2019, 17(8) Column
Chinese Optics Letters 第17卷 第8期
Optimization of temperature characteristics of a transportable 87Rb atomic fountain clock Download:973次
Download:973次
 Download:973次
Download:973次A high-performance transportable fountain clock is attractive for use in laboratories with high-precision time-frequency measurement requirements. This Letter reports the improvement of the stability of a transportable rubidium-87 fountain clock because of an optimization of temperature characteristics. This clock integrates its physical packaging, optical benches, microwave frequency synthesizers, and electronic controls onto an easily movable wheeled plate. Two optical benches with a high-vibration resistance are realized in this work. No additional adjustment is required after moving them several times. The Allan deviation of the fountain clock frequency was measured by comparing it with that of the hydrogen maser. The fountain clock got a short-term stability of
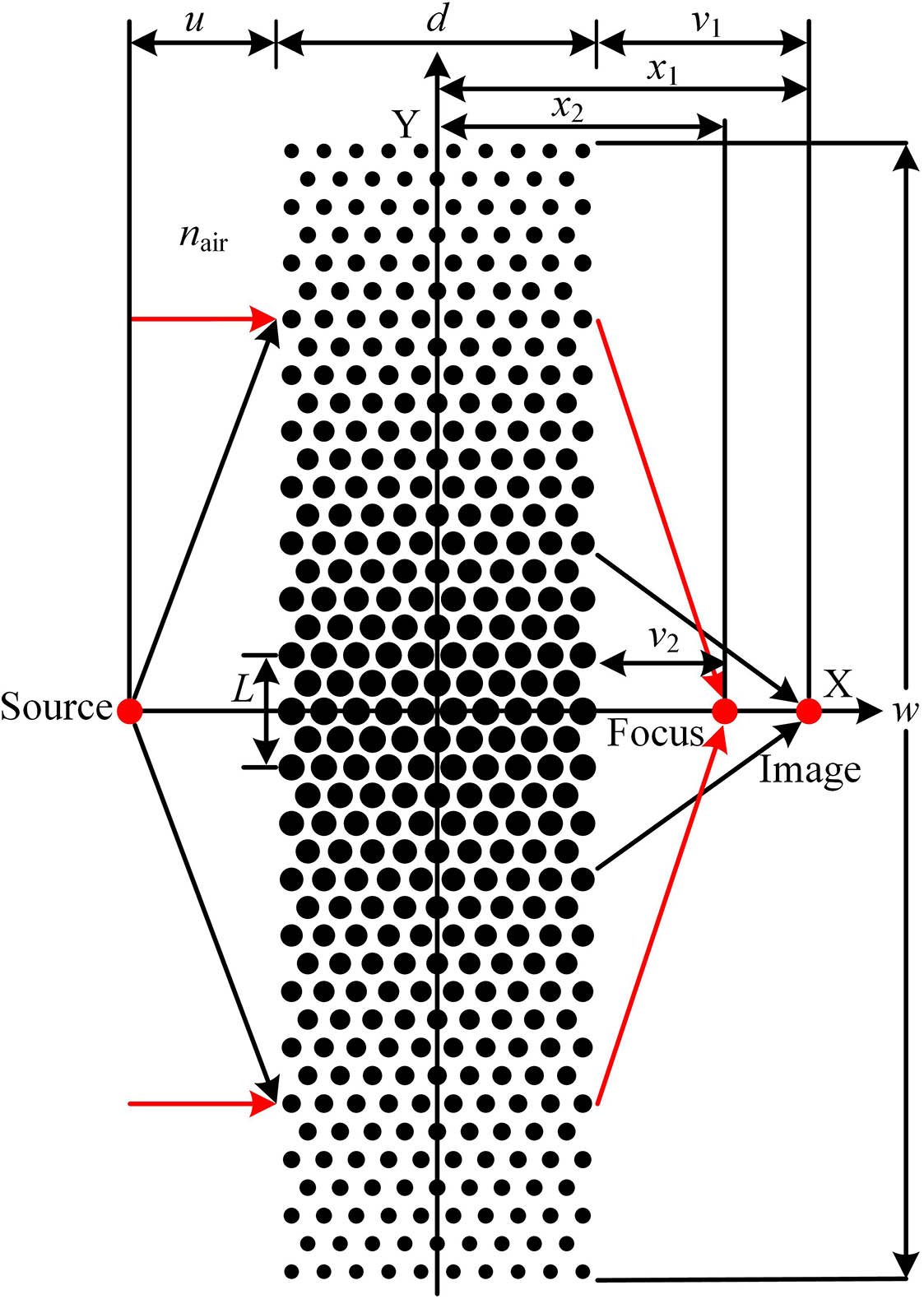
020.3320 Laser cooling 120.3940 Metrology 270.2500 Fluctuations, relaxations, and noise 270.5570 Quantum detectors Multi-band imaging and focusing of photonic crystal flat lens with scatterer-size gradient Download:903次
Download:903次
 Download:903次
Download:903次In this Letter, a photonic crystal (PC) flat lens with a scatterer-size gradient is proposed, which simultaneously achieves imaging of the point source and sub-wavelength focusing of the plane wave in the first, second, and fifth bands. The imaging of the point source breaks through the diffraction limit in the second and fifth bands. The PC flat lens with the scatterer-size gradient is expected to be used in a new multifunctional optical imaging and focusing device, which improves the application potential of a PC flat lens.
050.1965 Diffractive lenses 050.5298 Photonic crystals 050.6624 Subwavelength structures Vernier effect of fiber interferometer based on cascaded PANDA polarization maintaining fiber Download:702次
Download:702次
 Download:702次
