2018, 16(8) Column
Chinese Optics Letters 第16卷 第8期
Experimental demonstration of underwater optical wireless power transfer using a laser diode Download:833次
Download:833次
 Download:833次
Download:833次We experimentally demonstrate an underwater optical wireless power transfer (OWPT) using a laser diode (LD) as a power transmitter. We investigate the characteristics of a solar cell and a photodiode (PD) as a power receiver. We optimize the LD, the PD, and the solar cell to achieve the maximum transfer efficiency. The maximum transfer efficiency of the back-to-back OWPT is measured as 4.3% with the PD receiver. Subsequently, we demonstrate the OWPT in tap and sea water. Our result shows an attenuation of 3 dB/m in sea water.
010.3310 Laser beam transmission Average transmittance of multi-Gaussian (flat-topped and annular) optical beams in an anisotropic turbulent ocean is examined analytically based on the extended Huygens–Fresnel principle. Transmittance variations depending on the link length, anisotropy factor, salinity and temperature contribution factor, source size, beam flatness order of flat-topped beam, Kolmogorov microscale length, rate of dissipation of turbulent kinetic energy, rate of dissipation of the mean squared temperature, and thickness of annular beam are examined. Results show that all these parameters have effects in various forms on the average transmittance in an anisotropic turbulent ocean. Hence, the performance of optical wireless communication systems can be improved by taking into account the variation of average transmittance versus the above parameters.
010.4455 Oceanic propagation 010.7060 Turbulence 010.4450 Oceanic optics 350.5500 Propagation Generation of X-ray vortex with ultra-long depth of focus using axial line-focused spiral zone plates Download:724次
Download:724次
 Download:724次
Download:724次We propose axial line-focused spiral zone plates (ALFSZPs) for generating tightly focused X-ray vortex beams with ultra-long depth of focus (DOF) along the propagation direction. In this typical design, compared with the conventional spiral zone plates (SZPs) under the same numerical aperture (NA), the DOF of ALFSZPs has been extended to an ultra-length by optimizing the corresponding parameters. Besides, it also exhibits lower side lobes and smaller dark cores in the whole focus volume. The diameters of dark cores increase as the topological charge value increases.
050.1220 Apertures 050.1940 Diffraction 050.1965 Diffractive lenses A scheme for beam combination at any angles employing a specially designed multilayer grating is proposed. Such a grating is able to convert noncoaxial laser beams to coaxial ones, and the combined beams are able to output along the normal line of the grating. The intensity and the phase structure of combined beams can also be controlled. The experiments are carried out by loading an encoded grating on a liquid-crystal spatial light modulator. The results agree well with the simulations. This method of beam combination with a multilayer grating serves to simplify the complexity of beam combination.
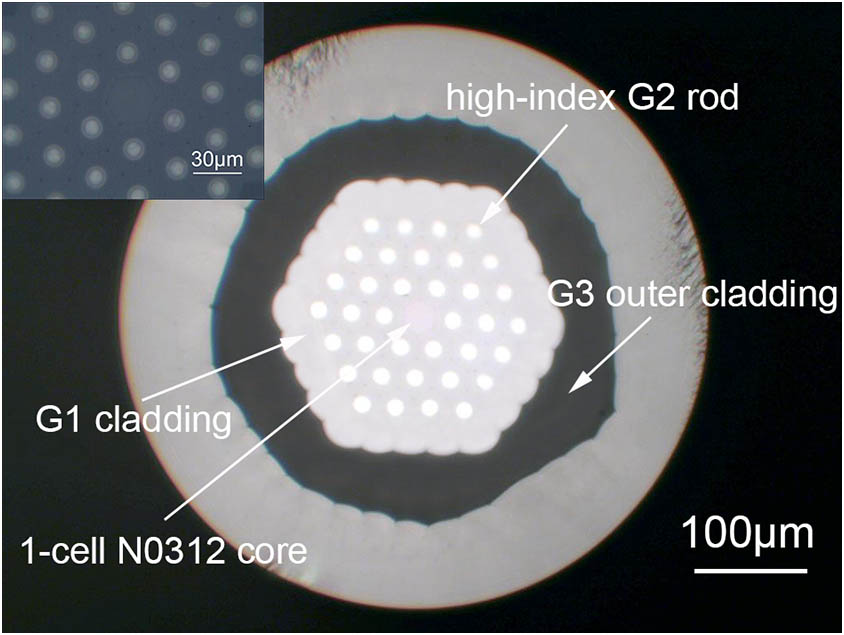
050.1950 Diffraction gratings 050.1960 Diffraction theory Large-mode-area neodymium-doped all-solid double-cladding silicate photonic bandgap fiber with an index step of ∼0.5% Download:680次
Download:680次
 Download:680次
Download:680次A large-mode-area neodymium-doped silicate photonic bandgap fiber was theoretically designed and experimentally demonstrated. The relative index step between the high-index rods and the background glass was ~0.5%, which is the lowest cladding index difference reported on rare-earth-doped all-solid photonic bandgap fibers to our knowledge. An output power of 3.6 W with a slope efficiency of 31% was obtained for a 100-cm-long fiber.
