2018, 16(3) Column
Chinese Optics Letters 第16卷 第3期
High-harmonic-generation-inspired preparation of optical vortex arrays with arbitrary-order topological charges Download:938次
Download:938次
 Download:938次
Download:938次In the process of high-harmonic generation with a Laguerre-Gaussian (LG) mode, it was well established that the topological charge could be of an N
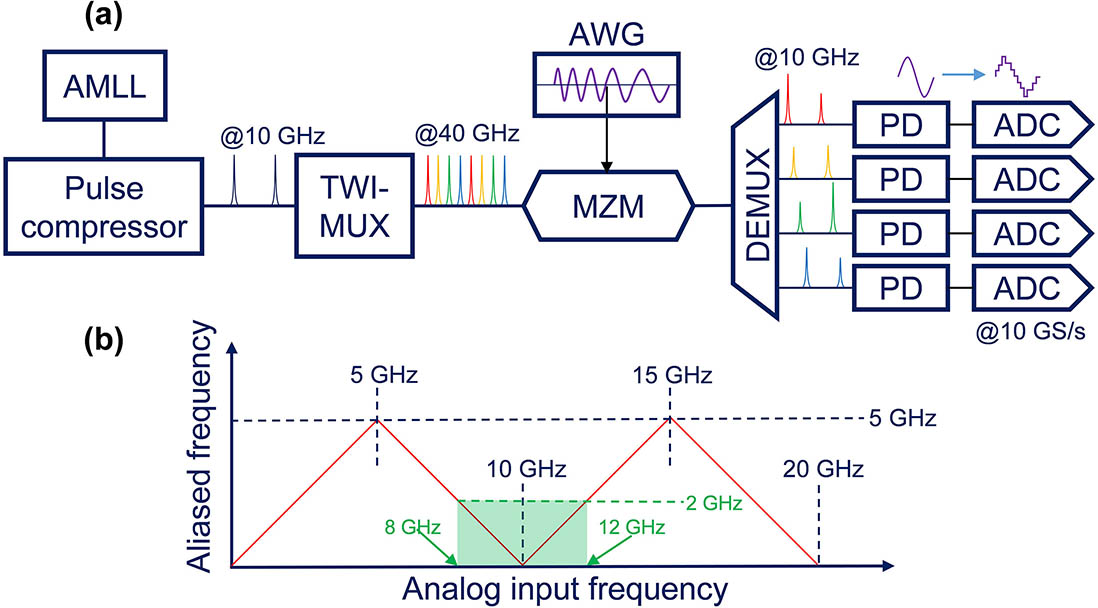
050.4865 Optical vortices 070.6120 Spatial light modulators 140.3300 Laser beam shaping This Letter demonstrates the effectiveness of a high-speed high-resolution photonic analog-to-digital converter (PADC) for wideband signal detection. The PADC system is seeded by a high-speed actively mode locked laser, and the sampling rate is multiplied via a time-wavelength interleaving scheme. According to the laboratory test, an X-band linear frequency modulation signal is detected and digitized by the PADC system. The channel mismatch effect in wideband signal detection is compensated via an algorithm based on a short-time Fourier transform. Consequently, the signal-to-distortion ratio (SDR) of the wideband signal detection is enhanced to the comparable SDR of the single-tone signal detection.
060.5625 Radio frequency photonics 230.0250 Optoelectronics 250.4745 Optical processing devices A mode field adapter (MFA) fabricated by the thermal expanded core (TEC) technique is investigated. Firstly, the mode field characteristics of the TEC large mode area fiber (LMAF) are analyzed. Compared with the single-mode fiber (SMF), the mode field diameter of the LMAF enlarged slower than that of the SMF. Secondly, the mode field characteristics of the different fibers with TEC treatment are discussed. Thirdly, the transmission efficiency of the MFA fabricated by the SMF and LMAF is also investigated. Finally, we used the 6/125 μm SMF and 15/130 μm LMAF to fabricate an MFA with transmission efficiency of 92% and the handling power as high as 100 W.
