2018, 16(12) Column
Chinese Optics Letters 第16卷 第12期
Average BER of coherent optical QPSK systems with phase errors over M turbulence channels Download:689次
Download:689次
 Download:689次
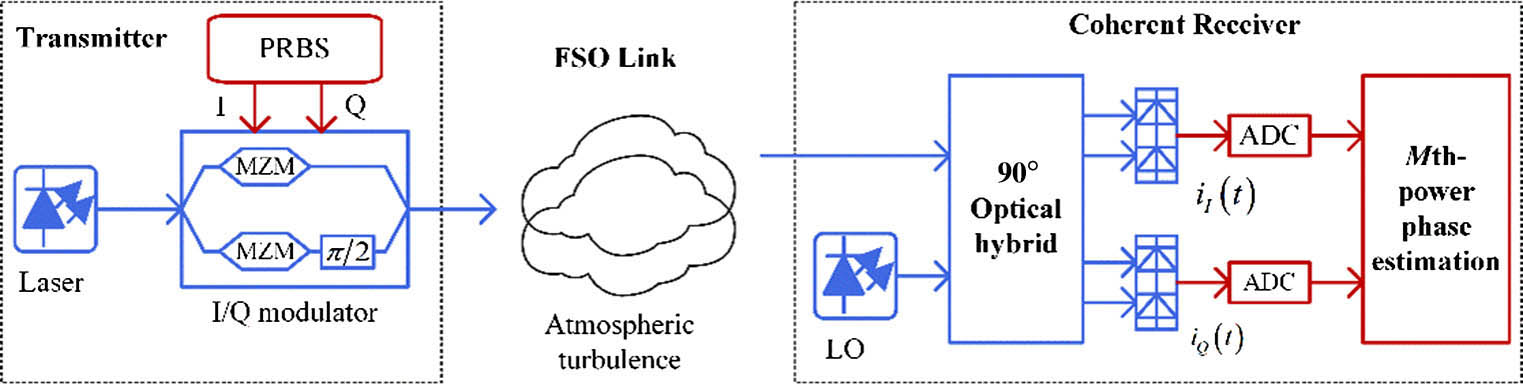
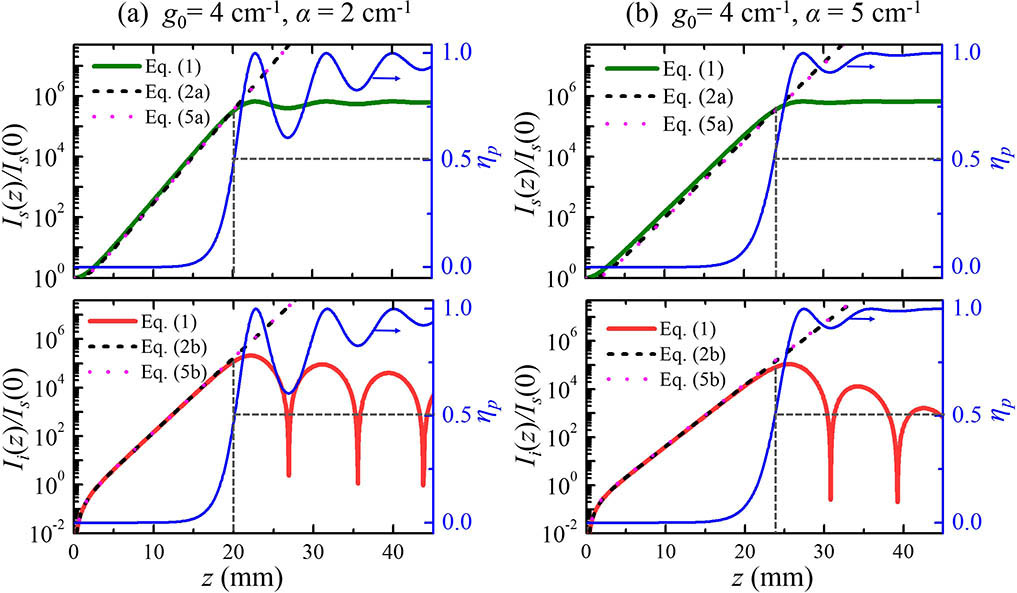
Download:689次The average bit-error-rate (BER) performance is studied for a coherent free-space optical communication system employing differentially encoded quadrature phase-shift keying (QPSK) with the M th-power phase estimation method. A closed-form expression, considering the combined effects of the Málaga (M) turbulence fading, pointing errors, and phase estimation errors, is derived in terms of Meijer’s G function. Numerical and Monte Carlo simulation results are presented to verify the derived expression.
