematical model for signal-to-noise evaluation is derived, including amplified spontaneous emission noise in the power compensation. Thanks to the improvement of the power efficiency by using parallel interleaving detection, the signal quality is enhanced.
110.2970 Image detection systems 320.7100 Ultrafast measurements 100.0100 Image processing Analysis of an integrated tunable spectrometer for the short to mid-infrared range based on a ring resonator Download:897次
Download:897次
 Download:897次
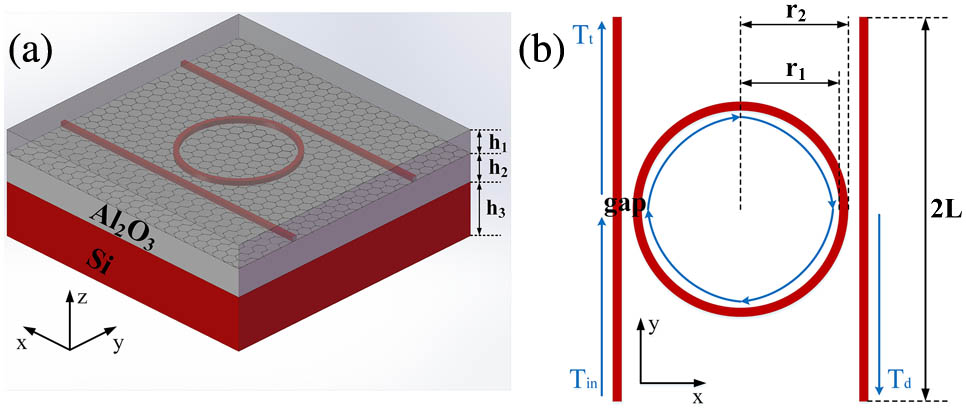
Download:897次An integrated, tunable spectrometer based on a silicon-on-sapphire platform is designed at wavelengths of 2.29–2.35 μm. Its pivotal component is a 4.7 μm-radius ring resonator on a graphene monolayer. Its full width at half-maximum and free spectral range are ~ 1.5 ~ 45 nm
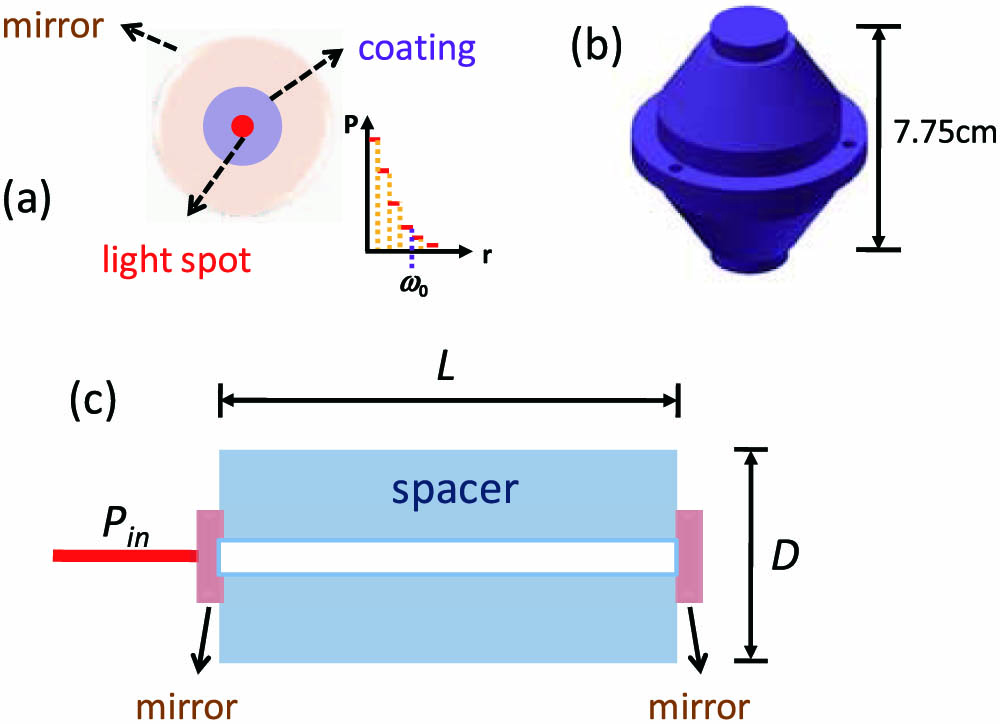
130.7408 Wavelength filtering devices 130.3120 Integrated optics devices 130.3990 Micro-optical devices 140.4780 Optical resonators The length stability of optical cavities is vital in ultra-stable, cavity-stabilized laser systems. Using finite element analysis, we study the length deviation of optical cavities due to thermal expansion and thermo-refractive effects when the incident light power is changed. The simulated fractional length sensitivity of a 7.75-cm-long football cavity to the power fluctuation of incident light is 5 × 10 14 / μW
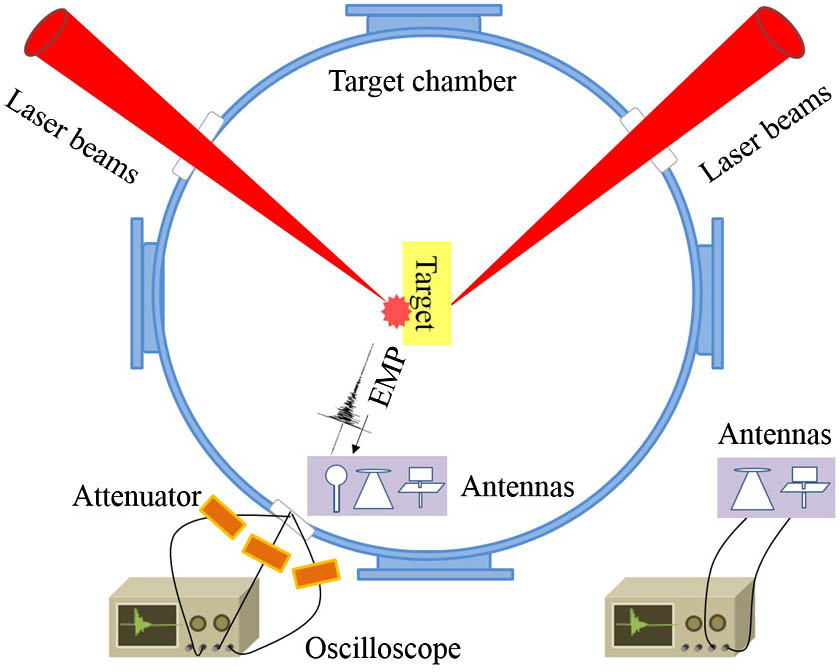
140.3425 Laser stabilization 140.4780 Optical resonators 120.2230 Fabry-Perot Characterization of electromagnetic pulses via arrays on ShenGuang-III laser facility laser Download:990次
Download:990次
 Download:990次
Download:990次Intensive electromagnetic pulses (EMPs) can be generated from interaction of the ultra-intense lasers and solid targets in inertial confinement fusion (ICF), which will detrimentally affect the data acquisition from some electric components. A diagnostic system for EMP measurement inside and outside the ShenGuang-III facility is designed and fabricated in this study. The experimental results indicate that the peak magnitude of EMP reaches up to 3210.7 kV/m and 6.02 T. The received signals depend most on the antenna and target