2018, 16(2) Column
Chinese Optics Letters 第16卷 第2期
Scientists are in the constant search of novel materials, or innovative applications of existing materials to solve problems we face in our everyday life. Although graphene, the two-dimensional (2D) form of carbon, has been a star player for the past decade, there is a significant shift towards other noncarbon materials in recent years. Apart from the large family of transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs), mono-elemental materials, such as phosphorene, arsenene, antimonene, and silicene, are rapidly gaining attention. Composites and heterogenous layered structures are also worthy of interest.
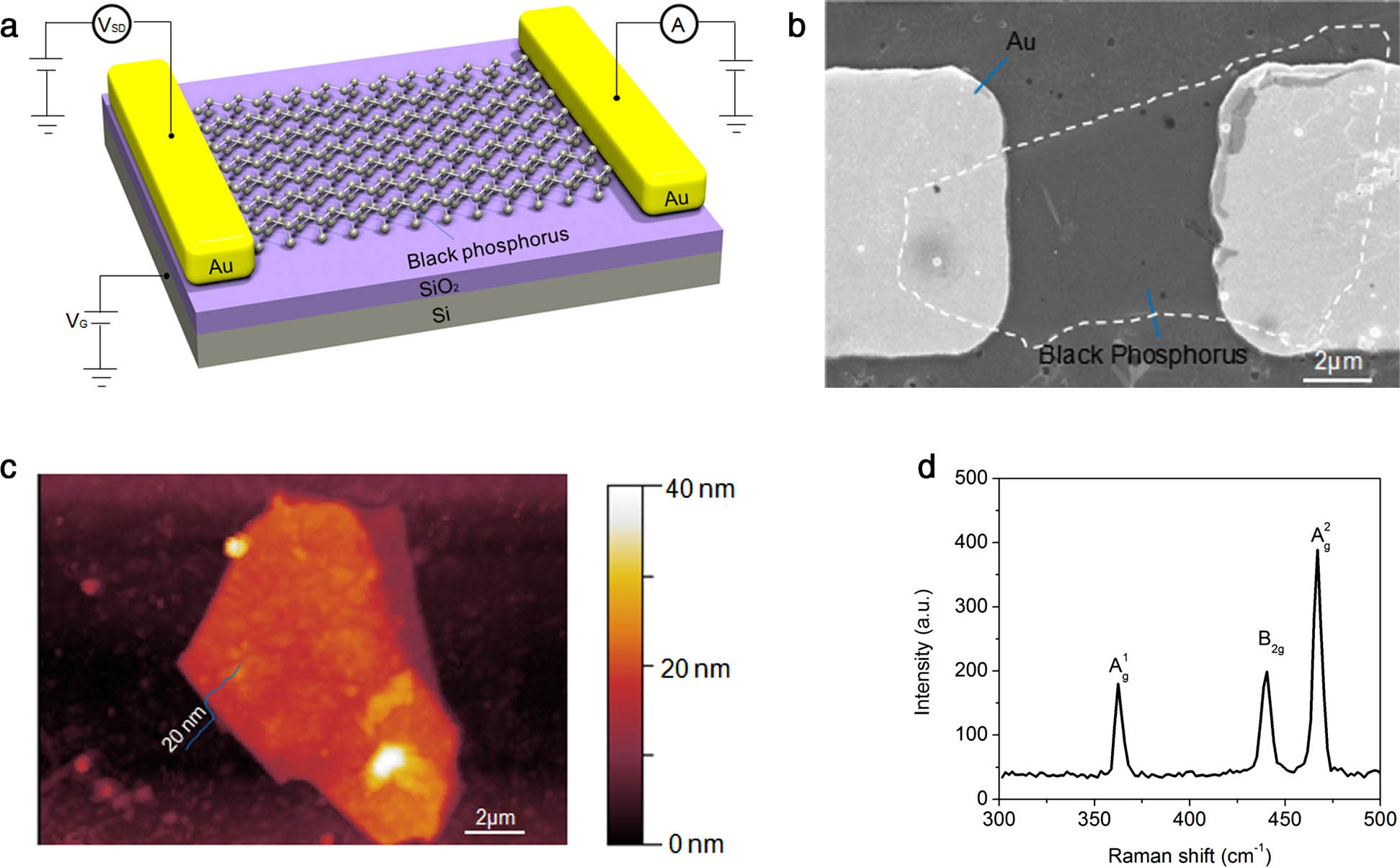
Black phosphorus (BP) is a promising material for ultrafast and broadband photodetection because of its narrow bandgap from 0.35 eV (bulk) to 1.8 eV (monolayer) and high carrier mobility. Although photodetectors based on BP with different configurations have been reported, high photosensitivity was mostly observed in the visible range. A highly efficient BP-based infrared photodetector operated in the telecom spectral range, especially at 1550 nm, has not been demonstrated. Here, we report a Schottky-type photodetector based on thin BP flakes, operating in a broad spectral range from visible (635 nm) to infrared (1550 nm). A responsivity as high as 230 A·W 1
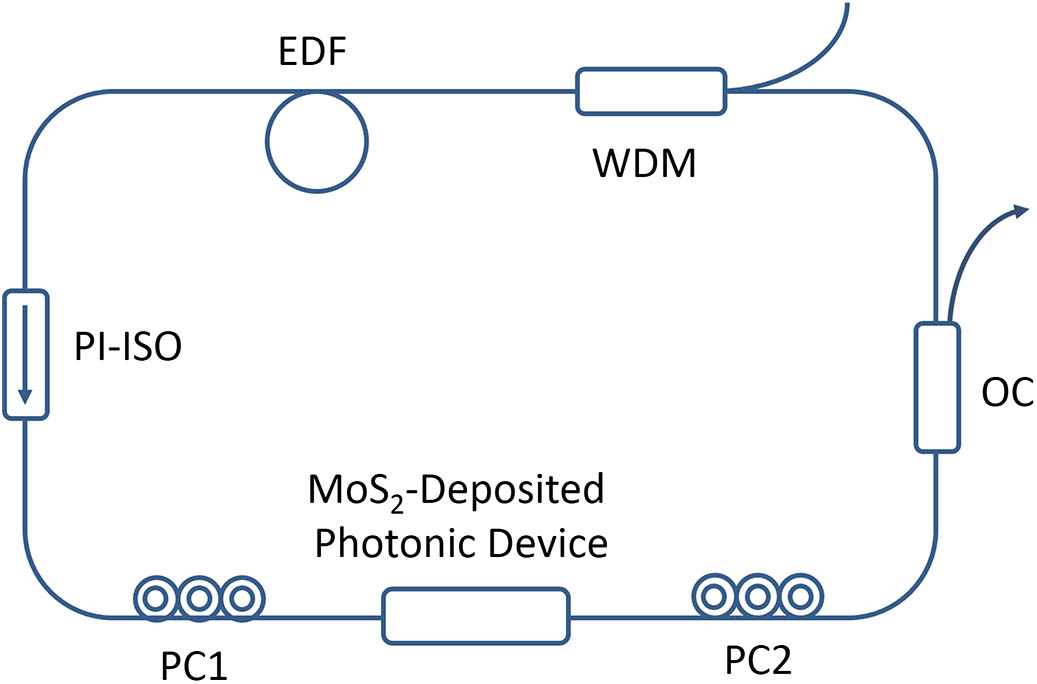
040.5160 Photodetectors 160.1890 Detector materials The all-optical approach plays an important role in ultrafast all-optical signal processing, and the all-fiber scheme has a wide application in optical communications. In this letter, we investigate an all-optical modulator using few-layer molybdenum disulfide (MoS 2 MoS 2 MoS 2