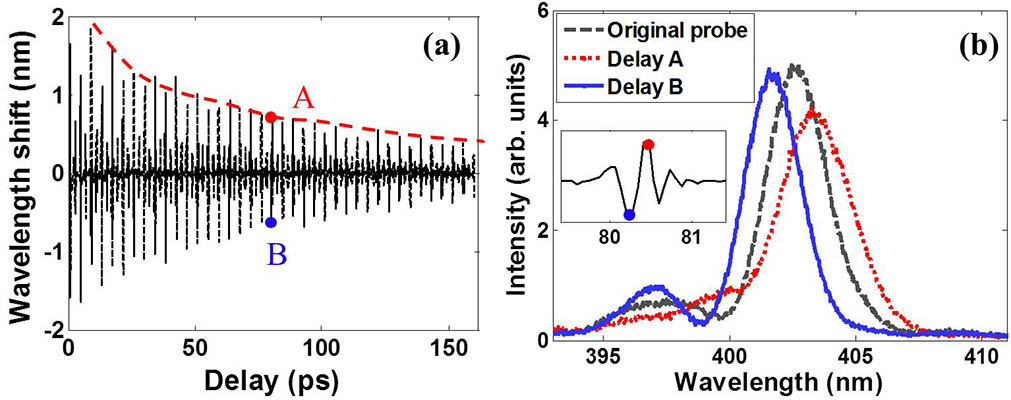
010.1300 Atmospheric propagation 010.1330 Atmospheric turbulence 060.1660 Coherent communications We report on an experimental investigation on the dynamic decoherence process of molecular rotational wavepackets during femtosecond laser filamentation based on time-dependent mean wavelength shifts of a weak probe pulse. Details of periodic revival structures of transient alignment can be readily obtained from the measured shifted spectra due to the periodic modulation of the molecular refractive index. Using the method, we measured decoherence lifetimes of molecular rotational wavepackets in N 2 O 2
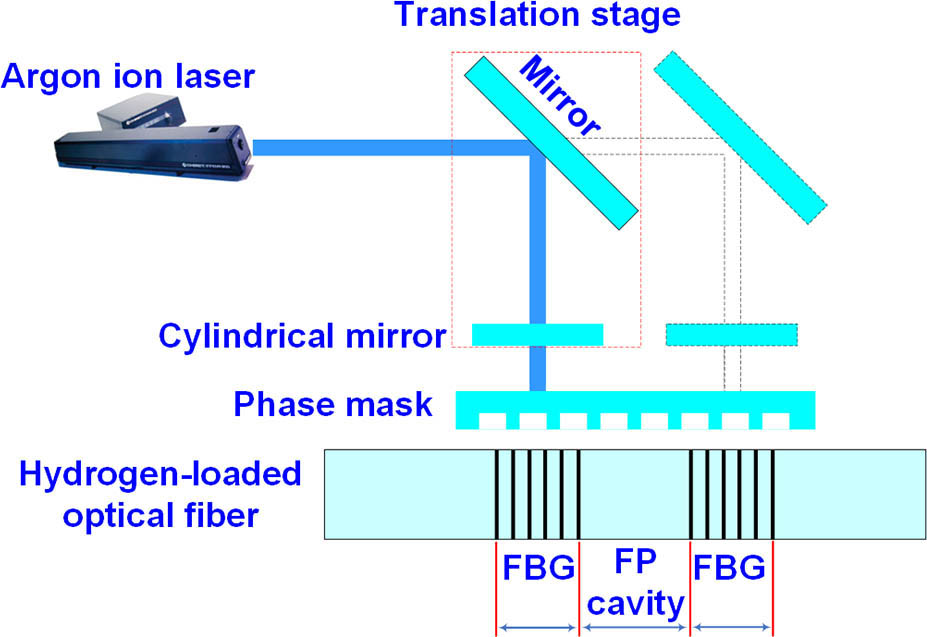
020.2649 Strong field laser physics 300.6530 Spectroscopy, ultrafast Thermal characteristics of Fabry–Perot cavity based on regenerated fiber Bragg gratings Download:544次
Download:544次
 Download:544次
Download:544次The Letter reports the thermal stability and strain response of Fabry–Perot (FP) cavity under different high temperatures. The FP cavity was made by thermal regeneration of two identical cascaded fiber Bragg gratings (FBGs). It is demonstrated that the FP cavity is capable of measuring temperatures from 300°C to 900°C with a temperature sensitivity of 15.97 pm/°C. The elongation of the fiber was observed through the drifted Bragg wavelength at 700°C or above when weight was loaded. The elongation was further inferred by the slight change in the interference spectra of the FP cavity at 900°C.
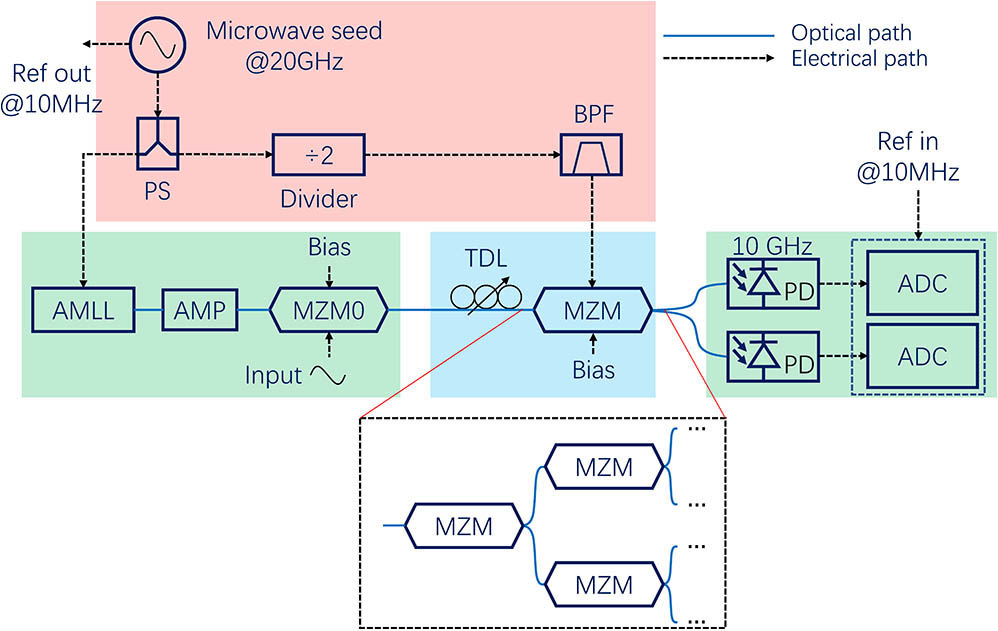
060.2370 Fiber optics sensors Switching response of dual-output Mach–Zehnder modulator in channel-interleaved photonic analog-to-digital converter Download:627次
Download:627次
 Download:627次
Download:627次This Letter theoretically and experimentally studies the response of photonic switching in a channel-interleaved photonic analog-to-digital converter (PADC) with high sampling rate and wide input frequency range. A figure of merit (FoM) is introduced to evaluate the switching response of the PADC when a dual-output Mach–Zehnder modulator (MZM) serves as the photonic switch to parallelize the sampled pulse train into two channels. After the optimization of the FoM and utilization of the channel-mismatch compensation algorithm, the system bandwidth of PADC is expanded and the signal-to-distortion ratio is enhanced.
