2017, 15(2) Column
Chinese Optics Letters 第15卷 第2期
Retrieval of C n 2 profile from differential column image motion lidar using the regularization method
We develop a regularization-based algorithm for reconstructing the C n 2 r 0 HV 5 / 7 C n 2
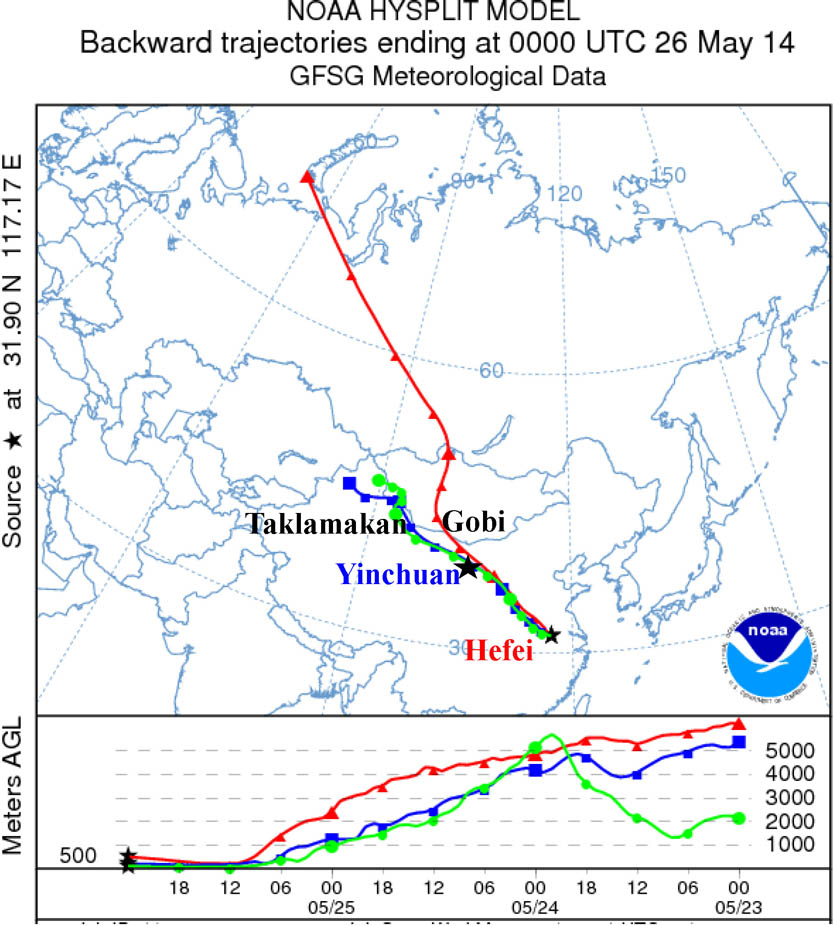
010.1330 Atmospheric turbulence 100.3190 Inverse problems 010.3640 Lidar 010.1290 Atmospheric optics As an extension of the Mie lidar technique to measure the extinction coefficient of the surface particles, a horizontally pointing Mie lidar is used for determining the optical properties of Asian dust, which is an approach without knowing the actual lidar ratio. A long lasting dust event is observed based on this approach in May 2014. The “no dust,” “pure dust,” and “polluted dust” stage is observed during this event, and their optical and hygroscopic properties are discussed. Some new optical and hygroscopic features are observed, which benefit from the quantitative, multi-wavelength, and continuous measurement of the extinction related optical properties of dust particles.
010.0010 Atmospheric and oceanic optics 140.0140 Lasers and laser optics 280.0280 Remote sensing and sensors 290.2200 Extinction We design a new kind of phase zone plates (PZPs) to improve the diffraction efficiency of soft x ray zone plates (ZPs). The design replaces blank parts of PZPs with metals of negative phase shift at the working energy, which is called as the positive and negative PZPs (PNPZPs). According to the calculation, PNPZPs have a higher maximum efficiency than conventional ZPs with the same zone width. With the help of a negative phase coefficient, it is much easier to achieve a π
050.1965 Diffractive lenses 050.1970 Diffractive optics Passively Q 0.002 MW / cm 2
060.0060 Fiber optics and optical communications 060.2310 Fiber optics 060.3510 Lasers, fiber 060.4370 Nonlinear optics, fibers Air turbulence effects on performance of optical wireless communication with crosstalk in server backplane Download:732次
Download:732次
 Download:732次
Download:732次Free space optical interconnections (FSOIs) are anticipated to become a prevalent technology for short-range high-speed communication. FSOIs use lasers in board-to-board and rack-to-rack communication to achieve improved performance in next generation servers and are expected to help meet the growing demand for massive amounts of inter-card data communication. An array of transmitters and receivers arranged to create an optical bus for inter-card and card-to-backplane communication could be the solution. However, both chip heating and cooling fans produce temperature gradients and hot air flow that results in air turbulence inside the server, which induces signal fading and, hence, influences the communication performance. In addition, the proximity between neighboring transmitters and receivers in the array leads to crosstalk in the received signal, which further contributes to signal degradation. In this Letter, the primary objective is to experimentally examine the off-axis crosstalk between links in the presence of turbulence inside a server chassis. The effects of geometrical and inter-chassis turbulence characteristics are investigated and first-and second-order statistics are derived.
