2016, 14(6) Column
Chinese Optics Letters 第14卷 第6期
A mobile vehicle lidar system has been developed and applied to detect urban air quality. On September 21 and 22, 2015, particulate matter observation with mobile vehicle lidar was carried out in the Binhai New Area of Tianjin. Combined with the latitude and longitude information acquired by a GPS, the three-dimensional distribution of the aerosol extinction coefficient was presented in the experimental area. Furthermore, the source, distribution, and the transportation path of the aerosols in the area were investigated based on lidar data, local meteorological data, and backward trajectory analysis. The results show that mobile vehicle lidar can detect the atmospheric aerosols and reflect the stereoscopic distribution properties of aerosols. The potential of this vehicle lidar system provides a new scientific basis for the study of the source, distribution, and transportation of atmospheric particles.
010.0010 Atmospheric and oceanic optics 140.0140 Lasers and laser optics 280.0280 Remote sensing and sensors 290.0290 Scattering A method for beam diffraction sidelobe suppression based on the combination of volume Bragg gratings (VBGs) with different thicknesses or periods for angular filtering is proposed and performed. Simulated and experimental results show that the beam diffraction sidelobe is reduced from 12% to less than 1% with the non-sidelobe angular filter. The non-sidelobe angular filtering based on VBGs with thicknesses of 2.5 and 2.9 mm is simulated and demonstrated. The near-field distribution of filtered beams through the non-sidelobe angular filter is obviously smoother than that of the single VBG. The near-field modulation and contrast ratio (C) of filtered beams are found to be improved 1.17 and 1.66 times that of the single VBG. The far-field C of the filtered beam is improved to about 100 ∶ 1
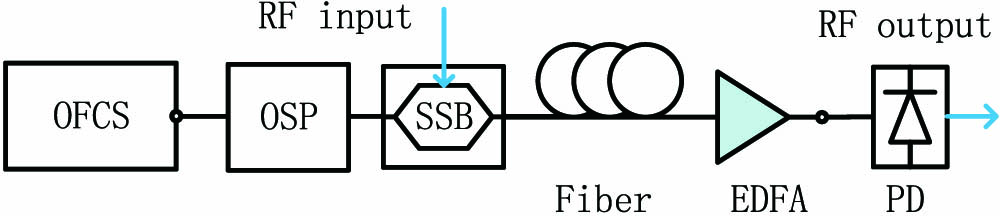
050.0050 Diffraction and gratings 090.0090 Holography Sidelobe suppression analysis of microwave photonic filter based on spectrum-shaped optical frequency combs Download:862次
Download:862次
 Download:862次
Download:862次A finite impulse-response microwave photonic filter is typically achieved based on spectrum-shaped optical frequency combs and a dispersive element. We propose an analytical model to describe the amplitude responses of the sidelobes. The model shows that the sidelobe suppression ratio is limited by the spectrum structure of the optical combs. By taking Gaussian-profiled combs as an example, it is both theoretically and experimentally proved that the suppression ratio can be improved by optimizing the spectral power range, which is defined as the ratio of the maximum tap weight to the minimum tap weight.
060.5625 Radio frequency photonics 070.2615 Frequency filtering 350.4010 Microwaves Reduction of FWM noise in WDM-based QKD systems using interleaved and unequally spaced channels Download:829次
Download:829次
 Download:829次
Download:829次To extensively deploy quantum key distribution (QKD) systems, copropagating with classical channels on the same fiber using wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) technology becomes a critical issue. We propose a user-based channel-interleaving WDM scheme with unequal frequency spacing (UFS-iWDM) to reduce the impairment on the quantum channels induced by four-wave mixing (FWM), and theoretically analyze its impact on quantum bit error rate (QBER). Numerical simulation results show that a UFS-iWDM can significantly reduce the FWM noise and improve QBER compared with the corresponding WDM scheme with equal frequency spacing (EFS), especially in the case of nonzero dispersion shifted fiber.