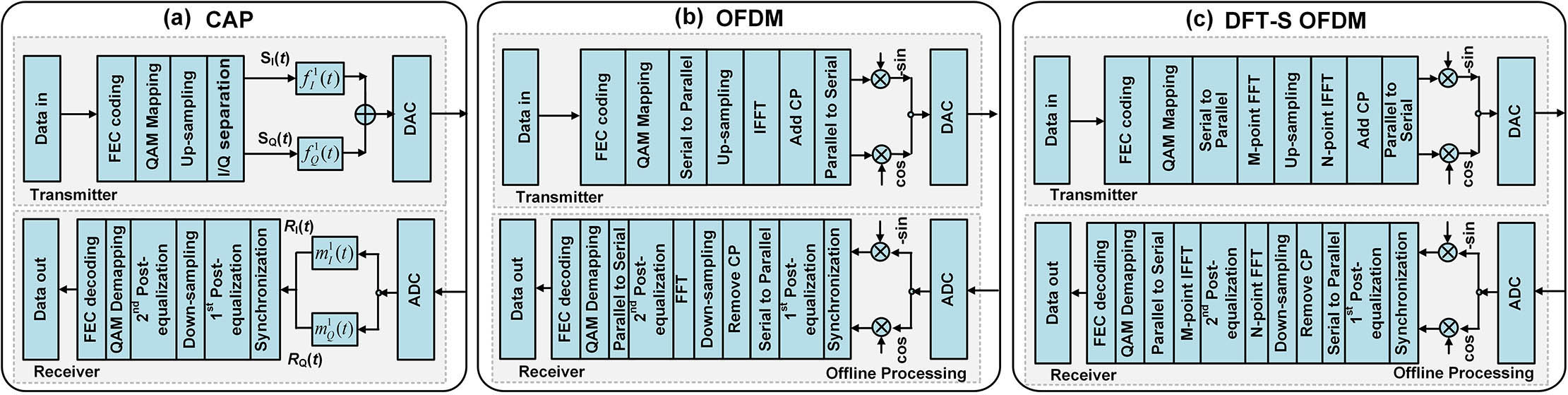
060.5625 Radio frequency photonics 230.0250 Optoelectronics 250.4745 Optical processing devices In this paper, we present a detailed comparison of applying three advanced modulation formats including carrierless amplitude and phase modulation (CAP), orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM), and discrete Fourier transform spread orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (DFT-S OFDM) in underwater visible light communication (UVLC) systems. Cascaded post-equalization schemes are suggested to compensate the system impairments. For the first time, a two-level post-equalizer is presented to mitigate the nonlinear effect and improve the system performance of UVLC. The first post-equalization is based on a novel recursive least square Volterra. These modulation formats are all experimentally demonstrated with corresponding digital signal processing (DSP) algorithms. The experimental results show that single carrier modulations including CAP and DFT-S OFDM can outperform OFDM. Our experiment results show that up to 3 Gb/s over a 1.2 m underwater visible light transmission can be achieved by using DFT-S OFDM 64QAM and CAP-64. The measured bit error rate is well under the hard decision-forward error correction (HD-FEC) threshold of 3.8 × 10 3
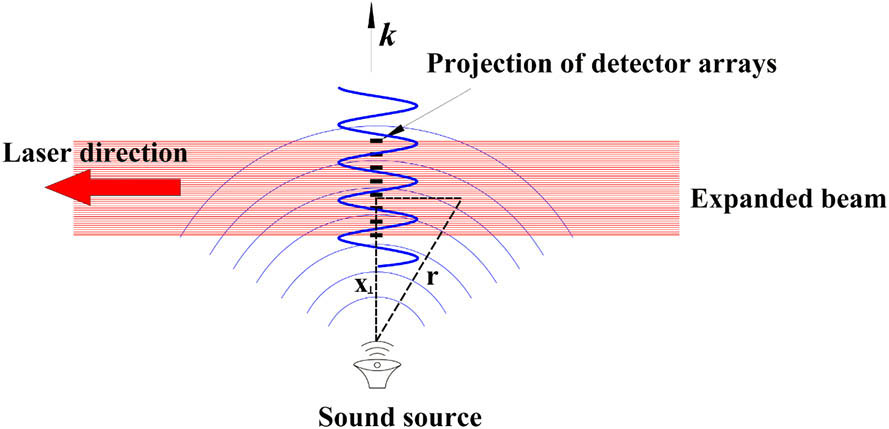
060.4080 Modulation System validation and density fluctuation calibration of phase contrast imaging (PCI) on an HL-2A tokamak are presented. Signals from different channels show not only a pronounced modulation of an incident laser beam induced by a sound wave, but also an excellent magnification and low image distortion of optics. The frequency-wavenumber spectrum is achieved by using two-dimensional Fourier transform of time series signals. The conversion coefficient between detected signal amplitude and chord integral plasma density fluctuation is 2.35 × 1013 m 2/mV, which promises a suitable signal level at the order of volts of the PCI in typical HL-2A discharges.