230.1150 All-optical devices 160.4330 Nonlinear optical materials 130.4815 Optical switching devices 2D noncarbon materials-based nonlinear optical devices for ultrafast photonics [Invited] Download:1034次
Download:1034次
 Download:1034次
Download:1034次Ultrafast lasers play an important role in a variety of applications ranging from optical communications to medical diagnostics and industrial materials processing. Graphene and other two-dimensional (2D) noncarbon materials, including topological insulators (TIs), transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDCs), phosphorene, bismuthene, and antimonene, have witnessed a very fast development of both fundamental and practical aspects in ultrafast photonics since 2009. Their unique nonlinear optical properties enable them to be used as excellent saturable absorbers (SAs) that have fast responses and broadband operation, and can be easily integrated into lasers. Here, we catalog and review recent progress in the exploitation of these 2D noncarbon materials in this emerging field. The fabrication techniques, nonlinear optical properties, and device integration strategies of 2D noncarbon materials are first introduced with a comprehensive view. Then, various mode-locked/Q -switched lasers (e.g., fiber, solid-state, disk, and waveguide lasers) based on 2D noncarbon materials are reviewed. In addition, versatile soliton pulses generated from the mode-locked fiber lasers based on 2D noncarbon materials are also summarized. Finally, future challenges and perspectives of 2D materials-based lasers are addressed.