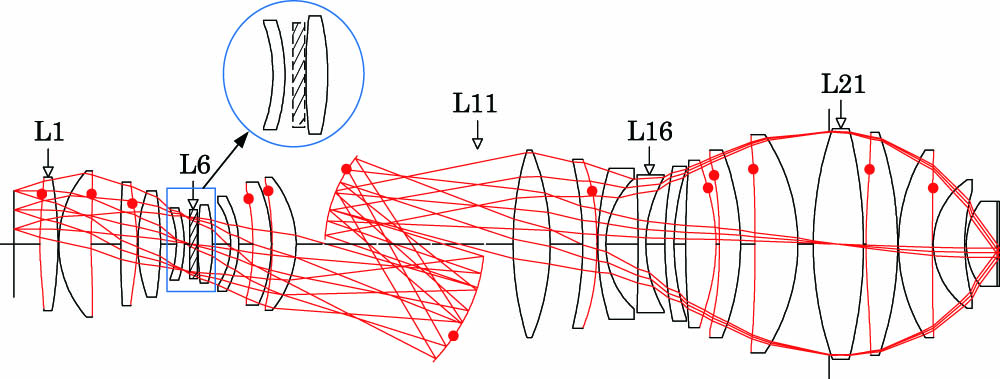
060.2340 Fiber optics components 060.2310 Fiber optics 140.3510 Lasers, fiber Design of a hyper-numerical-aperture deep ultraviolet lithography objective with freeform surfaces Download:855次
Download:855次
 Download:855次
Download:855次We have proposed and developed a design method of a freeform surfaces (FFSs) based hyper-numerical-aperture deep ultraviolet (DUV) projection objective (PO) with low aberration. With an aspheric initial configuration, lens-form parameters were used to determine the best position to remove elements and insert FFSs. The designed FFSs PO reduced two elements without increasing the total thickness of the glass materials. Compared with aspheric initial configuration, the wavefront error of the FFSs PO decreased from 0.006 λ 0.005 λ
080.2740 Geometric optical design 080.2468 First-order optics 120.4820 Optical systems This Letter demonstrates a novel lateral shear interferometer system for simultaneous measurement of three-dimensional (3D) shape and thickness of transparent objects. Multi-frequency fringe patterns can be created by tilting mirrors at different inclination angles. With a single camera, the multi-frequency fringes are recorded in one image. The phase-shift of the fringes can be generated synchronously only by moving a plane-parallel plate along an in-plane parallel direction. According to the feature of transparent materials, the thickness and 3D shape can be reconstructed simultaneously based on the relationship between the in-plane displacement and their characteristics. The experiment was conducted on a thin transparent film subjected to a shearing force, which verifies the feasibility of the proposed system.
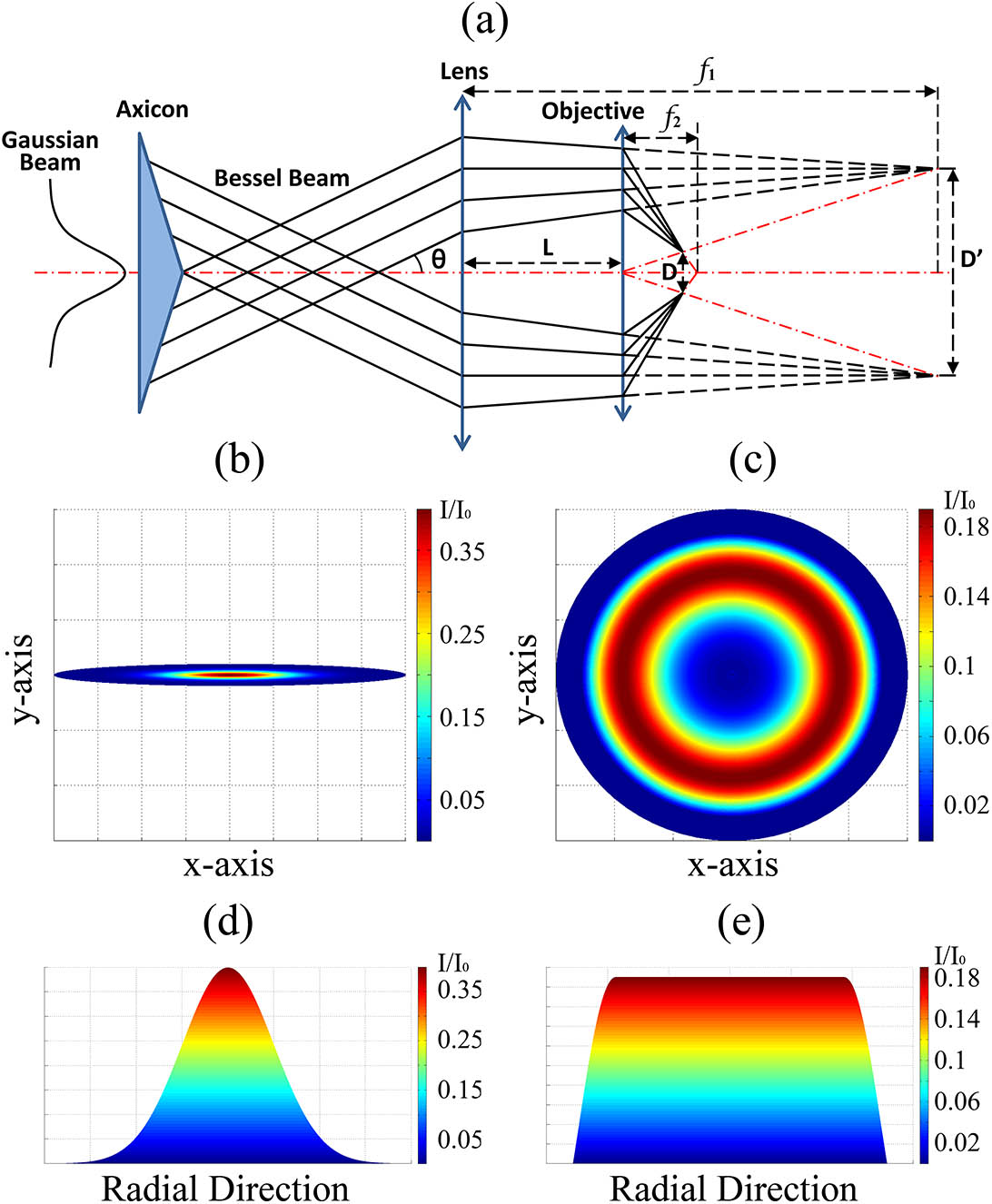
120.3180 Interferometry 120.6650 Surface measurements, figure Femtosecond laser highly-efficient plane processing based on an axicon-generated donut-shaped beam Download:735次
Download:735次
 Download:735次