270.5565 Quantum communications 060.2330 Fiber optics communications 060.4510 Optical communications In this Letter, a novel and compact freeform off-axis three-mirror imaging system and its detailed design method are proposed. The primary mirror and tertiary mirror of the system have the same surface analytical expression and they are integrated on one single freeform surface. In this way, the alignment process is made much easier due to the much fewer degrees of freedom. In addition, the difficulty and cost for the data handling, fabrication, and testing of the freeform surfaces and system can also be significantly reduced in some cases, especially compared with the configuration having multiple surfaces of different expressions integrated on one monolithic substrate. The final system has a 100 mm effective focal length and a 4 ° × 3 °
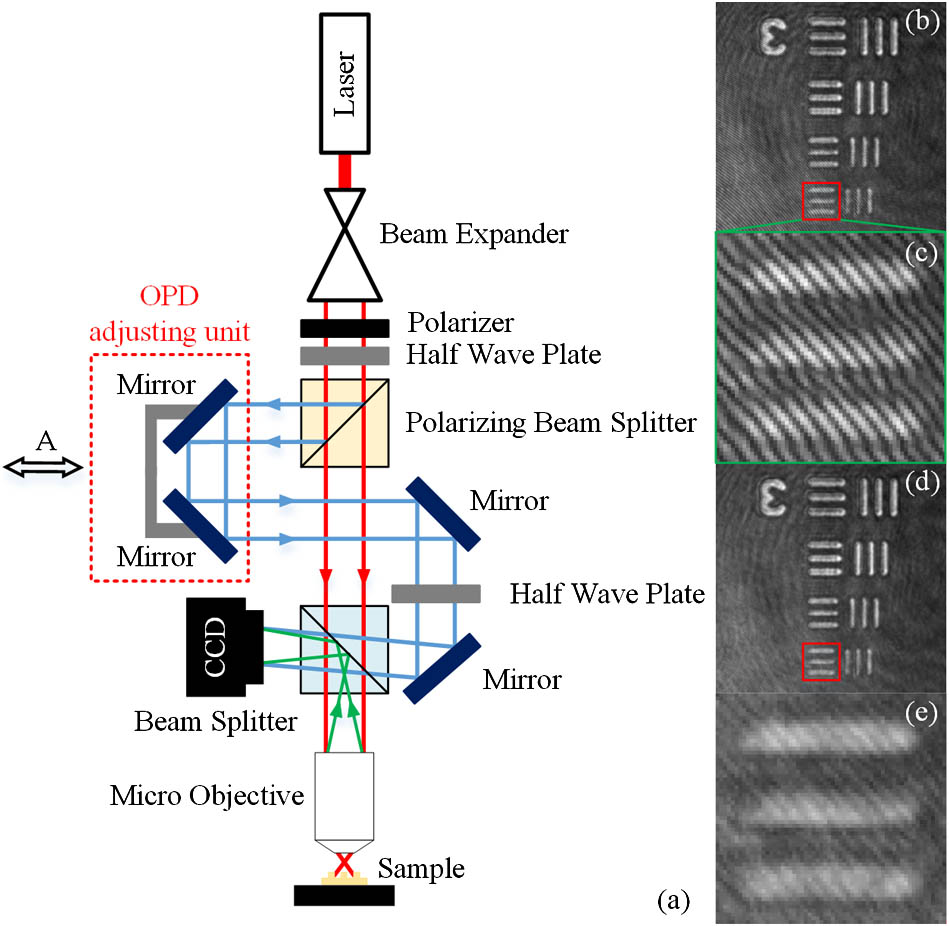
220.2740 Geometric optical design 080.4225 Nonspherical lens design 080.4228 Nonspherical mirror surfaces This Letter presents a novel approach to enhance the fringe contrast (visibility) in a digital off-axis hologram digitally, which can save several adjustment procedures. In the approach, we train a pair of coupled dictionaries from a low fringe contrast hologram and a high one of the same specimen, use the dictionaries to sparse code the input hologram, and finally output a higher fringe contrast hologram. The sparse representation shows good adaptability on holograms. The experimental results demonstrate the benefit of low noise in a three-dimensional profile and prove the effectiveness of the approach.
090.1995 Digital holography 100.2980 Image enhancement An algorithm is proposed for the fast reconstruction of off-axis digital holograms based on a combination of complex encoding (CE) and spatial multiplexing (SM). In this algorithm, every two off-axis holograms recorded in sequence are first assembled into a CE hologram using the CE method, and then four of the CE holograms are again encoded into one complex spatial multiplexing (CSM) hologram based on the SM algorithm. It is demonstrated that the eight holograms encoded into such one CSM hologram can be quickly reconstructed by performing a two-dimensional (2D) Fourier transform (FT) on the CSM hologram. Using this method, the eight 2D FTs required for the reconstruction of the eight holograms in the conventional spatial filtering methods can be simplified to a process with only one 2D FT, which can largely improve the computation efficiency with the resolution of the reconstructed images nearly unchanged.