140.3510 Lasers, fiber 140.4050 Mode-locked lasers 140.3540 Lasers, Q-switched The direct generation of passively Q-switched lasers at a green wavelength has rarely been investigated in the past. In this Letter, we demonstrate a passively Q-switched praseodymium-doped yttrium lithium fluoride green laser at 522 nm using CdTe/CdS quantum dots as a saturable absorber. A maximum average output power of 33.6 mW is achieved with the shortest pulse width of 840 ns. The corresponding pulse energy and peak power reached 0.18 μJ and 0.21 W, respectively. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first demonstration in regard to a quantum dots saturable absorber operating in the green spectral region.
140.3480 Lasers, diode-pumped 140.3540 Lasers, Q-switched Initiated by graphene, two-dimensional (2D) layered materials have attracted much attention owing to their novel layer-number-dependent physical and chemical properties. To fully utilize those properties, a fast and accurate determination of their layer number is the priority. Compared with conventional structural characterization tools, including atomic force microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, and transmission electron microscopy, the optical characterization methods such as optical contrast, Raman spectroscopy, photoluminescence, multiphoton imaging, and hyperspectral imaging have the distinctive advantages of a high-throughput and nondestructive examination. Here, taking the most studied 2D materials like graphene, MoS 2
120.6200 Spectrometers and spectroscopic instrumentation 160.4760 Optical properties 180.5655 Raman microscopy Materials in the transition metal dichalcogenide family, including WS 2 MoS 2 WSe 2 MoSe 2 WS 2 MoS 2 MoTe 2 MoTe 2 MoTe 2 Q -switched fiber laser operating at the wavelength of 1559 nm. The minimum pulse duration and signal-to-noise ratio are 677 ns and 63 dB, respectively. Moreover, the output power of 25 mW is impressive compared with previous work. We believe that MoTe 2 Q -switched fiber lasers.
160.4330 Nonlinear optical materials 140.3540 Lasers, Q-switched As the typical material of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs), few-layered MoS 2 MoS 2
160.4330 Nonlinear optical materials 140.4050 Mode-locked lasers 140.3510 Lasers, fiber A highly stable Q -switched laser incorporating a mechanically exfoliated tungsten sulphoselenide (WSSe) thin sheet saturable absorber (SA) is proposed and demonstrated. The SA assembly, formed by sandwiching a thin WSSe sheet between two fiber ferrules within the erbium-doped fiber laser, is used to effectively modulate the laser cavity losses. The WSSe-based SA has a saturation intensity of ~ 0.006 MW / cm 2 Q -switched laser output with a maximum repetition rate of 61.81 kHz and a minimum pulse width of 2.6 μs. The laser’s highest output power of 0.45 mW and highest pulse energy of 7.31 nJ are achieved at the maximum pump power of 280.5 mW. The tunability of the cavity’s output at the maximum pump power is analyzed with a C-band tunable bandpass filter, giving a broad tunable range of ~ 40 nm Q -switched laser correlates well with the gain spectrum of erbium-doped fibers, with the shift in the gain profile as a result of the saturated SA.