types. The half-hohlraum generates a more intensive EMP radiation than that from the other targets, and the large planar and medium discone capture much stronger signals than the other antennas. In addition, the mechanisms of EMP generation from different targets are discussed. The resulting conclusion are expected to provide the experimental basis for further EMP shielding design.
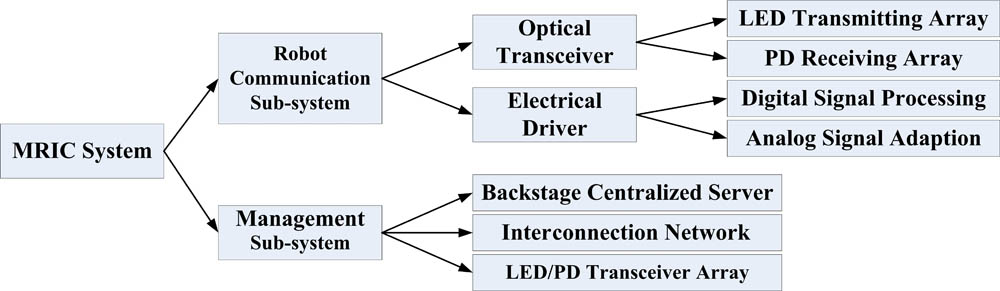
140.3320 Laser cooling 140.3538 Lasers, pulsed 350.5610 Radiation Indoor multi-robot intelligent coordination based on omni-directional visible light communication Download:920次
Download:920次
 Download:920次
Download:920次Multi-robot coordination (MRC) is a key challenge for complex artificial intelligence systems, and conventional wireless-communication-based MRC mechanisms that cannot be deployed in radio-frequency-limited environments. In this Letter, we present a promising solution that utilizes indoor omni-directional visible light communication (VLC) technology to realize efficient multi-robot intelligent coordination (MRIC). The specific design is presented along with the implemental details of a practical MRIC experimental platform. The experimental results show that a 50 Mb / s < 10 6
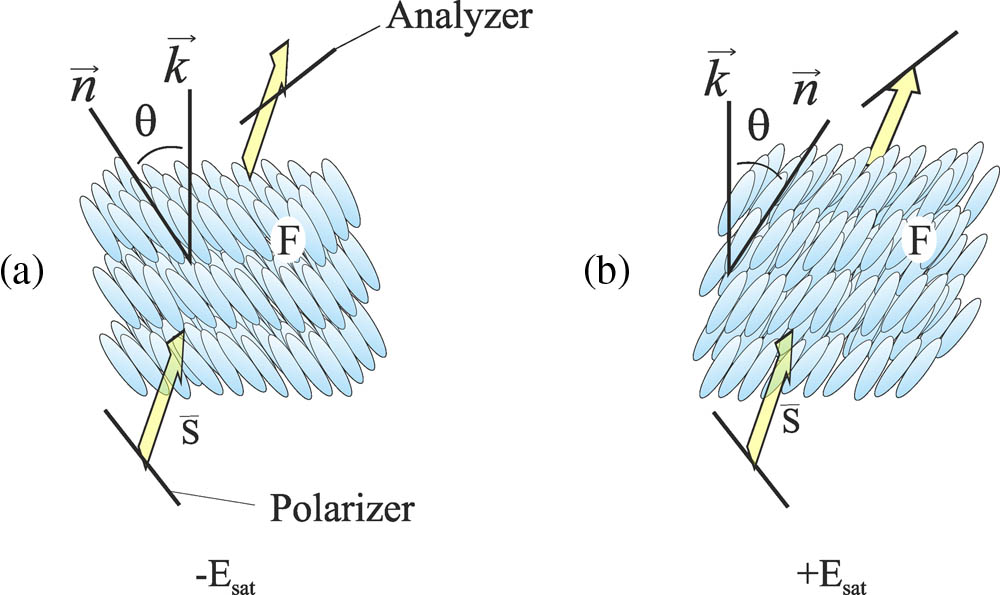
230.3670 Light-emitting diodes 060.2605 Free-space optical communication Charge distribution into illuminated dye-doped surface stabilized ferroelectric liquid crystal cell Download:832次
Download:832次
 Download:832次
Download:832次Surface stabilized (anti) ferroelectric liquid crystal cells can be used as an optically addressed media for optical data processing. The structure of the cell has to contain a photo sensible agent, i.e., an absorbing dye-doped orienting layer. The all-optical generation of the diffractive grating can be done due to the switching parameters of the smectic slab within cells with a sensitive layer. This Letter considers a study of the optically induced charge generation into the dye-doped layer, and the explanation of the phenomena of the selective molecular director reorientation, while cell driving what leads to the induction of phase grating.