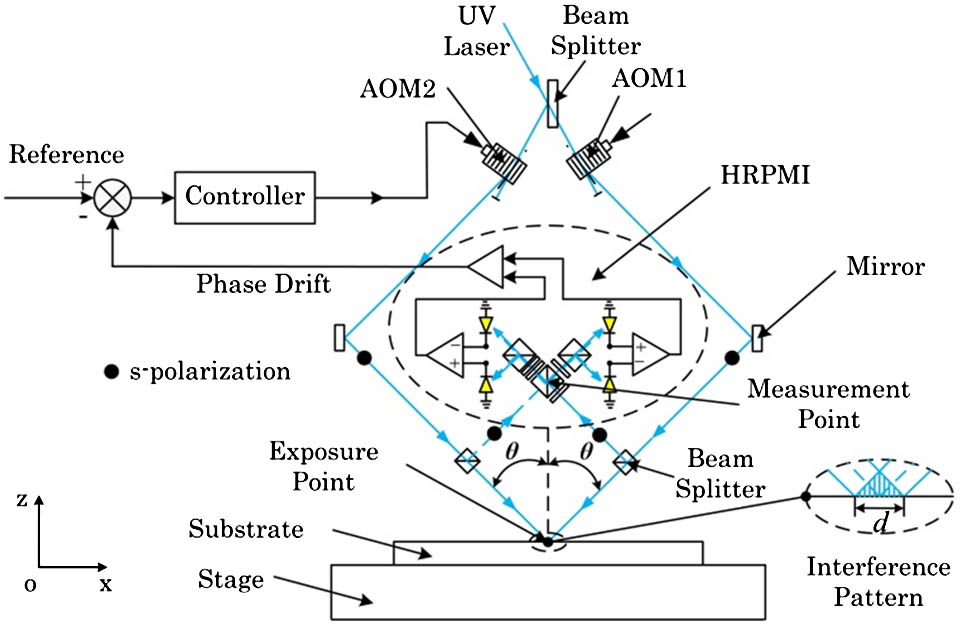
090.1995 Digital holography 090.4220 Multiplex holography 200.3050 Information processing We present a novel homodyne frequency-shifting interference pattern locking system to enhance the exposure contrast of interference lithography and scanning beam interference lithography (SBIL). The novel interference pattern locking system employs a special homodyne redundant phase measurement interferometer (HRPMI) as the sensor and an acousto-opto modulator (AOM) as the actuator. The HRPMI offers the highly accurate value as well as the direction recognition of the interference pattern drift from four quadrature interference signals. The AOM provides a very fine resolution with a high speed for phase modulation. A compact and concise system with a short optical path can be achieved with this new scheme and a small power laser head in tens of microwatts is sufficient for exposure and phase locking, which results in a relatively low-cost system compared with the heterodyne system. More importantly, the accuracy of the system is at a high level as well as having robustness to environmental fluctuation. The experiment results show that the short-time (4 s) accuracy of the system is ± 0.0481 rad ( 3 σ )
000.2170 Equipment and techniques 050.1950 Diffraction gratings 120.3180 Interferometry 220.3740 Lithography A multichannel polarization-entangled photon-pair source in an MgO-doped periodically poled lithium niobate (MgO:PPLN) waveguide is proposed. Based on type I quasi-phase-matched spontaneous parametric down conversion in a single MgO: PPLN waveguide placed inside a Sagnac interferometer and pumped by monochromatic light, a source capable of supporting tens to hundreds of channels of polarization-entangled photon pairs in fiber communication bands simultaneously can be achieved. An inherent channel switch of this source is investigated, which will be significant for future entanglement distribution networks.