Download:735次A simple technique is proposed for highly-efficient plane processing fully based on femtosecond laser beam shaping. The laser intensity distribution is transformed from a Gaussian to a donut shape. As the donut-shaped focus seems like a flat top from the side view, a plane with a high level of flatness is obtained directly by scanning once. By applying it to polishing experiments, the surface roughness can be improved significantly. The influence of scanning speed, laser pulse energy, and scanning times on the roughness is also discussed. Moreover, the scanning width can be flexibly controlled in a wide range.
140.7090 Ultrafast lasers 140.3300 Laser beam shaping We report a double Q -switched 946 nm laser with a magnesium-oxide-doped LiNbO 3 MoSe 2 φ 3 × 65 mm M x 2 = 3.849 M y 2 = 3.868 MoSe 2 Q -switching operation.
140.3580 Lasers, solid-state 140.3540 Lasers, Q-switched 160.4236 Nanomaterials We propose, design, and realize a compact stabilized laser system that can be tuned within 24 GHz automatically. This laser system consists of two distributed feedback (DFB) lasers, one of which is reference and locked to the D2 line of Rb 87 15 cm × 20 cm × 10 cm
140.2020 Diode lasers 140.3425 Laser stabilization A self-starting simple structured dual-wavelength passively mode-locked (ML) erbium-doped fiber (EDF) laser is proposed in this Letter. An all-fiber ring cavity is adopted and a transmission-type semiconductor saturable absorber is used as modelocker. In this laser, there are two gain humps located at the 1530 nm region and the 1550 nm region, respectively. Along with the length of EDF increasing, the intensity of the hump at 1530 nm region is gradually suppressed because of the re-absorption of emission by the ground state. With the proper length of EDF, the gain intensities of two regions are very close. When the pump power is above the ML threshold, the self-starting dual-wavelength ML operation is achieved easily without manual adjustment. The two spectral peaks with close intensities are located at 1532 and 1552 nm, respectively. The effect of intracavity dispersion on the output spectrum is also experimentally demonstrated.