140.3500 Lasers, erbium 140.3510 Lasers, fiber 140.3540 Lasers, Q-switched The simultaneous dual-band pulsed amplification is demonstrated from an Er/Yb co-doped fiber (EYDF), and consequently a high-power all-fiber single-mode 1.0/1.5 μm dual-band pulsed master oscillator power amplifier (MOPA) laser source is realized for the first time, to the best of our knowledge, based on one singlegain fiber. The simultaneous outputs at 1061 and 1548 nm of the laser source have the maximum powers of 10.7 and 25.8 W with the pulse widths of 9.5 ps and 2 ns and the pulse repetition rates of 178 and 25 MHz, respectively. This EYDF MOPA laser source is seeded by two separate preamplifier chains operating at 1.0 and 1.5 μm wavebands. The dependence of the laser output powers on the length of the large-mode area EYDF, the ratio of the powers of the two signals launched into the booster amplifier, and the wavelength of the 1 μm seed signal are also investigated experimentally.
140.3510 Lasers, fiber 140.3280 Laser amplifiers Q-switched operation of an Nd:LuAG laser using gold nanorods (GNRs) as the saturable absorber (SA) is reported, which also produces the highest average power among the nanosecond Nd-doped Q-switched lasers by GNRs-based SA. The applied GNRs are prepared using a seed-mediated growth method and then dropped onto the quartz substrate to fabricate the SA. The average power of the Q-switched laser is 516 mW with the shortest pulse duration of 606.7 ns and the repetition rate of 265.1 kHz.
160.3380 Laser materials 140.3540 Lasers, Q-switched 160.4236 Nanomaterials We have prepared the graphene / MoS 2 Q -switched operation of an Er 3 + ZrF 4 - BaF 2 - LaF 3 - AlF 3 - NaF ~ 2.8 μ m Q -switched Er 3 + graphene / MoS 2