Download:702次This Letter shows the Vernier effect based on two segments of PANDA polarization maintaining fiber (PMF), whose lengths are 28 and 23 cm, respectively. The two PMFs are spliced together, and the angle between the fast axes is set to 45°. This cascaded PMF is inserted in a Sagnac loop to form an interferometer that can generate the Vernier effect. The spectrum consists of finesse fringe and envelope and realizes simultaneous measurement of strain and temperature. The envelope can provide strain and temperature sensitivities of 58.0 pm/με and 1.05 nm/°C. The finesse fringe provides sensitivities of 5.9 pm/με and 1.36 nm/°C.
060.2370 Fiber optics sensors 060.2420 Fibers, polarization-maintaining 120.3180 Interferometry Demonstration of high-dimensional free-space data coding/decoding through multi-ring optical vortices Download:733次
Download:733次
 Download:733次
Download:733次Multi-ring optical vortices are a kind of structured beams that carry orbital angular momentum (OAM) and have concentrical doughnut intensity distributions. In this Letter, we present both theoretically and experimentally a scheme that employs the dimensions of both the OAM states and radial index of multi-ring optical vortices simultaneously to accomplish high-dimensional free-space data coding/decoding transmissions. Such a scheme can further improve the coding efficiency when limited OAM states are available. In the proof-of-concept experiment, 64-ary coding/decoding employing 16 OAM states and four radial indices are present. Also, the coding/decoding performance when facing various atmosphere turbulences is evaluated. Furthermore, a 64 × 64 gray image (totally, 32,768 bits) is also transmitted through multi-ring optical vortices coding in free-space successfully, showing good transmission performance.
060.2605 Free-space optical communication 050.4865 Optical vortices 050.1950 Diffraction gratings A passively Q -switched erbium-doped fiber (EDF) laser is proposed and demonstrated utilizing a zirconium disulfide (ZrS2)-based saturable absorber (SA). ZrS2 nanosheets are prepared, whose modulation depth, saturation intensity, and nonsaturable absorbance are measured to be 14.7%, 0.34 MW/cm2, and 17.4%, respectively. Then, a Q -switched EDF laser is implemented by the ZrS2-SA. The pulse repetition rate varies from 40.65 to 87.1 kHz when the pump power changes from 55 to 345 mW. The shortest pulse width is 1.49 μs with pulse energy of 33.5 nJ. As far as we know, this is the shortest pulse width obtained by a ZrS2-SA so far.