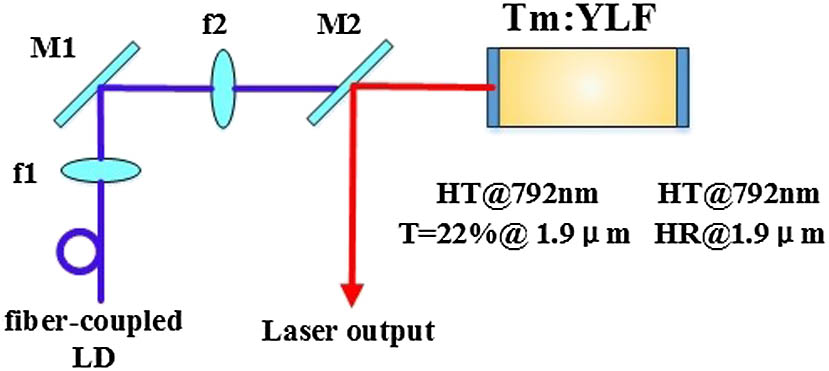
130.3730 Lithium niobate 130.7405 Wavelength conversion devices 190.0190 Nonlinear optics We report a monolithic Tm:YLF micro laser in this Letter. In order to improve the relaxation oscillation of the laser, both ends of the crystal are coated, making the Tm:YLF crystal itself a resonant cavity. The micro laser is pumped by a 792 nm laser diode operated in the continuous wave (CW) mode. We obtain maximum output powers of 7.78 and 10.4 W at the total incident power of 43.6 W with focus lenses of 37.5 and 40 mm, respectively, corresponding to the slope efficiencies of 25.6% and 40.0% and the optical–optical conversion efficiencies of 17.8% and 23.8%. It is clear that the amplitude of the relaxation oscillation is smaller and the beam quality is better with the focus length of 37.5 mm; however, the laser with the focus length of 40 mm produces a higher output power and a more stable wavelength centering at 1878.44 nm.
140.3480 Lasers, diode-pumped 140.3425 Laser stabilization 140.3430 Laser theory Measurements of the excitation power-dependence and temperature-dependence photoluminescence (PL) are performed to investigate the emission mechanisms of InGaN/GaN quantum wells (QWs) in laser diode structures. The PL spectral peak is blueshifted with increasing temperature over a certain temperature range. It is found that the blueshift range was larger when the PL excitation power is smaller. This particular behavior indicates that carriers are thermally activated from localized states and partially screen the piezoelectric field present in the QWs. The small blueshift range corresponds to a weak quantum-confined Stark effect (QCSE) and a relatively high internal quantum efficiency (IQE) of the QWs.
140.0140 Lasers and laser optics 300.6260 Spectroscopy, diode lasers We demonstrate a diode-pump Tm 3 +