160.4330 Nonlinear optical materials 140.3070 Infrared and far-infrared lasers A diode-pumped Tm:YLF passively Q -switched laser at 2 μm was first demonstrated by using graphene oxide (GO) as a saturable absorber (SA). In this letter, continuous-wave (CW) laser and pulse laser performances were studied meticulously and systematically. It reasonably showed the dependence of the pulse duration, pulse energy, and pulse repetition rate on the absorbed power. A maximum repetition rate of 38.33 kHz and a single pulse energy of 9.89 μJ were obtained.
140.3380 Laser materials 140.3480 Lasers, diode-pumped 140.3540 Lasers, Q-switched A tunable passively Q -switched ytterbium-doped fiber laser using few-layer gallium selenide (GaSe) as a saturable absorber (SA) is demonstrated. The few-layer GaSe SA, which is fabricated by the mechanical exfoliation method, is able to generate a Q -switched fiber laser that has a maximum repetition rate of 92.6 kHz and a minimum pulsed width of 2.3 μs. The highest pulse energy exhibited by the generated pulse is 18.8 nJ with a signal to noise ratio of ~ 40 dB
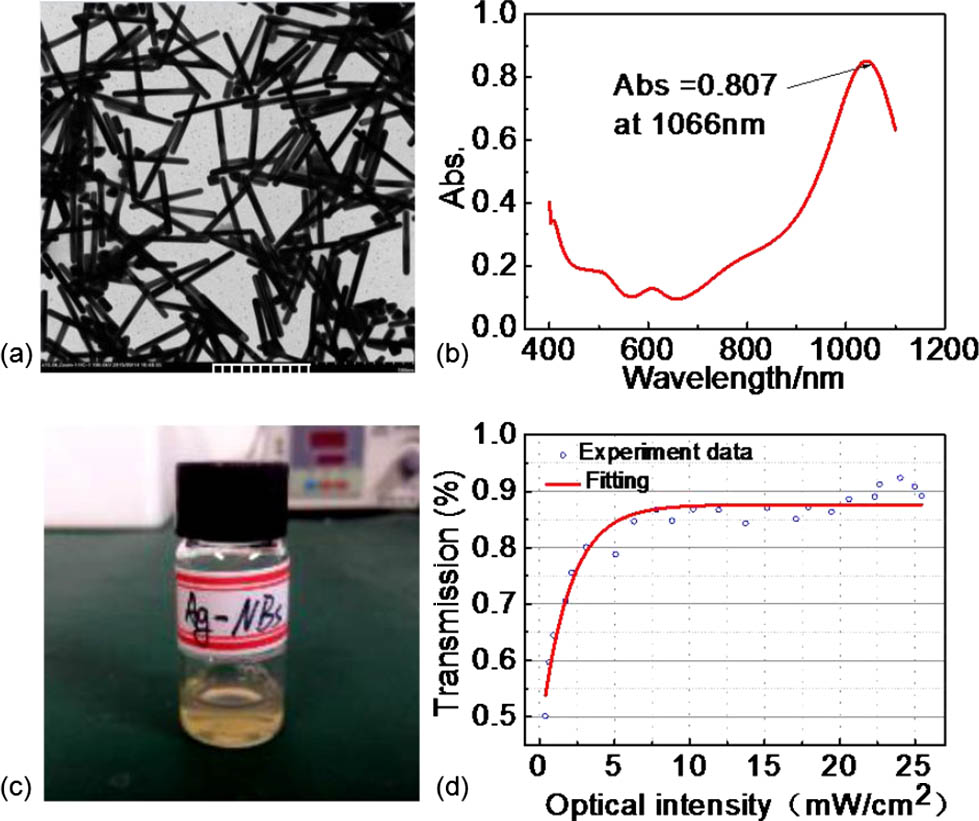
060.3510 Lasers, fiber 140.3540 Lasers, Q-switched Using a novel silver nanorods absorber with a localized surface plasmon resonance absorption peak at 1.06 μm, we obtain a diode-pumped passively Q-switched (PQS) Nd,Gd : CaF 2
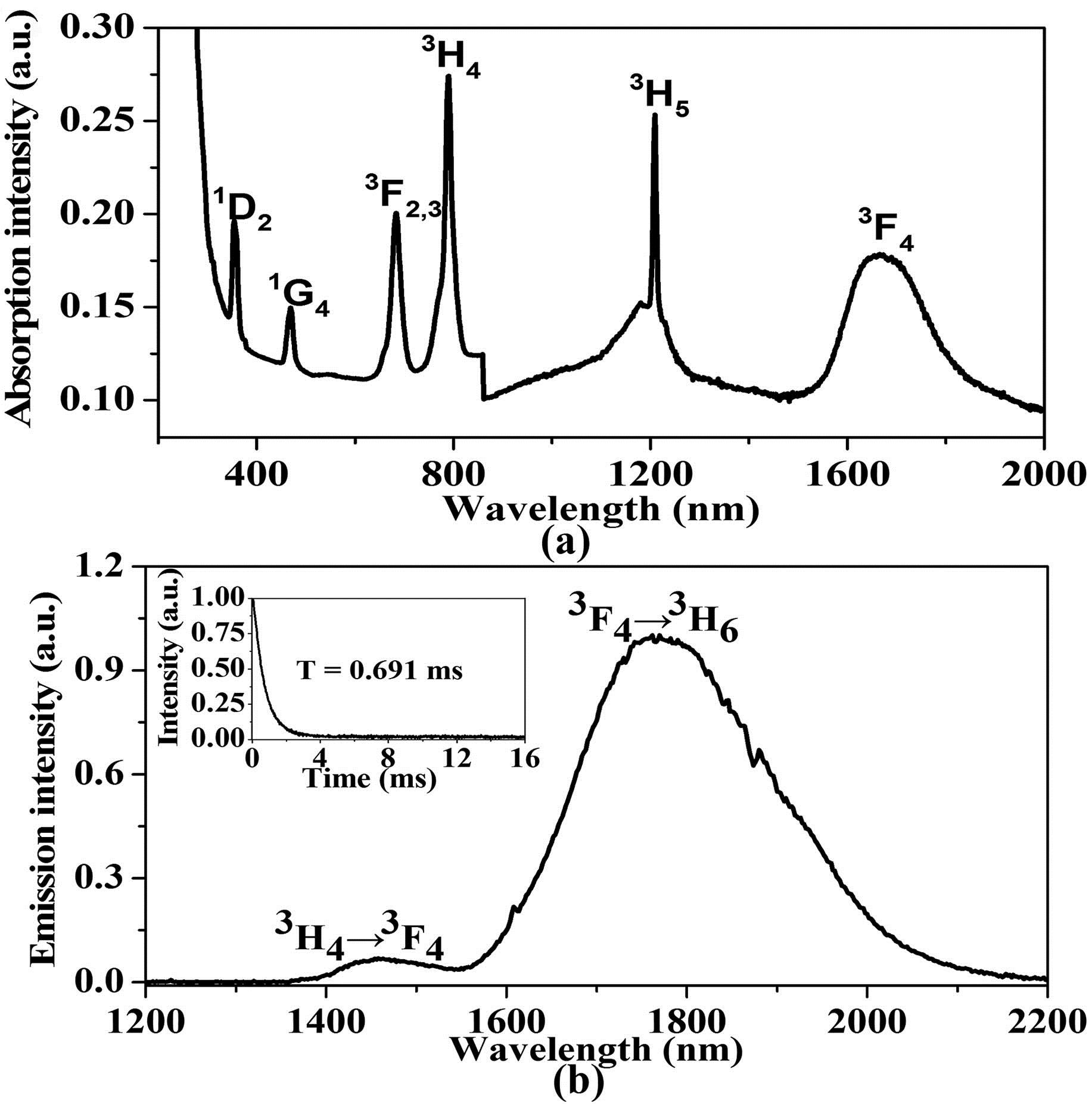
140.0140 Lasers and laser optics 140.3380 Laser materials 140.3480 Lasers, diode-pumped 140.3540 Lasers, Q-switched We demonstrate a dual-wavelength passively Q-switched Nd 3 + Bi 2 Se 3 Bi 2 Se 3