120.5050 Phase measurement 150.1488 Calibration 350.5400 Plasmas 120.5060 Phase modulation Experimental research on impulse coupling effect of a multi-pulse laser on an aluminum target Download:541次
Download:541次
 Download:541次
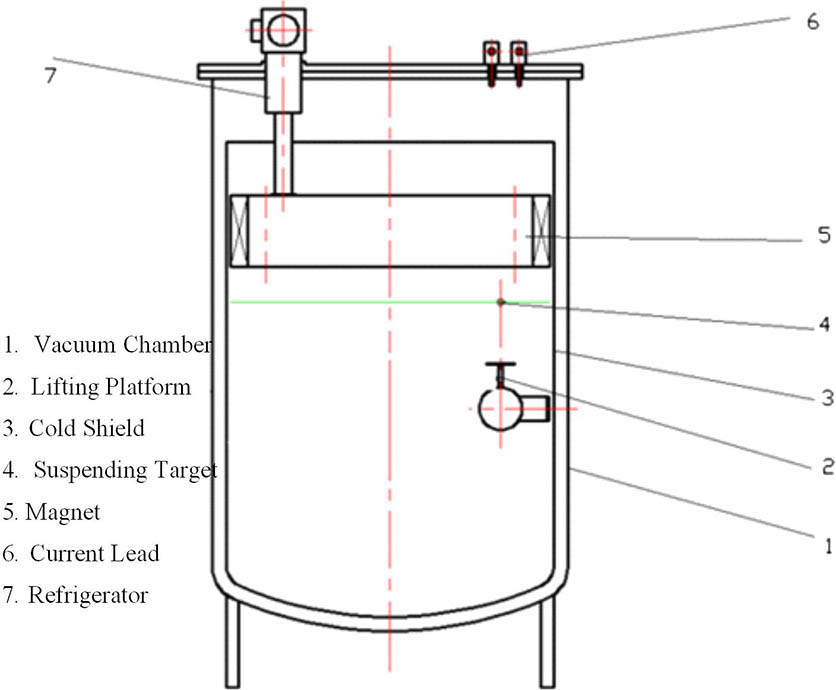
Download:541次Impact and torsion pendulums are applied in impulse coupling experiments of high-energy laser irradiation of space debris. It is difficult to achieve a multi-pulse experiment and thus hard to analyze the multi-pulse impulse coupling effect. Here, we designed a new recoil impulse experimental measurement system of non-contact, multi-degrees of freedom, and multi-pulse irradiation. The system used a low-pressure and low-temperature vacuum chamber to simulate the space environment, the pinning effect of magnetic levitation to achieve aluminum target suspension, and high-speed cameras to record the displacement over time to calculate the impulse of the target. Then the impulse coupling experiment of multi-pulse laser irradiation on the aluminum target was performed. The result shows that the multi-pulse impulse coupling effect is not the linear accumulation of coupling results by every single-pulse and multi-pulse coefficient that decreases with the increase of the number of pulses, and eventually stabilizes as the decrease gets smaller.