140.3510 Lasers, fiber 060.2320 Fiber optics amplifiers and oscillators 060.2390 Fiber optics, infrared A Ce 3 + α - NaYF 4 NaF : KF : YF 3 : CeF 3 30 ∶ 18 ∶ 48 ∶ 4 Ce 3 + α - NaYF 4 Ce 3 + : α - NaYF 4 Ce 3 + : α - NaYF 4 5 d → F 5 / 2 2 5<
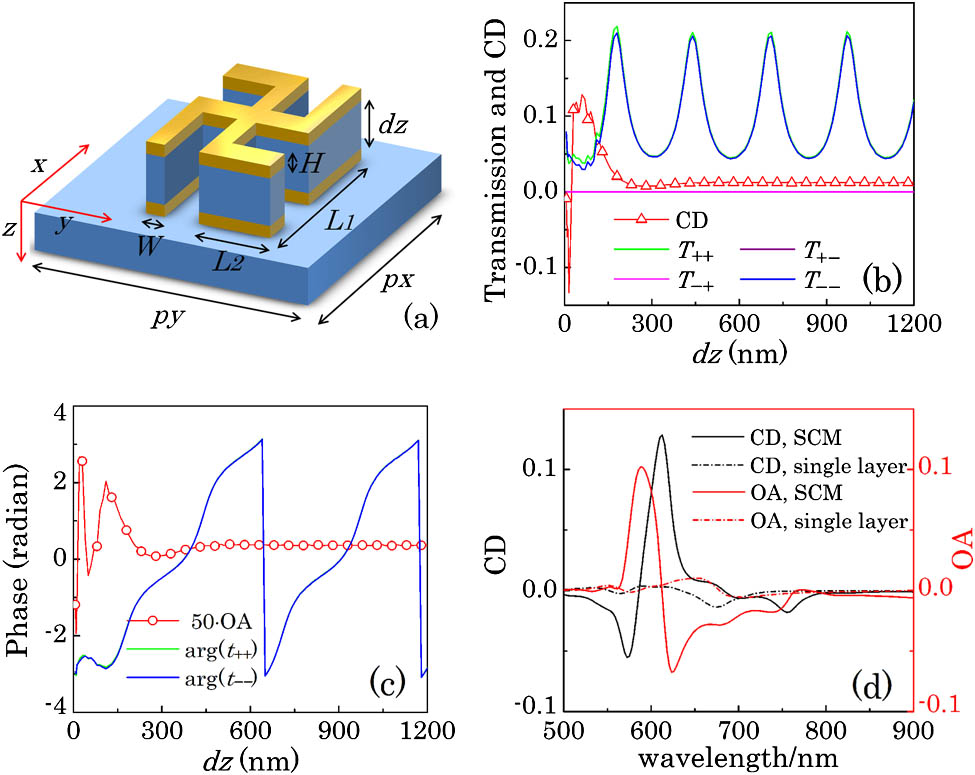
160.0160 Materials 230.0230 Optical devices 260.1180 Crystal optics 300.0300 Spectroscopy Tailoring enhanced chiroptical effect with Fabry–Perot cavity-coupled sandwich chiral metamaterials Download:760次
Download:760次
 Download:760次
Download:760次Cavity-coupled plasmonic structure is demonstrated to be a simple and effective tool to manipulatelight, enhance the biosensing figure of merit, and control the polarization state. In this Letter, we demonstrate the tunability of the chiroptical effect of cavity-coupled chiral structure, i.e., sandwich chiral metamaterials (SCMs), in whichradiation coupling dominates the interaction between particles. Two types of SCMs whose building blocks are 3D chiral and 2D chiral, respectively, are numerically studied. Distinct responses are observed in these two materials. The chiroptical effect can be effectively manipulated and enhanced in the 2D case, while the SCMs consisting of 3D chiral layers keep the chiroptical effecta constant. A theoretical analysis based on matrix optics is developed to explain the corresponding phenomena, which gives a reasonable agreement with numerical simulations.
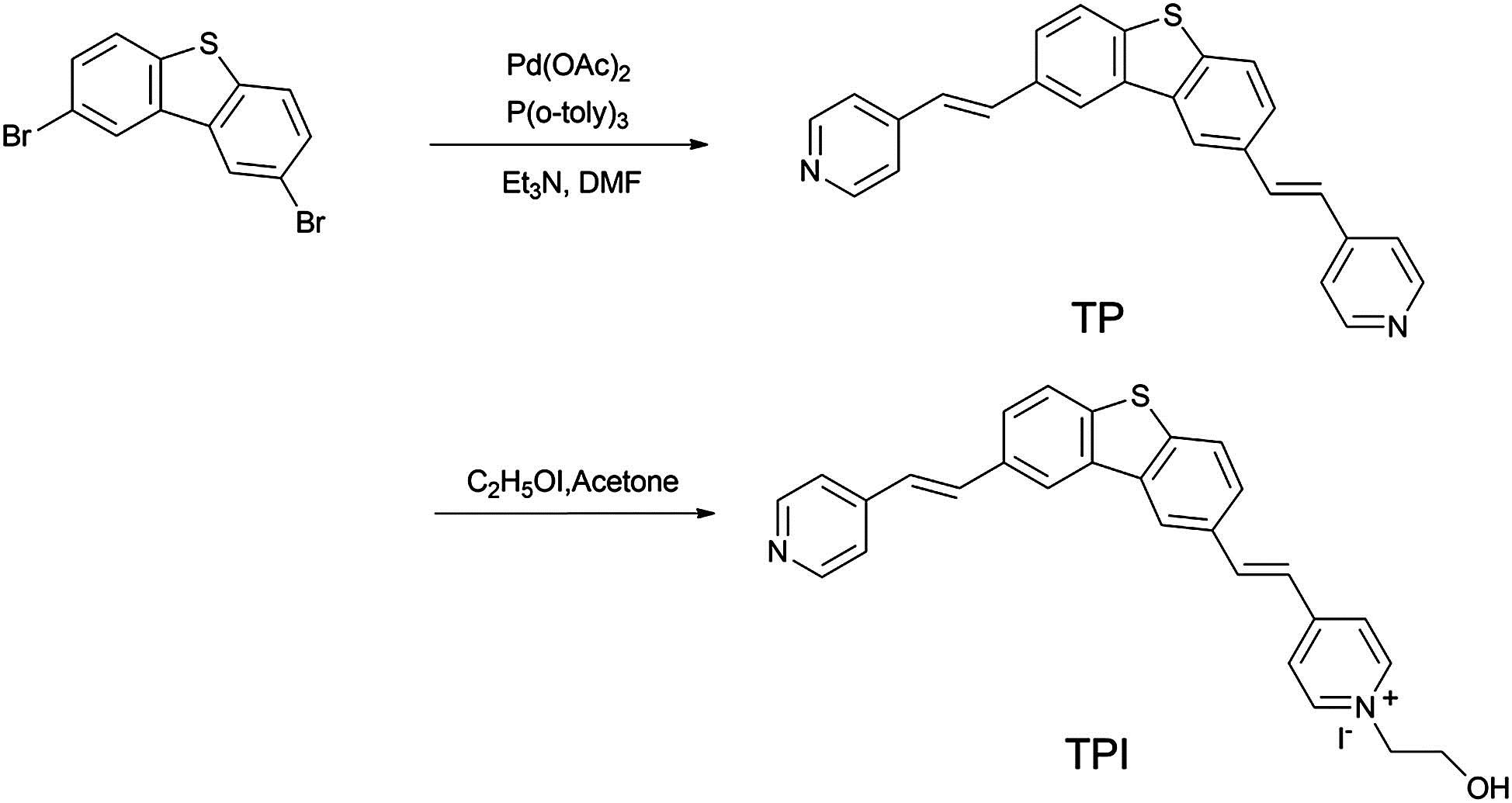
160.1585 Chiral media 160.4760 Optical properties 160.3918 Metamaterials Preparation of two-photon fluorescent probe and biological imaging application in cells Download:777次
Download:777次
 Download:777次