060.2605 Free-space optical communication 200.2605 Free-space optical communication 010.7060 Turbulence Temperature-insensitive refractive index sensor based on Mach–Zehnder interferometer with two microcavities Download:1116次
Download:1116次
 Download:1116次
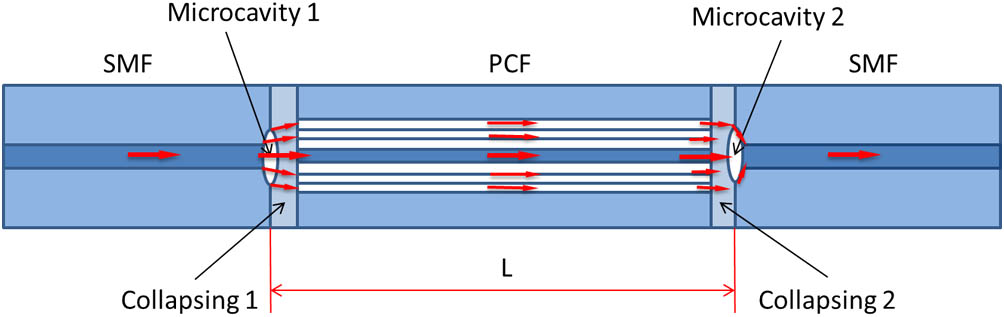
Download:1116次We propose a temperature-insensitive refractive index (RI) fiber sensor based on a Mach–Zehnder interferometer. The sensor with high sensitivity and a robust structure is fabricated by splicing a short photonic crystal fiber (PCF) between two single-mode fibers, where two microcavities are formed at both junctions because of the collapse of the PCF air holes. The microcavity with a larger equatorial dimension can excite higher-order cladding modes, so the sensor presents a high RI sensitivity, which can reach 244.16 nm/RIU in the RI range of 1.333–1.3778. Meanwhile it has a low temperature sensitivity of 0.005 nm/°C in the range of 33°C–360°C.
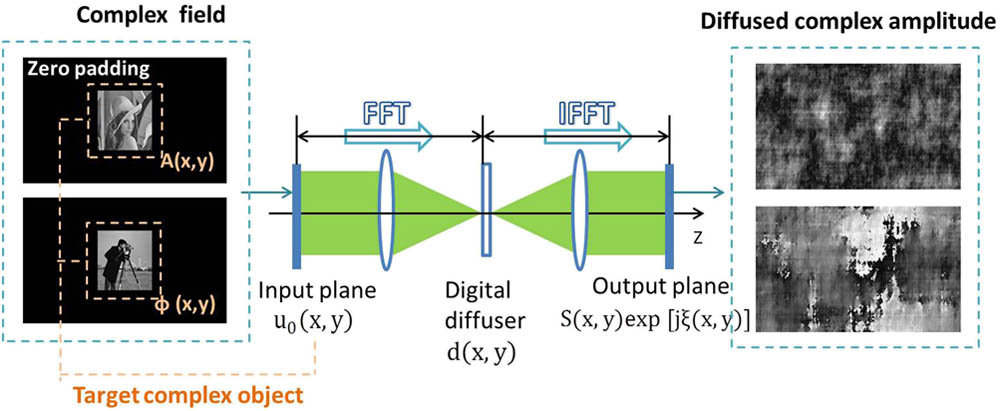
060.2280 Fiber design and fabrication 060.2370 Fiber optics sensors A method is proposed to realize accurate spatial complex modulation based on the spatial cross-modulation method (SCMM) via a phase-only spatial light modulator. The conventional SCMM cannot achieve high quality reconstruction, especially when the diffusion ratio is small. We propose an iterative algorithm in the calculation of a computer-generated hologram to implement accurate complex modulation. It enables us to generate a high quality reconstruction under a small diffusion ratio. The feasibility of the method is verified by both a numerical simulation and an optical experiment.