060.2410 Fibers, erbium 060.3510 Lasers, fiber 160.4330 Nonlinear optical materials 320.7090 Ultrafast lasers We experimentally demonstrate a 10 Gb/s free-space optical wiretap channel based on a spatial-diversity scheme and optical code division multiple access. In weak and middle turbulence cases, the bit error rate of a legitimate user can be decreased, and physical layer security can be simultaneously enhanced.
060.2605 Free-space optical communication 060.4785 Optical security and encryption We report on a data center network (DCN) architecture based on hybrid optical circuit switching (OCS) and optical burst switching (OBS) interconnect for dynamic DCN connectivity provisioning. With the combination of the centralized and distributed control of the software-defined optical networks, the proposed interconnect can achieve unprecedented flexibility in dealing with both mice and elephant flow in the DCN. Numerical simulation is employed to investigate the performance of the proposed architecture. The results show that the OBS module has preferable performance in dealing with a larger burst packet, and the throughput is constrained by the capacity of the server random access memory module.
060.4510 Optical communications 060.6719 Switching, packet 060.6718 Switching, circuit Non-collinear phase-matching sum-frequency generation based on boundary total reflection in bulk KDP Download:832次
Download:832次
 Download:832次
Download:832次Collinear phase-matching of sum-frequency generation (SFG) has been studied thoroughly previously, while non-collinear schemes are sometimes more flexible in application. However, this phase-matching type is more difficult to meet and control. We employ a convenient method to obtain harmonic generation in bulk potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KDP), using an incident wave vector and a reflected wave vector to create a triangle phase-matching relationship. With a simple, flexible set-up, we can observe 351 nm SFG, and the conversion efficiency is up to ~3.6% per reflection. Furthermore, we believe this approach has potential application value and improvement space.
140.3610 Lasers, ultraviolet 190.2620 Harmonic generation and mixing 190.4400 Nonlinear optics, materials Spatio-temporal coupling characteristics of ultrafast laser pulses are quantitatively tailored. An asymmetric microstructure is induced in the focal volume when the laser scans perpendicularly to the direction of the spatial chirp in fused silica. The tilted direction reverses when adding a Dove prism into the light path. The sign of the pulse front tilt can be turned from positive to negative by changing the group delay dispersion by steps. We reveal that the tilted direction of a microstructure depends on spatial chirp, and the interplay between spatio-temporal chirp leads to the change of tilted angles.
140.3390 Laser materials processing 220.4000 Microstructure fabrication 320.5540 Pulse shaping Excess frequency noise induced by mechanical vibration is the dominant noise source at low Fourier frequencies in fiber-delay-line stabilized lasers. To resolve this problem, a double-winding fiber spool is designed and implemented that has ultralow acceleration sensitivity in all spatial directions. By carefully choosing the optimal geometry parameters of the fiber spool, we achieve acceleration sensitivity of 8 × 10 11/g and 3 × 10 11/g (g denotes the gravitational acceleration) in axial and radial directions, respectively.
140.3425 Laser stabilization 120.7280 Vibration analysis 060.2310 Fiber optics We demonstrate a Fe:ZnSe laser gain-switched by a ZnGeP2 optical parametric oscillator (OPO) under the pulse repetition frequency of 1 kHz at room temperature. The 2.9 μm signal light of the OPO is employed as the pump for the Fe:ZnSe laser. The maximum output power of the Fe:ZnSe laser is 58 mW with the pulse duration of 2.7 ns under the incident pump power of 280 mW, corresponding to a peak pulse power of 21.5 kW and an optical-to-optical efficiency of 20.7%. The spectrum of the Fe:ZnSe laser has a range of 4030.2–4593.6 nm with a dip at 4187.1–4340.4 nm due to the absorption of CO2.