Download:777次We report on a novel dibenzothiophene-based two-photon fluorescent probe for selective nuclear bioimaging, which contains bilaterally symmetrical pyridine rings connected by a central conjugated-bridge dibenzothiophene. This probe possesses a large two-photon absorption cross-section of 471 GM, yields a 25-fold enhancement of the fluorescence titration, and a stronger photostability for nuclei labeling than existing probes. The real-time observation period is a minimum of 1800 s under a femtosecond laser excitation, which is significantly longer than that of 4 ′
160.0160 Materials 160.4670 Optical materials 160.2540 Fluorescent and luminescent materials 190.4400 Nonlinear optics, materials 180.2520 Fluorescence microscopy 170.3880 Medical and biological imaging Tris-(8-hydroxyquinoline)-aluminum ( Alq 3 )
250.3680 Light-emitting polymers 310.6870 Thin films, other properties Effectiveness of inserting an InGaN interlayer to improve the performances of InGaN-based blue-violet laser diodes Download:617次
Download:617次
 Download:617次
Download:617次Electron leakage still needs to be solved for InGaN-based blue-violet laser diodes (LDs), despite the presence of the electron blocking layer (EBL). To reduce further electron leakage, a new structure of InGaN-based LDs with an InGaN interlayer between the EBL and p
250.0250 Optoelectronics 250.5960 Semiconductor lasers We propose schemes for the efficient information transfer between a propagating photon and a quantum-dot (QD) spin qubit in an optical microcavity that have no auxiliary particles required. With these methods, the information transfer between two photons or two QD spins can also be achieved. All of our proposals can work with high fidelity, even with a high leakage rate. What is more, each information transfer process above can also be seen as a controlled-NOT (CNOT) operation. It is found that the information transfer can be equivalent to a CNOT gate. These proposals will promote more efficient quantum information networks and quantum computation.