060.2280 Fiber design and fabrication 060.3510 Lasers, fiber 060.5295 Photonic crystal fibers Color representation method using RGB color binary-weighted computer-generated holograms Download:703次
Download:703次
 Download:703次
Download:703次We propose a method for color electroholography using a simple red–green–blue (RGB) gradation representation method without controlling the respective brightness of the reference RGB-colored lights. The proposed method uses RGB multiple bit planes comprising RGB binary-weighted computer-generated holograms with various light transmittances. The object points of a given three-dimensional (3D) object are assigned to RGB multiple bit planes according to their RGB gradation levels. The RGB multiple bit planes are sequentially displayed in a time-division-multiplexed manner. Consequently, the proposed method yields a color gradation representation of a reconstructed 3D object.
090.1705 Color holography 090.1760 Computer holography Noise reduction and signal to noise ratio improvement in magneto-optical polarization rotation measurement Download:586次
Download:586次
 Download:586次
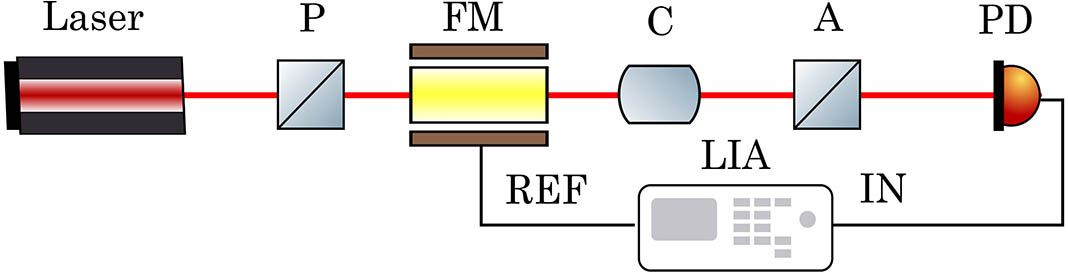
Download:586次The measurement of an extremely small magneto-optical polarization rotation angle with high sensitivity is integral to many scientific and technological applications. In this Letter, we have presented a technique based on Faraday modulation combined with the optical differential method to measure an extremely small polarization rotation angle with high sensitivity. The theoretical and experimental results show that common mode noise is reduced appreciably and signal to noise ratio is enhanced. The effectiveness of this technique has been demonstrated by measuring the Verdet constant of terbium gallium garnet glass and measuring the small polarization rotation angle. A sensitivity of enhancement of one order of magnitude has been achieved using differential detection based on Faraday modulation.
120.5410 Polarimetry 000.3110 Instruments, apparatus, and components common to the sciences 040.1880 Detection Experimental realization of a switchable filter based on a dynamically transformable array Download:561次
Download:561次
 Download:561次
Download:561次We introduce a geometrically reconfigurable metasurface whose artificial “atoms” will reorient within unit cells in response to a thermal stimulus in the microwave spectrum. It can alternate between two contrasting behaviors under different temperatures and serve as a switchable filter that allows the incident energy to be selectively transmitted or reflected with an excess of 10 dB isolation at certain frequencies for both polarizations. The experimental results are consistent with the theoretical simulations, verifying the availability of an innovative method for manipulating electromagnetic waves with the merits of higher controllability for dynamic behavior and greater flexibility in the design process.