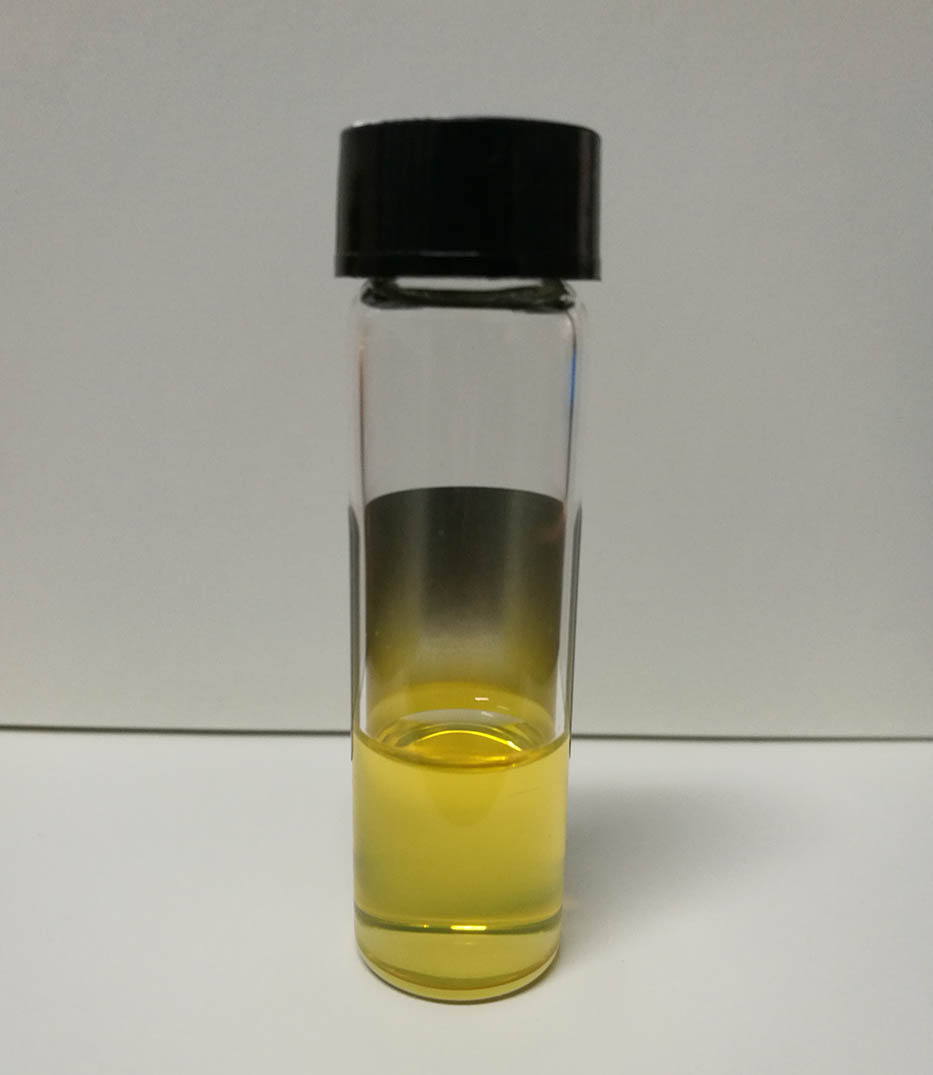
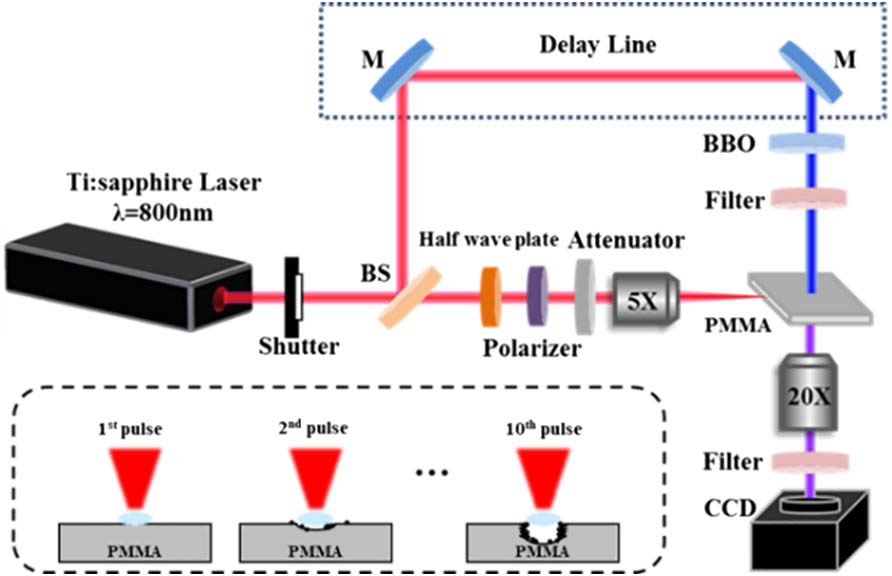
140.3070 Infrared and far-infrared lasers 140.3295 Laser beam characterization Cylindrical shockwaves inside polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) generated simultaneously with two hemispherical shockwaves induced by a femtosecond Gaussian beam laser were investigated using an ultrafast pump–probe imaging technique. The evolutions of these three shockwaves with probe delay and incident pulse number have been systematically analyzed. The plasma intensity and filament length in the center of cylindrical shockwave both decayed with pulse number. Moreover, the self-focused filament moved downstream towards the output surface with an increased pulse number. The experimental results and mechanism illustrated that energy deposition was suppressed by a degraded nonlinear effect due to a pre-ablated structure in multi-pulse irradiation.