090.2870 Holographic display 090.1760 Computer holography 110.7348 Wavefront encoding We present in this work a new mathematical model to analyze and evaluate optical phenomena occurring in the nonuniform optical waveguide used in integrated optics as an optical coupler. By introducing some modifications to the intrinsic integral, we perfectly assess the radiation field present in the adjacent medium of the waveguide and, thus, follow the evolution of the optical coupling from the taper thin film to the substrate and cladding until there is a total energy transfer. The new model that is introduced can be used to evaluate electromagnetic field distribution in three mediums that constitute any nonuniform optical couplers presenting great or low wedge angles.
130.3120 Integrated optics devices 080.1510 Propagation methods 130.3130 Integrated optics materials 230.7370 Waveguides Propagation of a filamentary femtosecond laser beam with high intensities at an air-solid interface Download:797次
Download:797次
 Download:797次
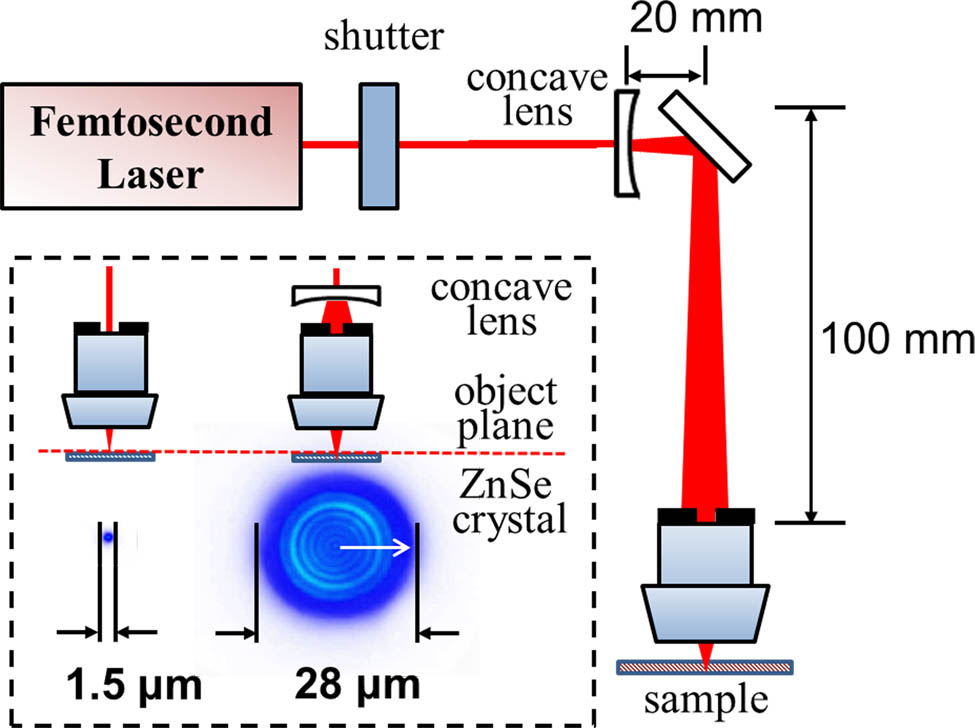
Download:797次The propagation of a filamentary laser beam at an air-glass surface is studied by setting the incident angle satisfying the total reflection condition. The images of the trajectory of the filamentary laser beam inside the sample and the output far-field spatial profiles are measured with varying incident laser pulse energies. Different from the general total reflection, a transmitted laser beam is detected along the propagation direction of the incident laser beam. The energy ratio of the transmitted laser beam depends on the pulse energies of the incident laser beam. The background energy reservoir surrounding the filament core can break the law of total reflection at the air-glass surface, resulting in the regeneration of the transmitted laser beam.