140.4050 Mode-locked lasers 140.7090 Ultrafast lasers We propose and simulate a method for generating a three-dimensional (3D) optical cage in the vicinity of focus by focusing a double-ring shaped radially and azimuthally polarized beam. Our study shows that the combination of an inner ring with an azimuthally polarized field and an outer ring with a radially polarized field and a phase factor can produce an optical cage with a dark region enclosed by higher intensity. The shape of the cage can be tailored by appropriately adjusting the parameters of double-mode beams. Furthermore, multiple 3D optical cages can be realized by applying the shift theorem of the Fourier transform and macro-pixel sampling algorithm to a double-ring shaped radially and azimuthally polarized beam.
050.1960 Diffraction theory 260.5430 Polarization Ellipsometry is a powerful and well-established optical technique used in the characterization of materials. It works by combining the components of elliptically polarized light in order to draw information about the optical system. We propose an ellipsometric experimental set-up to study polarization interference in the total internal reflection regime for Gaussian laser beams. The relative phase between orthogonal states can be measured as a power oscillation of the optical beam transmitted through a dielectric block, and the orthogonal components are then mixed by a polarizer. We show under which conditions the plane wave analysis is valid, and when the power oscillation can be optimized to reproduce a full pattern of oscillation and to simulate quarter- and half-wave plates.
140.3430 Laser theory 260.3160 Interference With the increasing output power of the monolithic fiber laser oscillators, the stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) effect becomes one of the main limitations of power scaling. Employing fiber with a larger mode area is an effective technique to mitigate the SRS, but, for the monolithic fiber laser oscillators, the difficulty of the inscription of the high-reflection fiber Bragg gratings (FBGs) increases with the fiber mode area. In this work, we demonstrated a high-power monolithic fiber laser oscillator based on the home-made large mode area FBGs and ytterbium-doped fiber (YDF) with 25 μm core diameters. A maximum output power of 4.05 kW is achieved at the central wavelength of ~ 1080 nm ~ 6.7 kW ~ 25 dB M 2 ~ 2.2
140.3510 Lasers, fiber 140.3615 Lasers, ytterbium Measurement of ocular axial length using full-range spectral-domain low-coherence interferometry Download:666次
Download:666次
 Download:666次
Download:666次We demonstrate a system for measuring the ocular axial length (AL) with high sensitivity and high speed using spectral-domain low-coherence interferometry (SD-LCI). To address the limit in measuring such a large range by using SD-LCI, we propose a full-range method to recognize the positive and negative depths. The reference arm length is changed synchronously with the shift of the focal point of the probing beam. The system provides a composite depth range that is sufficient to cover the whole eye. We demonstrate the performance of the presented system by measuring the ALs of five volunteers. This system can provide the A-scan ocular biometric assessment of the corneal thickness and AL in 0.1 s.