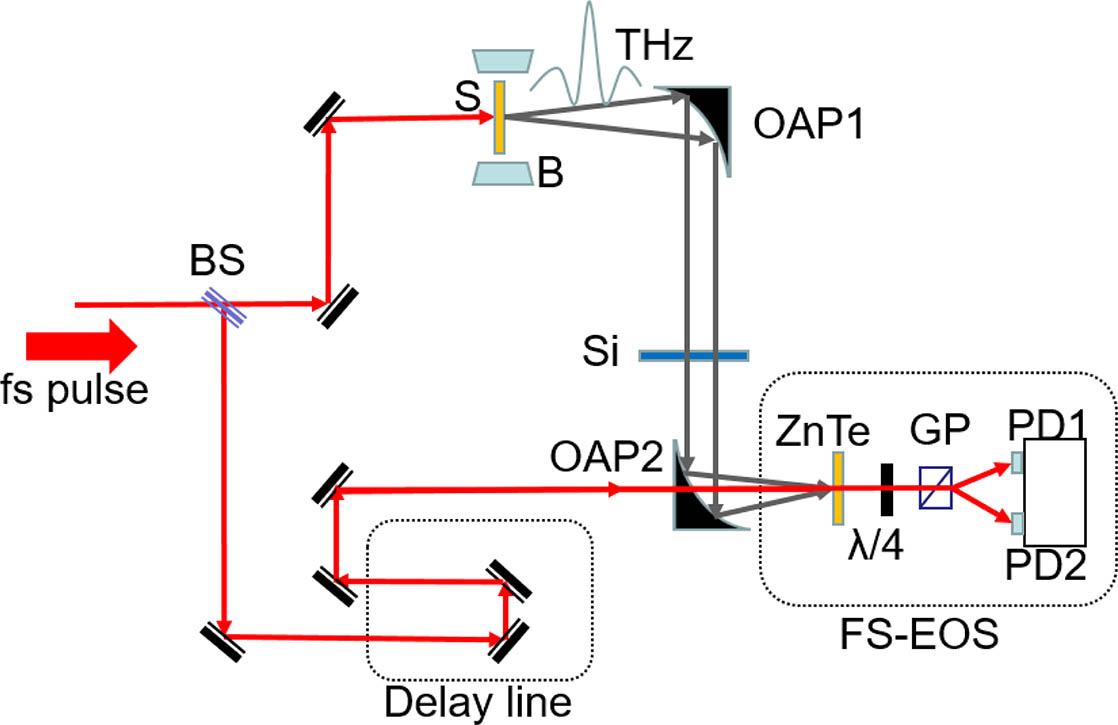
140.7090 Ultrafast lasers 320.7120 Ultrafast phenomena 350.5400 Plasmas 350.3390 Laser materials processing Comparative study of coherent terahertz emission from Fe/Pt ferromagnetic heterostructures Download:877次
Download:877次
 Download:877次
Download:877次The ultrafast spin dynamic of in-plane magnetized Fe/Pt films was investigated by terahertz emission spectroscopy. The amplitude of the emitted terahertz wave is proportional to the intensity of the exciting laser beams. Both the amplitude and polarity of the terahertz wave can be adjusted by modifying the external magnetic field. The dependency of the amplitude on external magnetic fields is coincident to the hysteresis loops of the sample. Also, the polarity of the terahertz wave is reversed, as the magnetization orientation is reversed. The super-diffusive transient spin current with an inverse spin Hall effect is attributed to the main mechanism of the terahertz emission.
