2017, 15(3) Column
Chinese Optics Letters 第15卷 第3期
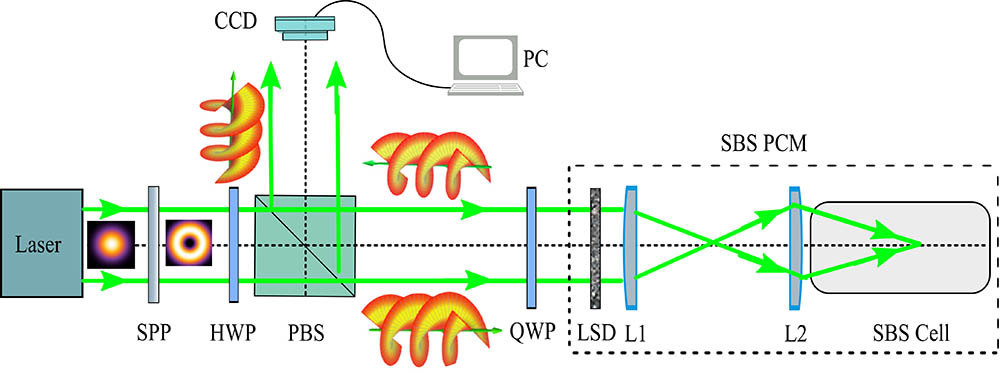
Recently there is an increasing interest in tailored optical fields with complex amplitude, phase and polarization spatial distributions, as well as specifically designed temporal waveforms. Scalar optical vortices carrying orbital angular momentum and vectorial vortices such as radially and azimuthally polarized beams are among the most intensively studied examples. Comprehensive summaries of earlier developments can be found in several recent articles and edited books, e.g., by Zhan (
 Download:1077次
Download:1077次 Download:673次
Download:673次 Download:1242次
Download:1242次 Download:918次
Download:918次 Download:931次
Download:931次 Download:1312次
Download:1312次 Download:700次
Download:700次 Download:836次
Download:836次 Download:1057次
Download:1057次 Download:1046次
Download:1046次 Download:823次
Download:823次动态信息
激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