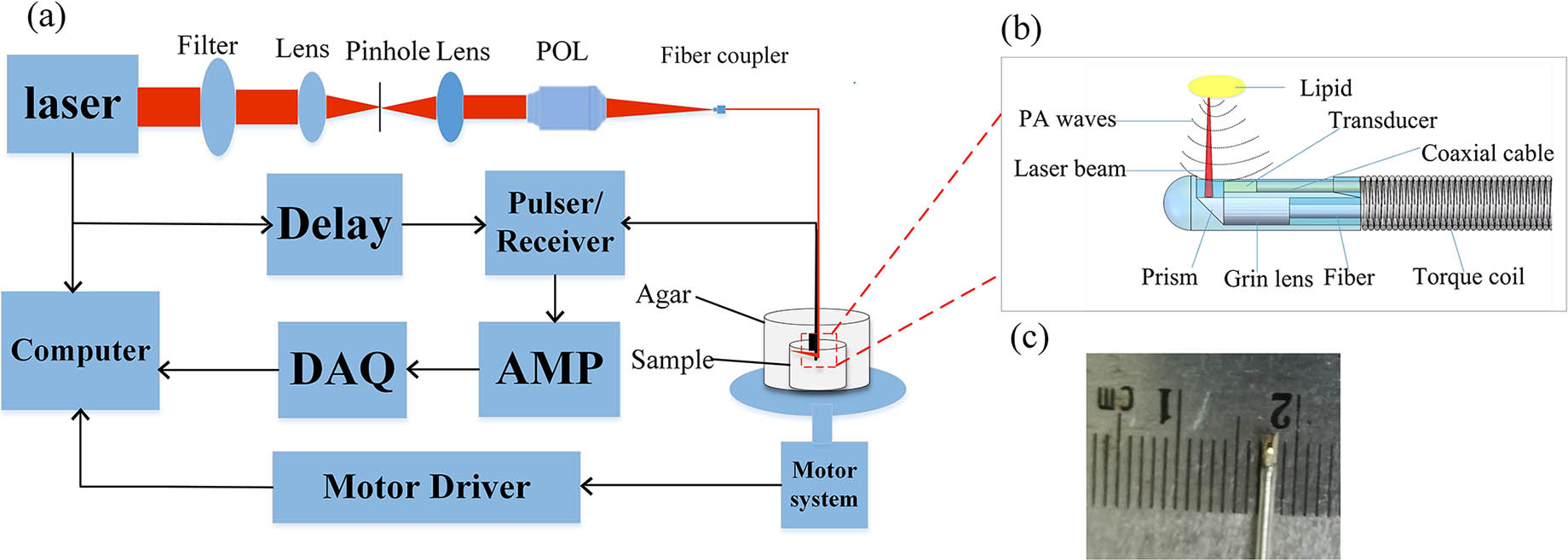
170.4500 Optical coherence tomography 170.4460 Ophthalmic optics and devices Photoacoustic characteristics of lipid-rich plaques under ultra-low temperature and formaldehyde treatment Download:710次
Download:710次
 Download:710次
Download:710次Photoacoustic imaging (PAI) has been used to characterize the spatial and quantitative features of lipid-rich atherosclerotic plaques with high sensitivity and specificity. In this Letter, we first validate that the ultra-low temperature and formaldehyde treatment have no effect on photoacoustic characteristics of the artery samples. Comparative experiments between the PAI and histological results demonstrate that the ultra-low temperature or formaldehyde treatment has few effects on the PAI of the lipid-rich atherosclerotic plaques; the lipid relative concentration and the lipid percentage by PAI hold high correlation with histology.
170.5120 Photoacoustic imaging Four-level phase pair encoding and decoding with single interferometric phase retrieval for holographic data storage Download:800次
Download:800次
 Download:800次
Download:800次We propose four-level phase pair encoding and decoding with single interferometric phase retrieval for holographic data storage. Inherent with phase pair encoding, phase shifting is generated by assigning a certain phase difference between two pixels of the phase pair. Multiple phase shifting operations are not required. In addition, a phase-readout reference beam can be a plane beam with an arbitrary phase in our method because phase shifting can be encoded on the phase-only spatial light modulator easily and accurately. Therefore, our method can not only increase the data transfer rate, but also improve the robustness of the holographic data storage system. Although the code rate of our method needs to be sacrificed by half, the code rate is still twice that of amplitude code when four-level phase encoding is used. We demonstrated experimentally that there is only a 1 × 10 2
210.2860 Holographic and volume memories Useful way to compensate for intrinsic birefringence caused by calcium fluoride in optical lithography systems Download:768次
Download:768次
 Download:768次
Download:768次Calcium fluoride is widely used in optical lithography lenses and causes retardation that cannot be ignored. However, few studies have been conducted to compensate for the retardation caused by calcium fluoride in optical lithography systems. In this Letter, a new index based on orientation Zernike polynomials is established to describe the value of retardation. Then, a method of retardation compensation is described. The method is implemented by clocking calcium fluoride lens elements, and the optimal rotation angles are calculated using a population-based stochastic optimization algorithm. Finally, an example is provided to validate the method.