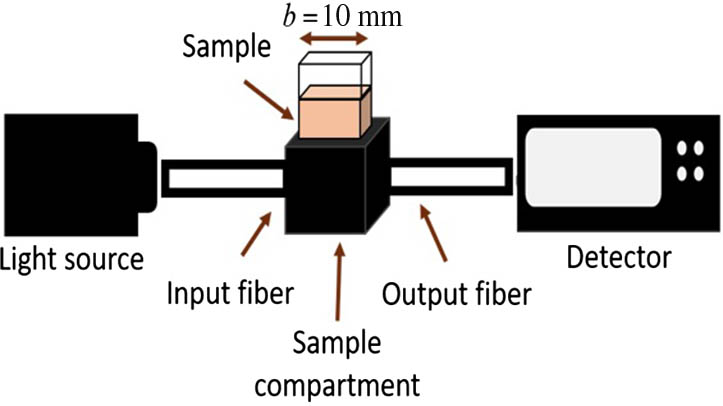
160.3820 Magneto-optical materials 310.6845 Thin film devices and applications 320.2250 Femtosecond phenomena A spectrophotometer with an LED as the light source for uric acid detection is proposed in this work. The mechanism of uric acid detection is based on energy absorbed by sodium urate, which is a chemical product of uric acid and sodium hydroxide solution. For the performance validation, comparison between the spectrophotometer with an LED and halogen lamp is carried out. Measurement results suggest that the spectrophotometer system with LED light has better sensitivity than that with halogen light. At a 460 nm wavelength, the sensitivity for the spectrophotometer with an LED is 0.0046 dL/mg, which is 73% higher than that with halogen light that records 0.0012 dL/mg. This enhanced sensitivity is attributed to the higher luminous efficacy of the LED light beam. As a result, a larger amount of flux interacts with the sample, leading to the sensitivity enhancement. The spectrophotometer with an LED is also applied for the detection of uric acid in a real human urine sample. Based on the experimental data at a 460 nm wavelength, the method manages to achieve the sensitivity of 0.0016 dL/mg, accuracy of 96.01%, limit of detection of 4.79 mg/dL, and limit of quantification of 14.52 mg/dL. These findings show that the use of LED as the input light source is promising for the spectrophotometer.