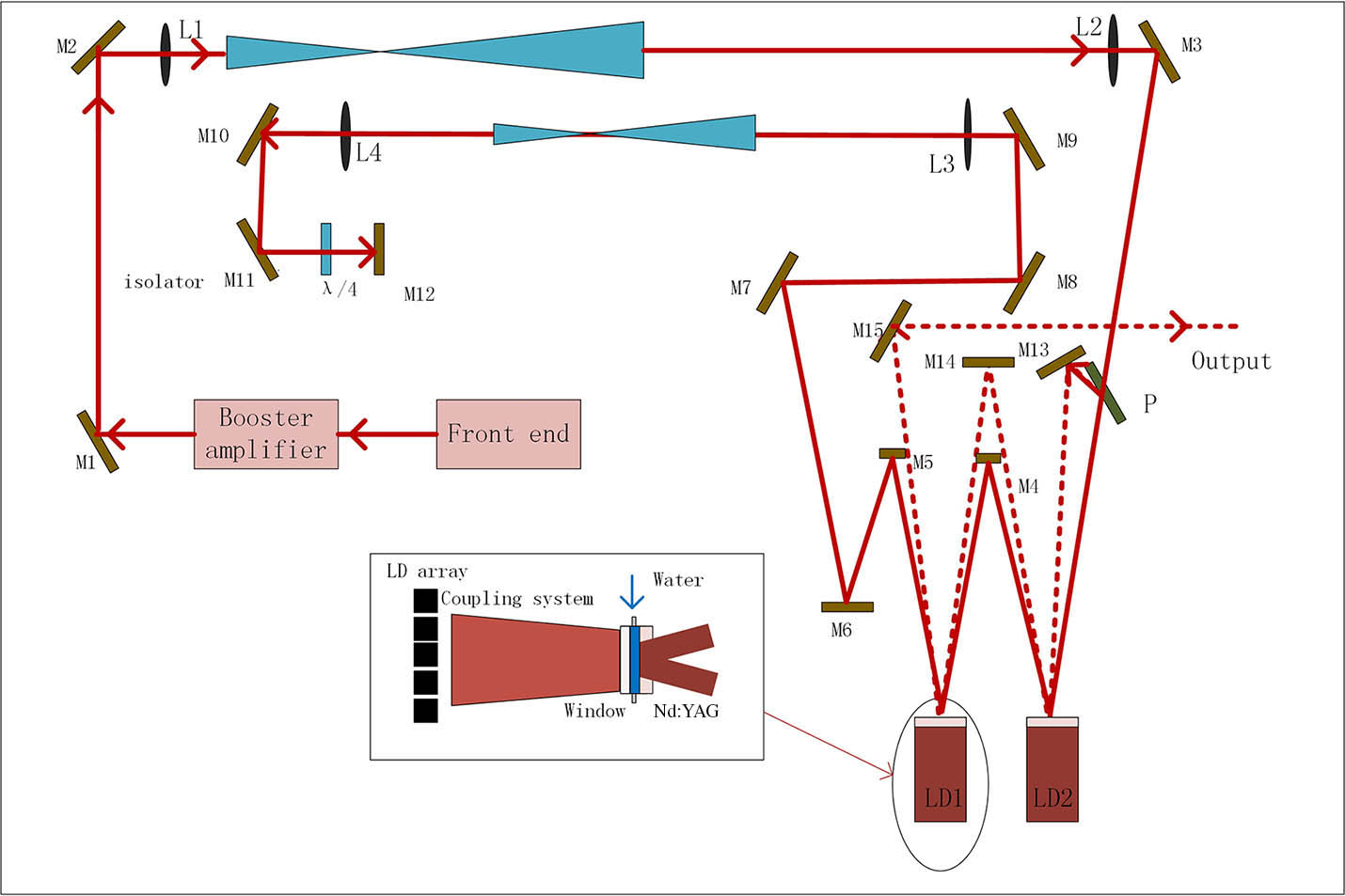
140.3325 Laser coupling 140.3390 Laser materials processing A high-beam-quality diode-pumped neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet (Nd:YAG) active mirror laser amplifier was demonstrated. The size of the Nd:YAG crystal was 48 mm × 42 mm × 11 mm with 0.6 at.% Nd doped. When the pump energy was 26.8 J and the input energy was 0.3 J, the output pulse energy reached 5.4 J, and the pulse width of 11.3 ns at a 5 Hz repetition rate was obtained for the two gain modules in three-pass amplification, with corresponding optical-to-optical efficiency of 21.2%. The beam quality was measured as M x 2 = 2.48 M y 2 = 2.43
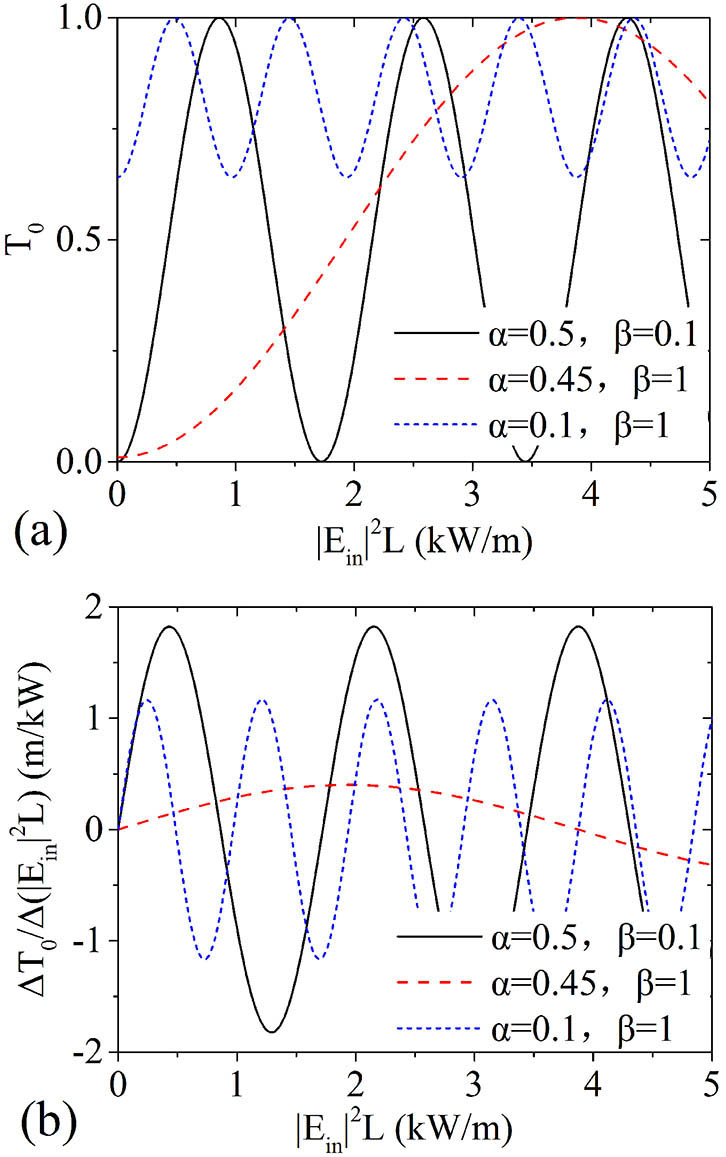
140.3280 Laser amplifiers 140.3460 Lasers We demonstrate a proposal for making an ultrastable laser referenced to a multi-cavity, enabling a lower thermal noise limit due to the averaging effect. In comparison with a single-cavity system, relative frequency instability of the synthesized laser can be improved by a factor of the square root of the cavity number. We perform an experiment to simulate a two-cavity system with two independent ultrastable lasers. Experimental results show that the relative frequency instability (Allan deviation) of the synthesized laser is 5 × 10 16, improved by a factor of √2 from a single-cavity-stabilized laser.