220.3740 Lithography 260.1440 Birefringence We propose a plasmonic sensor with variable refractive index (RI), which exhibits high sensitivity and extraordinary optical transmission (EOT). Its variable RI is attributed to its dielectric layers and metallic slit arrays. According to simulation results, the third resonant wavelength has a wavelength sensitivity of 800 nm/RIU and an ultra-high transmittance of 0.8 by adjusting the RIs of the upper and lower dielectrics, incident light angle, and structural geometric parameters. With its unique features, the proposed structure holds considerable potential for extensive application to metal–dielectric grating sensors operating at visible and near-infrared frequencies.
230.3990 Micro-optical devices 250.5403 Plasmonics Excited-state population distributions of alkaline-earth metal in a hollow cathode lamp Download:764次
Download:764次
 Download:764次
Download:764次The intensities of fluorescence spectral lines of Ca atoms and Sr atoms in two different hollow cathode lamps (HCLs) are measured by element-balance-detection technology. In the wavelength range of 350–750 nm in the visible spectral region, using the individual strongest line (Ca 422.67 nm, Sr 460.73 nm) as the bench mark, the population ratios between the excited states of Ca atoms and Sr atoms are calculated by rate equations and the spontaneous transition probabilities. The HCLs with populations at excited states can be used to realize the frequency stabilization reference of the laser frequency standard.
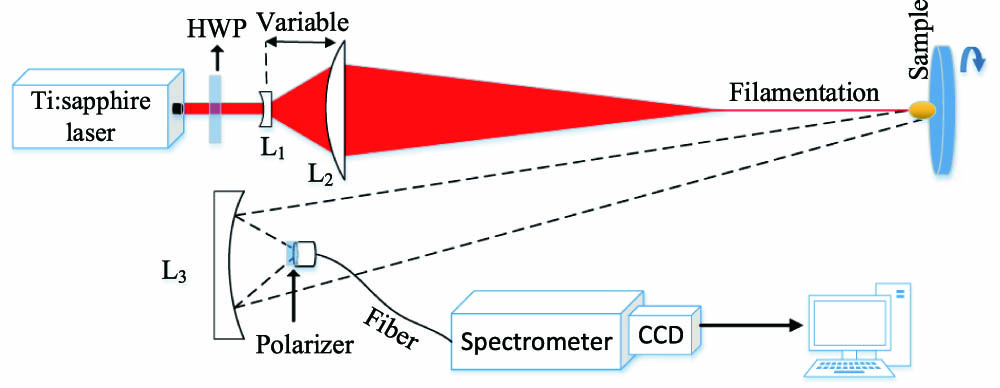
300.6210 Spectroscopy, atomic 020.1335 Atom optics We demonstrate a simple technique to filter out the continuum background in filament-induced remote breakdown spectroscopy. By inserting a polarizer before the detector, the continuum background was reduced by more than 42% in filament-induced breakdown spectroscopy at a distance of 3.8 m, while the fluorescence intensity of aluminum atomic lines remains constant. Supercontinuum through self-phase modulation during filamentation mainly contributes to the continuum background. The polarization-gated technique provides a simple way to remove the continuum background in filament-induced remote breakdown spectroscopy.
120.0280 Remote sensing and sensors 260.5430 Polarization 300.6365 Spectroscopy, laser induced breakdown 动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 | 经典导波与拓扑单向波间的高效转换动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 主编推荐 | 单片集成硅基灵活栅格MWSS为突破“容量危机”提供新策略动态信息 丨 2024-04-10
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 封面 |构造任意自相似类贝塞尔光束构造新方法动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 |声光调制的干涉增强效应,助力光学量子信息技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 基于时空耦合效应的超宽带频率转换技术激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