230.3720 Liquid-crystal devices 160.3710 Liquid crystals 090.2890 Holographic optical elements 190.4400 Nonlinear optics, materials We theoretically present a concise and tunable dual-band metamaterial absorber composed of a typical metal-dielectric-metal structure in the terahertz regime. The dual-band absorption originates from two different resonance modes induced in one square ring, which is different from the common dual-band absorber composed of a super unit with several different-sized structures. The proposed absorber can realize dynamic tunability through changing the permittivity of the dielectric layer by applying different temperatures. Other good performances, such as a wide incident angle and polarization insensitivity, are also available for the proposed absorber. Such a metamaterial absorber is a promising candidate for terahertz imaging and detection.
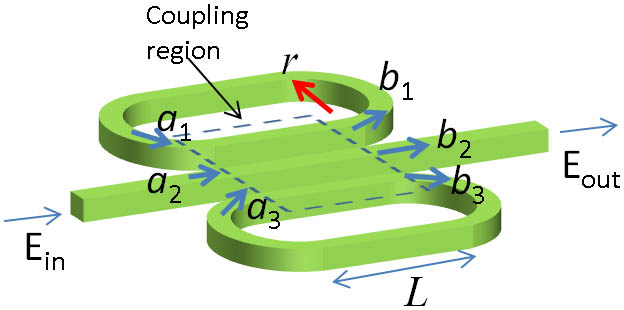
230.0230 Optical devices 160.0160 Materials Parallel-coupled dual-racetrack silicon microresonators can potentially be used for quadrature amplitude modulation. We analyze the evolution of the coverage of coherent output states of devices with varying device parameters. As the coupling constant increases, the coverage of coherent states initially improves then degrades, which is unexpected based on a prior preference for overcoupling. Increasing the quality factor generally improves the coverage. The influence of the refractive index modulation is found to saturate after reaching a certain level. Analytic formulas are developed to provide insight into the coverage evolution. These results are fairly robust against a small asymmetry of device parameters.
230.5750 Resonators 250.7360 Waveguide modulators 250.4745 Optical processing devices 动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-10
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 封面 |构造任意自相似类贝塞尔光束构造新方法动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 |声光调制的干涉增强效应,助力光学量子信息技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 基于时空耦合效应的超宽带频率转换技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 21, Iss. 11): 综述:太赫兹偏振光谱和手性光谱传感检测技术新应用动态信息 丨 2024-03-21
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 全光学的相位目标边缘提取,助力高分辨生物医学成像激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