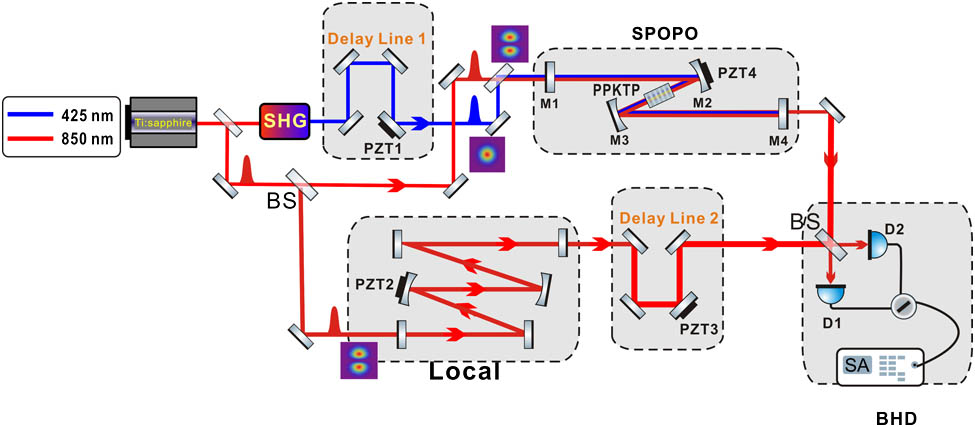
270.0270 Quantum optics 270.5565 Quantum communications 270.5585 Quantum information and processing Nonclassical optical frequency combs find tremendous utility in quantum information and high-precision quantum measurement. The characteristics of a type-I synchronously pumped optical parametric oscillator with the TEM 01 TEM 01
270.6570 Squeezed states 190.4410 Nonlinear optics, parametric processes 190.7110 Ultrafast nonlinear optics Combination of differential discrimination and direct discrimination in pulsed laser time-of-flight systems Download:859次
Download:859次
 Download:859次
Download:859次The output amplitude of the differential circuit is studied for differential discrimination in pulsed laser time-of-flight systems. Based on the studies of the probability of detection and the probability of false alarms, the minimum detectable input signal of differential discrimination can be calculated. The results indicate that the differential discrimination detectability of the small signal will be reduced. A combined discrimination is proposed in this Letter to improve the time resolution of the large signal and ensure the probability of detection of the small signal at the same time. A proper value of the circuit parameter is found to balance the time resolutions of the small and large signals.
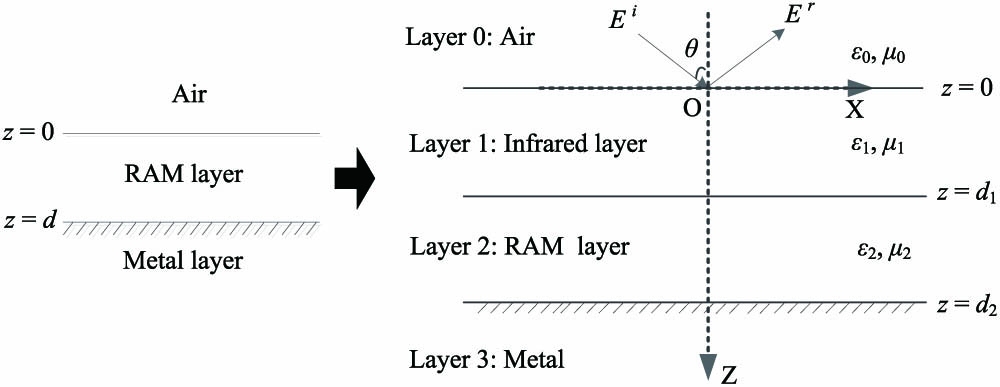
280.3400 Laser range finder 150.5670 Range finding 280.3640 Lidar 150.6910 Three-dimensional sensing Millimeter-wave emission characteristics of bilayer radar-infrared compound stealth material Download:1081次
Download:1081次
 Download:1081次
Download:1081次To achieve radar and infrared stealth, an infrared stealth layer is usually added to the radar absorbing material (RAM) of stealth aircraft. By analyzing the millimeter-wave (MMW) emissivities of three stealth materials, this Letter investigates the impact of the added infrared stealth layer on the originally “hot” MMW emission of RAM. The theoretical and measured results indicate that, compared with the monolayer RAM, the MMW emission of the bilayer material is still strong and its emissivity is reduced by 0.1–0.2 at almost every incident angle. The results partially demonstrate the feasibility of detecting stealth aircraft coated with this bilayer stealth material.
280.4991 Passive remote sensing 350.4010 Microwaves 120.1880 Detection 290.6815 Thermal emission 动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-10
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 封面 |构造任意自相似类贝塞尔光束构造新方法动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 |声光调制的干涉增强效应,助力光学量子信息技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 基于时空耦合效应的超宽带频率转换技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 21, Iss. 11): 综述:太赫兹偏振光谱和手性光谱传感检测技术新应用动态信息 丨 2024-03-21
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 全光学的相位目标边缘提取,助力高分辨生物医学成像激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