140.3440 Laser-induced breakdown 100.6640 Superresolution 210.4770 Optical recording 180.1790 Confocal microscopy A scheme for measuring the intra-cavity round-trip loss of an all-solid-state single-frequency laser by inserting a type-I noncritical phase-matching nonlinear crystal introducing nonlinear loss into the resonator is presented. The intra-cavity round-trip loss is theoretically deduced by analyzing the dependence of the fundamental-wave (FW) and second-harmonic-wave (SHW) powers on the pump factor and the nonlinear conversion factor of the single-frequency laser and experimentally measuring them by recording different FW and SHW powers, which are decided by the temperature of the nonlinear crystal. The measured intra-cavity round-trip loss and pump factor are 4.84% and 6.91 % W 1
140.3410 Laser resonators 140.3515 Lasers, frequency doubled 140.3570 Lasers, single-mode 140.3580 Lasers, solid-state 160.4330 Nonlinear optical materials A burst of six pulses with an average power of 38.7 W are obtained for a pulse-burst picosecond 1064 nm laser system at 1 kHz. The six pulses have equal amplitudes and pulse spacings of 800 ps, the beam quality of the M 2 Nd : YVO 4
140.0140 Lasers and laser optics 140.3280 Laser amplifiers 140.7090 Ultrafast lasers Experimental research of laser-induced periodic surface structures in a typical liquid by a femtosecond laser Download:824次
Download:824次
 Download:824次
Download:824次A constant elastic alloy is a widely used material with a high elastic modulus and an excellent wave velocity consistency. Different morphologies on the constant elastic alloy surface are observed through femtosecond laser irradiation. When the laser average fluence is set to 0.58 J / cm 2
320.2250 Femtosecond phenomena 220.4241 Nanostructure fabrication 100.0118 Imaging ultrafast phenomena Origin and suppression of back conversion in a phase-matched nonlinear frequency down-conversion process Download:834次
Download:834次
 Download:834次
Download:834次Back conversion is an intrinsic phenomenon in nonlinear frequency down-conversion processes. However, the physical reason for its occurrence is not well understood. Here, we theoretically reveal that back conversion is the result of a π
190.4223 Nonlinear wave mixing 190.4975 Parametric processes 190.7110 Ultrafast nonlinear optics Periodic surface structures on Ni–Fe film induced by a single femtosecond laser pulse with diffraction rings Download:781次
Download:781次
 Download:781次
Download:781次This Letter reports the formation of periodic surface structures on Ni–Fe film irradiated by a single femtosecond laser pulse. A concave lens with a focus length of 150 mm 100 × NA = 0.9
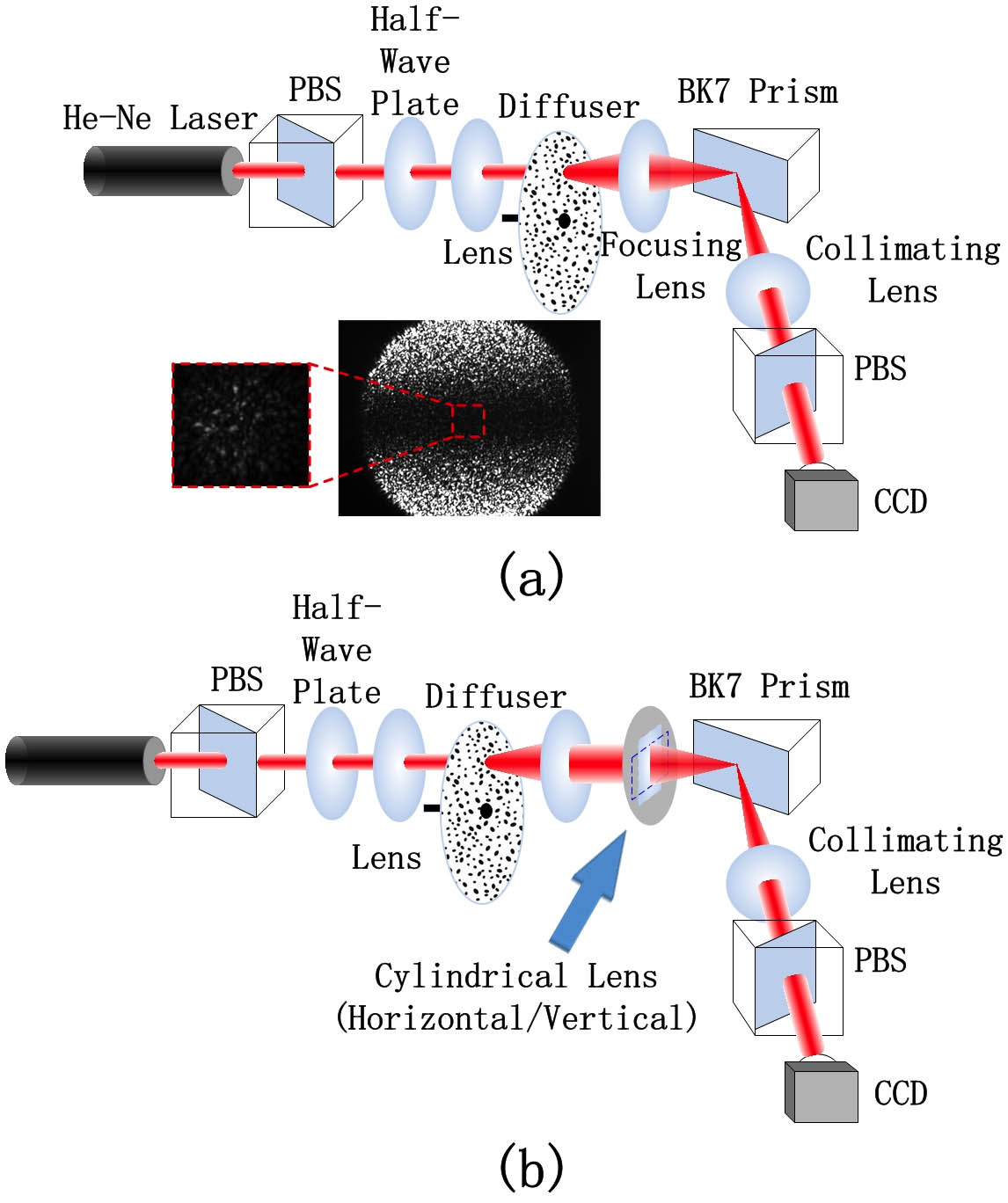
220.4241 Nanostructure fabrication 160.3900 Metals 240.6700 Surfaces 320.7090 Ultrafast lasers The spin Hall effect of light (SHEL) can be observed by the dark strip resulting from weak measurement. We find that the SHEL of a partially coherent beam (PCB) has a similar phenomenon as well. However, the dark strip in the SHEL of a PCB cannot be explained by considering the beam as an assemblance of coherent speckles. Also, the dark strip in a PCB is not purely dark. By analyzing the autocorrelation, we show that the SHEL of a PCB is the result of overlapping coherent speckles’ SHEL. We further prove our conclusion by adjusting convergence and incident angles. Finally, we develop a qualitative theory to clarify the SHEL of a PCB.