120.2440 Filters 160.3918 Metamaterials 260.5740 Resonance 350.4010 Microwaves A model-based adaptive non-null interferometry (MANI) is proposed for steep optical freeform surfaces in situ testing. The deformable mirror (DM) affording the flexible compensation is monitored with the beam in the interferometer by a wavefront sensor. The residual wavefront aberration in the non-null interferogram is eliminated by the multi-configuration ray tracing algorithm based on the system model, especially the DM surface model. The final figure error can be extracted together with the surface misalignment aberration correction. Experiments proving the feasibility of the MANI are shown.
120.3180 Interferometry Microlasers based on high quality (Q ) whispering-gallery mode (WGM) resonance are promising low threshold laser sources for bio-sensing and imaging applications. In this Letter, dye-doped polymer microspheres were fabricated by a controlling emulsion solvent evaporation method. WGM lasing with low threshold and high Q factors was realized in an individual microsphere under femtosecond laser pumping. The slight change of environmental relative humidity (RH) can be monitored by measuring the shift of the lasing modes at the exposure of water molecules, which demonstrates the sensitivity is as high as 6 pm/RH%. The results would offer an insight into employing microlasers as sensors.
140.2020 Diode lasers 160.2540 Fluorescent and luminescent materials Few-layer graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) nanosheets were fabricated and utilized as a saturable absorber for mode-locking in an Er-doped fiber laser with net normal dispersion. The g-C3N4/polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) hybrid-film-based saturable absorber has a modulation depth of 4.01% and a saturation intensity of 7.5 MW/cm2. By integrating g-C3N4-PVA mode-locker into the laser cavity, a mode-locked operation could be obtained. The achieved mode-locking pulse centered at 1530.3 nm has a pulse width of 530 ps. Its repetition rate is 40.8 MHz, and the corresponding signal-to-noise ratio is about 55 dB.
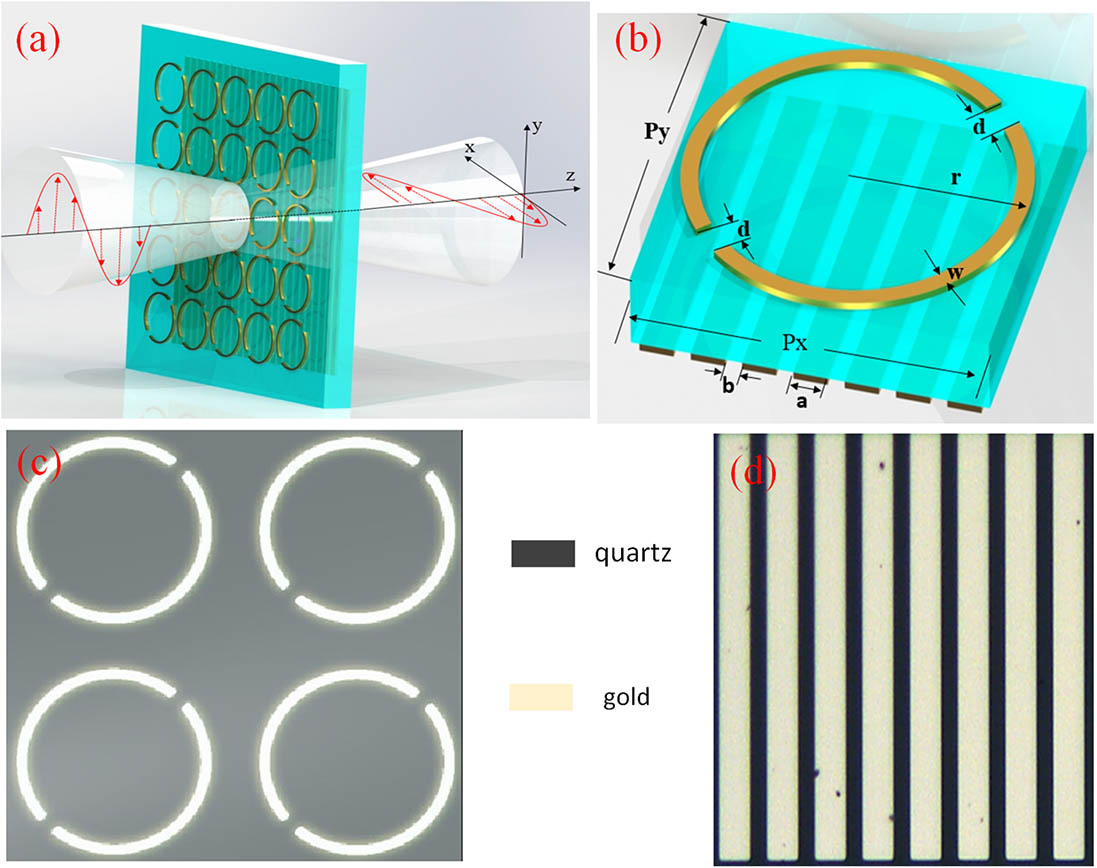
140.4050 Mode-locked lasers 160.4236 Nanomaterials 140.3500 Lasers, erbium Linear polarization conversion of transmitted terahertz wave with double-layer meta-grating surfaces Download:639次
Download:639次
 Download:639次
Download:639次In this Letter, we demonstrate a linear polarization conversion of transmitted terahertz wave with double-layer meta-grating surfaces, which integrated the frequency selectivity of a split ring resonator metasurface and the polarization selectivity of a metallic grating surface. Since the double-layer can reduce the loss, and the Fabry–Perot like resonant effect between the two layers can improve the conversion efficiency, this converter can rotate the incident y x 2 dB
160.3918 Metamaterials 050.2230 Fabry-Perot 3D depth-coded photoacoustic microscopy with a large field of view for human skin imaging Download:805次
Download:805次
 Download:805次