140.4780 Optical resonators 120.4820 Optical systems 140.3518 Lasers, frequency modulated In this Letter, we report on a novel architecture for a self-starting mode-locked figure-eight erbium-doped fiber laser using a loss-imbalanced nonlinear optical loop mirror (NOLM) with a bidirectional output coupler. An all-polarization-maintaining structure is adopted. A 2 × 2 optical coupler with a splitting ratio of 50:50 is used at the junction to form an NOLM. Another coupler with a splitting ratio of 10:90 is introduced at one end of the fiber loop. The 10:90 coupler plays two roles: power attenuator and bidirectional output coupler. This architecture can achieve both large modulation depth and good self-starting ability simultaneously. With this architecture, the self-starting mode-locking operation is achieved easily with pump power above the threshold. The clockwise and counter-clockwise mode-locked output powers are 10.1 and 10.3 mW, respectively, with the repetition rate of 3.63 MHz. The spectral bandwidths of the clockwise and counter-clockwise mode-locked output pulses are 7.4 and 2.9 nm, and the corresponding pulse widths of the direct outputs are 530.6 fs and 1.55 ps, respectively.
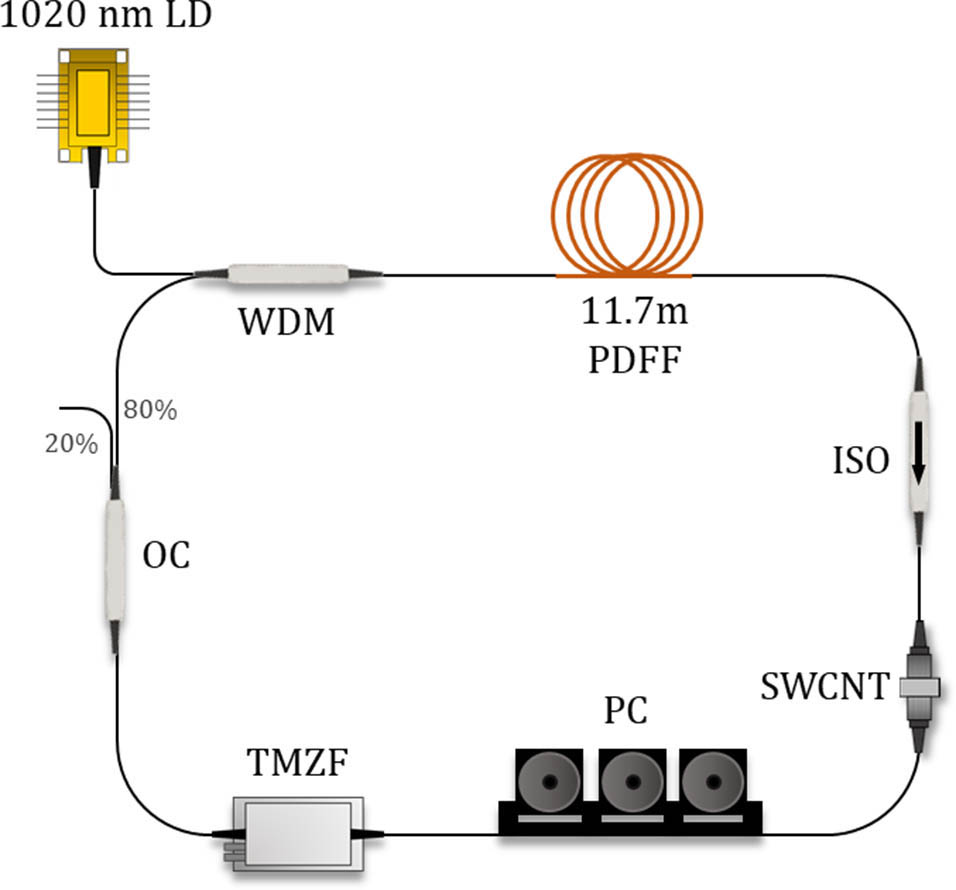
140.3510 Lasers, fiber 140.4050 Mode-locked lasers The interest in tunable ultrafast fiber lasers operating in the 1.3 μm region has seen a significant increase due to rising demands for bandwidth as well as the zero-dispersion characteristic of silica fibers in this wavelength region. In this work, a tunable mode-locked praseodymium-doped fluoride fiber (PDFF) laser using single-walled carbon nanotubes as a saturable absorber is demonstrated. The mode-locked pulses are generated at a central wavelength of 1302 nm with a pulse repetition rate of 5.92 MHz and pulse width of 1.13 ps. The tunability of the mode-locked PDFF laser covers a tuning range of 11 nm.