060.3510 Lasers, fiber 140.3540 Lasers, Q-switched 140.3530 Lasers, neodymium The potential of bulk-like WTe 2 Q -switch operating at the 1 μm wavelength was investigated. The WTe 2 WTe 2 WTe 2 ~ 2.18 % Q -switched pulses were readily achieved.
140.3510 Lasers, fiber 140.3540 Lasers, Q-switched We report the fabrication of an MoS 2 MoS 2
140.3540 Lasers, Q-switched We propose and demonstrate a passively harmonic mode-locked erbium-doped fiber laser (EDFL) using carbon nanotubes polyvinyl alcohol (CNTs-PVA) film. The laser allows generation of the pulses with a repetition rate of 580 MHz, which corresponds to the 22nd harmonics of a 26.3 MHz fundamental repetition rate under 323 mW pump power. A particularly noteworthy feature of the pulses is the super-mode suppression ratio (SMSR), which is over 40 dB, indicating a stable operation.
140.3500 Lasers, erbium 160.4236 Nanomaterials High-power ultrafast fiber lasers operating at the 2 μm wavelength are extremely desirable for material processing, laser surgery, and nonlinear optics. Here we fabricated large-core (LC) double-cladding Tm-doped silica fiber via the sol-gel method. The sol-gel-fabricated Tm-doped silica (SGTS) fiber had a large core diameter of 30 μm with a high refractive index homogeneity (Δ n = 2 × 10 4
060.2290 Fiber materials 060.3510 Lasers, fiber 140.4050 Mode-locked lasers 动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 | 经典导波与拓扑单向波间的高效转换动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 主编推荐 | 单片集成硅基灵活栅格MWSS为突破“容量危机”提供新策略动态信息 丨 2024-04-10
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 封面 |构造任意自相似类贝塞尔光束构造新方法动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 |声光调制的干涉增强效应,助力光学量子信息技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 基于时空耦合效应的超宽带频率转换技术激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