Download:805次Photoacoustic (PA) microscopy comes with high potential for human skin imaging, since it allows noninvasively high-resolution imaging of the natural hemoglobin at depths of several millimeters. Here, we developed a PA microscopy to achieve high-resolution, high-contrast, and large field of view imaging of skin. A three-dimensional (3D) depth-coding technology was used to encode the depth information in PA images, which is very intuitive for identifying the depth of blood vessels in a two-dimensional image, and the vascular structure can be analyzed at different depths. Imaging results demonstrate that the 3D depth-coded PA microscopy should be translated from the bench to the bedside.
170.5120 Photoacoustic imaging 170.0110 Imaging systems 170.3880 Medical and biological imaging A highly efficient laser system output at the H-β Fraunhofer line of 486.1 nm has been demonstrated. A high pulse energy single-frequency hybrid 1064 nm master oscillator power amplifier was frequency-tripled to achieve 355 nm laser pulses, which acted as the pump source of the beta barium borate nanosecond pulse optical parametric oscillator. With pump energy of 190 mJ, the laser system generated a maximum output of 62 mJ blue laser pulses at 486.1 nm, corresponding to conversion efficiency of 32.6%. The laser spectrum width was measured to be around 0.1 nm, being in conformity with the spectrum width of the solar Fraunhofer line.
190.4970 Parametric oscillators and amplifiers 190.2620 Harmonic generation and mixing 140.3538 Lasers, pulsed A full-transparent zone plate (FTZP), which can reuse the wave blocked in the focusing of the Fresnel zone plate (FZP), is proposed to improve the efficiency of terahertz (THz) focusing without aberration. We find that the substrate thickness of the FTZP has a great influence on the focusing intensity, which results from the Fabry–Perot effect. The focusing efficiency of FTZPs could be about twice as high as that of FZPs, but the widths of both focus spots are comparable with the wavelength. The experimental results are in good agreement with the simulation.
260.3090 Infrared, far We demonstrate the generation of non-classical photon pairs in a warm Rb 87 23 ± 3
270.5290 Photon statistics We propose a feasible scheme of generating multipartite entanglement with the dipole induced transparency (DIT) effect in indirectly coupled dipole-microcavity systems. It is shown that the transmission spectrum is closely related with the interference of dipole-microcavity systems, and we can generate different classes of multipartite entanglement, e.g., the Greenberger–Horne–Zeilinger state, the W state, and the Dicke state, of the dipole emitters just by choosing an appropriate frequency of the incident photon. Benefiting from the DIT effect, the schemes may work in the bad or low-Q cavity regime only if the large Purcell factor of the dipole-microcavity system is fulfilled, and they are also insensitive to experimental noise, which may be feasible with present accessible technology.
270.5580 Quantum electrodynamics 动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-10
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 封面 |构造任意自相似类贝塞尔光束构造新方法动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 |声光调制的干涉增强效应,助力光学量子信息技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 基于时空耦合效应的超宽带频率转换技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 21, Iss. 11): 综述:太赫兹偏振光谱和手性光谱传感检测技术新应用动态信息 丨 2024-03-21
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 全光学的相位目标边缘提取,助力高分辨生物医学成像激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