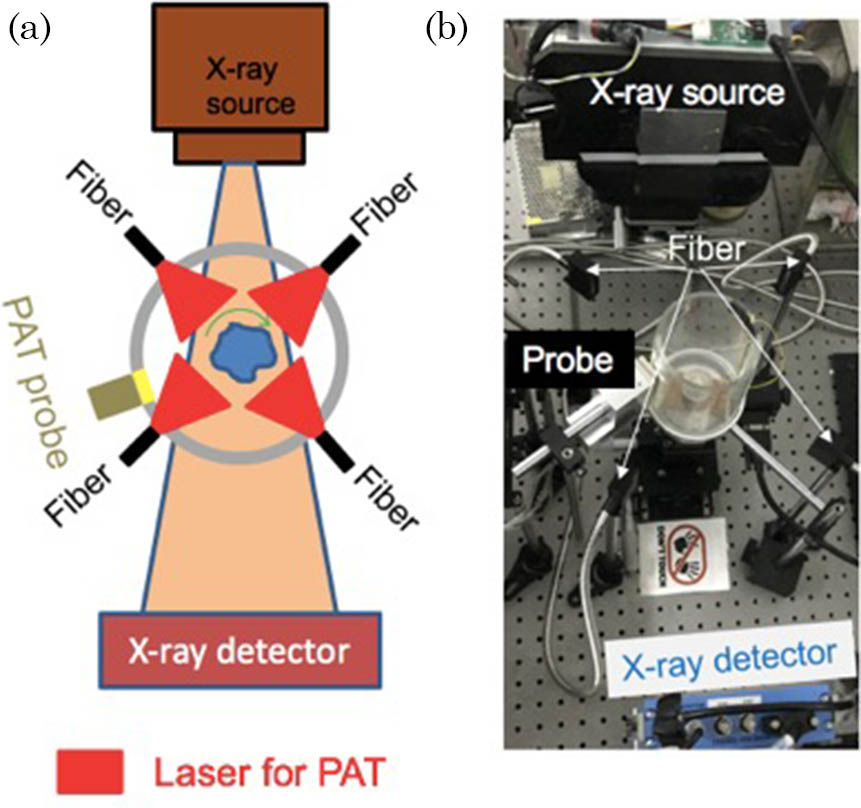
140.3510 Lasers, fiber Photoacoustic (PA) tomography (PAT) breaks the barrier for high-resolution optical imaging in a strong light-scattering medium, having a great potential for both clinical implementation and small animal studies. However, many organs and tissues lack enough PA contrast or even hinder the propagation of PA waves. Therefore, it is challenging to interpret pure PAT images, especially three-dimensional (3D) PA images for deep tissues, without enough structural information. To overcome this limitation, in this study, we integrated PAT with X-ray computed tomography (CT) in a standalone system. PAT provides optical contrast and CT gives anatomical information. We performed agar, tissue phantom, and animal studies, and the results demonstrated that PAT/CT imaging systems can provide accurate spatial registration of important complementary contrasts.
170.5120 Photoacoustic imaging Analysis and evaluation of idler absorption for quasi-parametric chirped-pulse amplification Download:650次
Download:650次
 Download:650次
Download:650次Quasi-parametric chirped-pulse amplification (QPCPA) can improve the signal amplification efficiency and stability by inhibiting the back-conversion, in which the idler absorption plays a critical role. This Letter theoretically studies the impacts of idler absorption on the QPCPA performance in both the small-signal and saturation regimes. We demonstrate that there exists an optimal idler absorption that enables the achievement of maximum pump depletion within a minimum crystal length. To overcome the reduction in small-signal gain induced by idler absorption, the configuration of gradient idler absorption is proposed and demonstrated as a superior alternative to constant idler absorption. The results provide guidelines to the design of state-of-the-art QPCPA lasers.
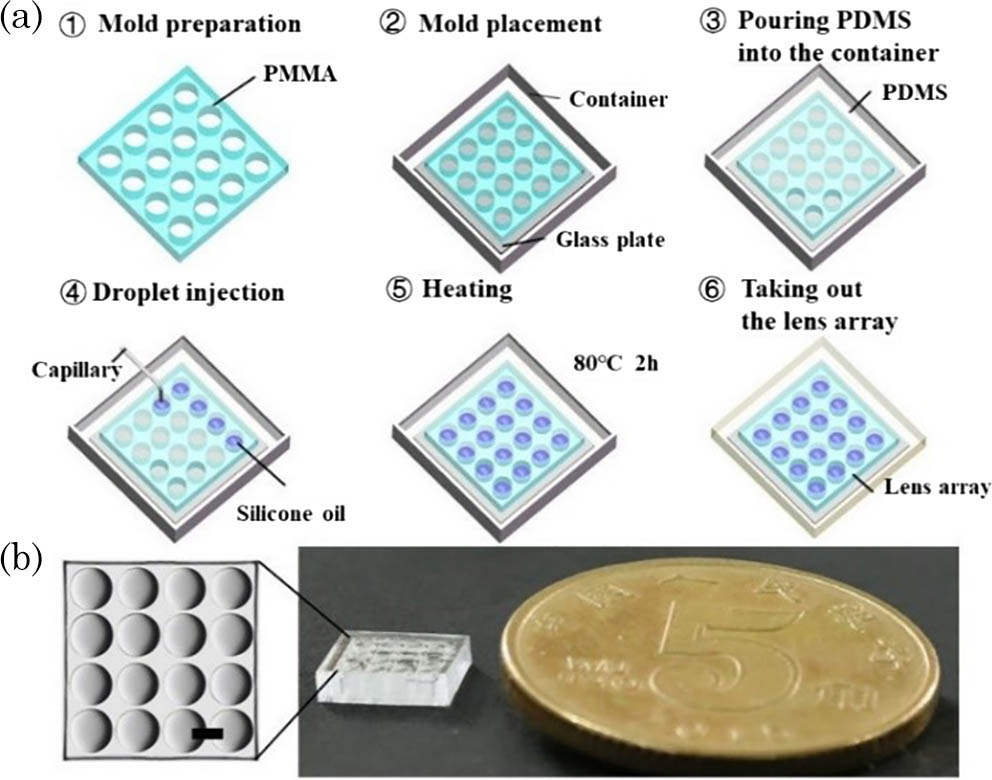
190.4410 Nonlinear optics, parametric processes A rapid and cost-effective method for fabricating mini lens arrays is proposed. The lenses are made of silicone oil droplets and filled inside a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) elastomer. The lens arrays of different initial focal lengths and apertures can be fabricated by using the droplets of different volumes. Due to good elastic behavior of PDMS, the droplet lenses can be flexibly deformed, and the focal length and numerical aperture can be tuned by applying an external force on the PDMS elastomer. Furthermore, an apparatus for focal length tuning is designed and employed in the imaging system.