240.3695 Linear and nonlinear light scattering from surfaces 030.1640 Coherence 070.0070 Fourier optics and signal processing Vertical integration of self-rolled-up microtube and silicon waveguides: a two-channel optical add–drop multiplexer Download:868次
Download:868次
 Download:868次
Download:868次A novel design of a two-channel optical add–drop multiplexer based on a self-rolled-up microtube (SRM) is presented. This design consists of an SRM that has a parabolic lobe-like pattern along the tube’s axial direction, as well as straight silicon waveguides and a 180° waveguide bend. The vertical configuration of the SRM and waveguides is analyzed by the coupled mode theory for achieving the optimum gap. In the critical coupling regime, when the device serves as an optical demultiplexer, the minimum insertion loss is 1.94 dB, and the maximum channel crosstalk is 6.036 dB 11.9 dB
250.5300 Photonic integrated circuits 230.0230 Optical devices 230.3990 Micro-optical devices 230.5750 Resonators We extensively discuss 25 Gb/s per wavelength capacity in both IEEE and ITU-T standardization to support the increasing bandwidth requirement. In this Letter, we propose to use the optical dispersion compensation technique in an optical line terminal (OLT) combined with a bandwidth-limited electro-absorption modulated laser in an optical network unit to achieve 25 Gb/s capacity for the upstream link. We evaluate the positive and negative dispersion tolerances of 25 Gb/s electrical duo-binary (EDB) and pulse-amplitude modulation (PAM-4) signals. We achieve 39.5 and 31 dB upstream loss budgets for the 25 Gb/s EDB and PAM-4 signals by using 600 500 ps / nm
250.4110 Modulators 230.0040 Detectors In this Letter, we propose an efficient compression algorithm for multi-spectral images having a few bands. First, we propose a low-complexity removing spectral redundancy approach to improve compression performance. Then, a bit plane encoding approach is applied to each band to complete the compression. Finally, the experiments are performed on multi-spectral images. The experiment results show that the proposed compression algorithm has good compressive property. Compared with traditional approaches, the proposed method can decrease the average peak signal noise ratio by 0.36 dB at 0.5 bpp. The processing speed reaches 23.81 MPixels/s at the working frequency of 88 MHz, which is higher than the traditional methods. The proposed method satisfies the project application.
280.4788 Optical sensing and sensors 110.5200 Photography 动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 | 经典导波与拓扑单向波间的高效转换动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 主编推荐 | 单片集成硅基灵活栅格MWSS为突破“容量危机”提供新策略动态信息 丨 2024-04-10
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 封面 |构造任意自相似类贝塞尔光束构造新方法动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 |声光调制的干涉增强效应,助力光学量子信息技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 基于时空耦合效应的超宽带频率转换技术激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