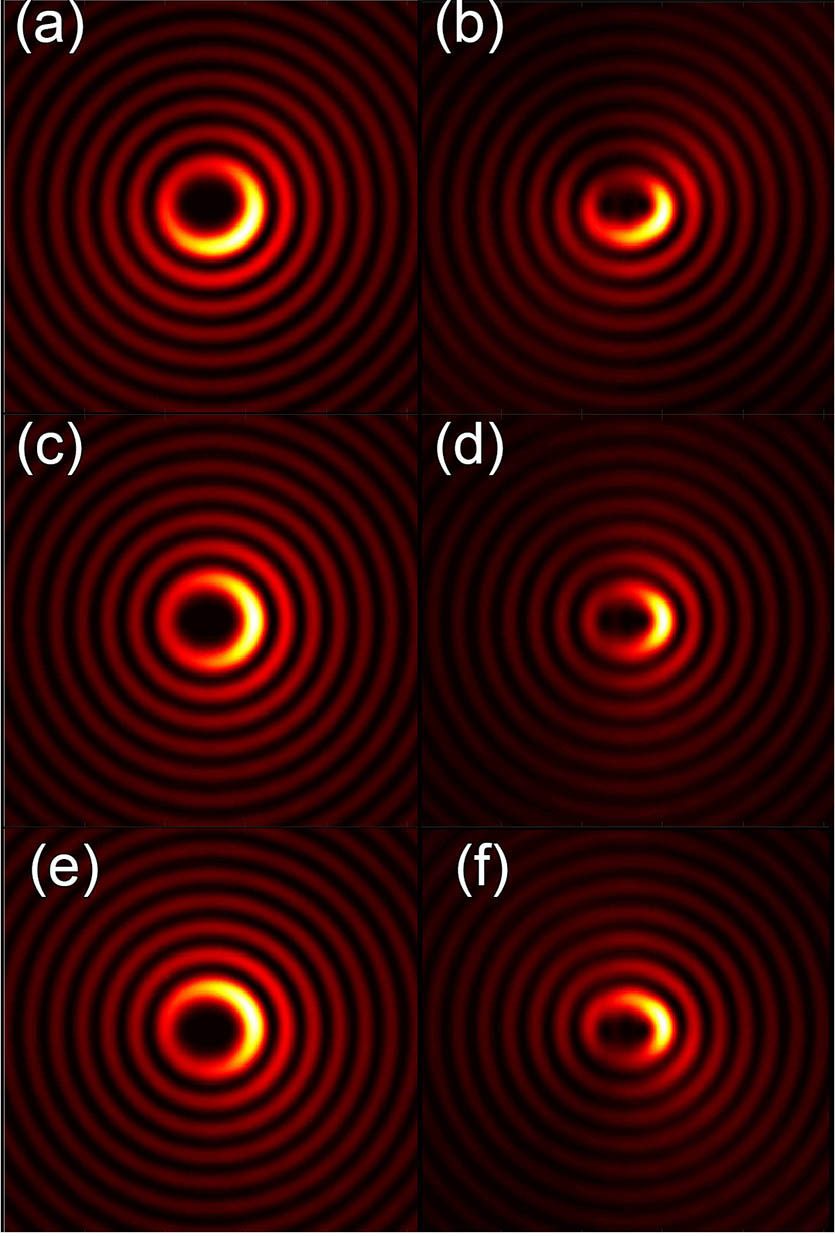
220.0220 Optical design and fabrication We report the generation of asymmetric Mathieu beams: invariant intensity optical profiles that can be described by three parameters. The first one describes the amount of ellipticity, the second one takes into account the degree of asymmetry of the profile, and the third parameter denotes the angular position, where it is localized with the respective asymmetry. We propose a simple angular spectrum to generate these nondiffracting beams, and we report how it changes their distribution of power and orbital angular momentum in function with their ellipticity and degree of asymmetry. We confirm the existence of these invariant beams by propagation in an experimental setup.
260.1960 Diffraction theory 140.3300 Laser beam shaping 动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-10
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 封面 |构造任意自相似类贝塞尔光束构造新方法动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
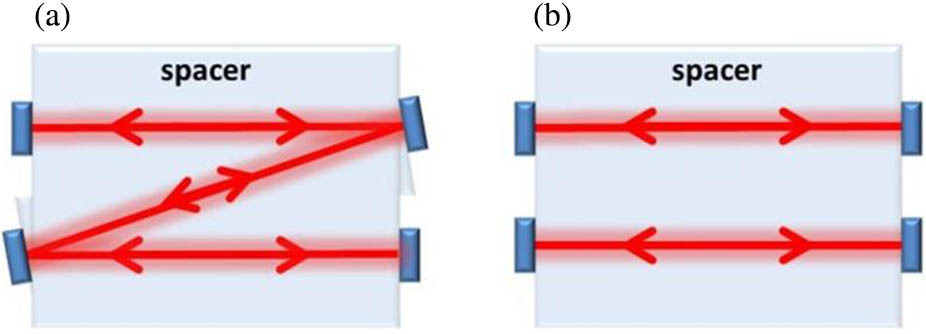
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 |声光调制的干涉增强效应,助力光学量子信息技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 基于时空耦合效应的超宽带频率转换技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 21, Iss. 11): 综述:太赫兹偏振光谱和手性光谱传感检测技术新应用动态信息 丨 2024-03-21
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 全光学的相位目标边缘提取,助力高分辨生物医学成像激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