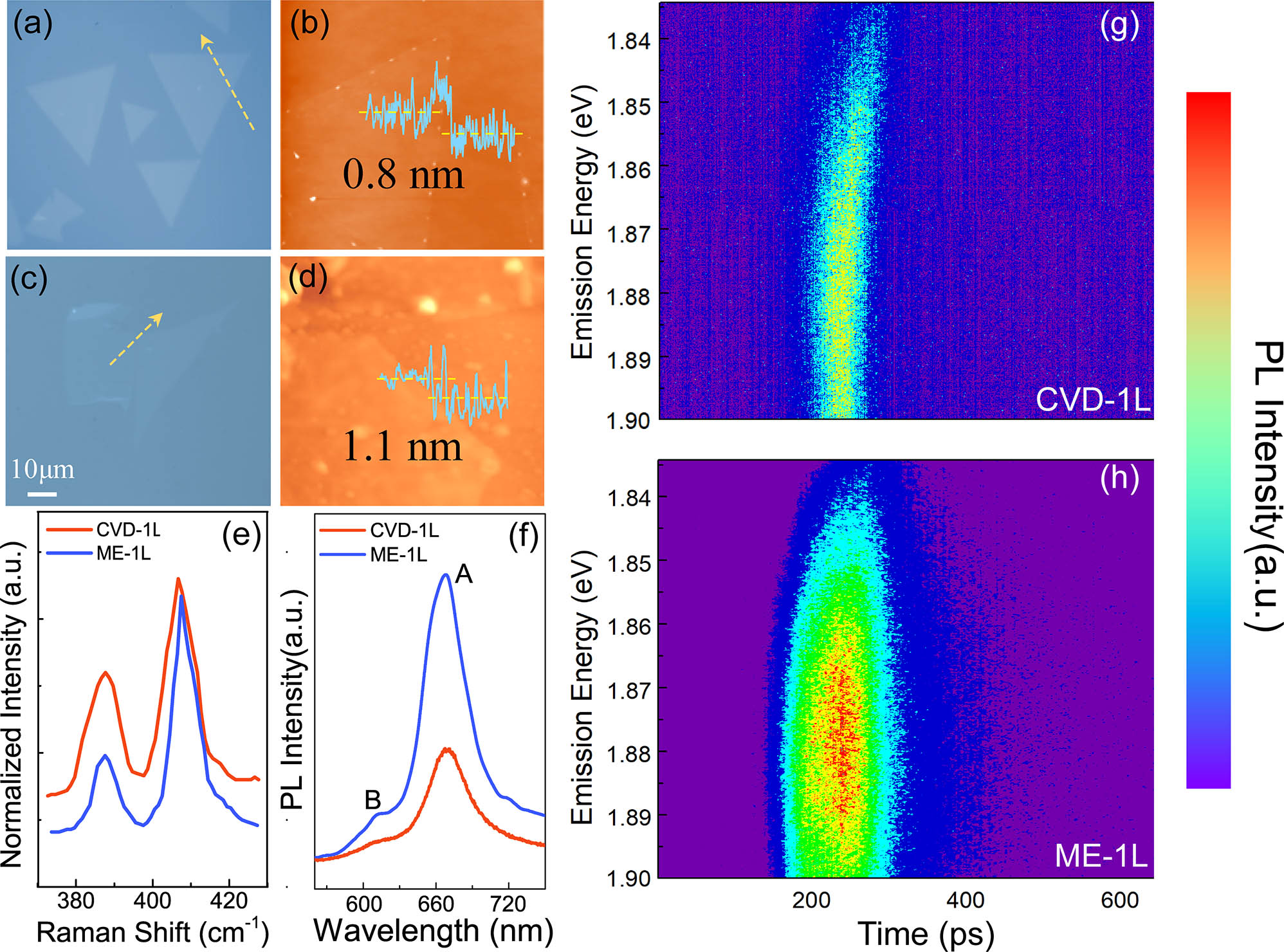
170.6280 Spectroscopy, fluorescence and luminescence 300.6190 Spectrometers Two-photon absorption towards pulse modulation in mechanically exfoliated and CVD monolayer cascaded MoS2 structures Download:786次
Download:786次
 Download:786次
Download:786次Mechanical exfoliation (ME) and chemical vapor deposition (CVD) MoS2 monolayers have been extensively studied, but the large differences of nonlinear optical performance between them have never been clarified. Here, we prepared MoS2 monolayers using ME and CVD methods and investigated the two-photon absorption (TPA) response and its saturation. We found that the TPA coefficient of the ME monolayer was about (1.88 ± 0.21) × 103 cm/GW, nearly two times that of the CVD one at (1.04 ± 0.15) × 103 cm/GW. Furthermore, we simulated and compared the TPA-induced optical pulse modulation in multilayer cascaded structures, which is instructive and meaningful for the design of optical devices such as a beam shaper and optical limiter.
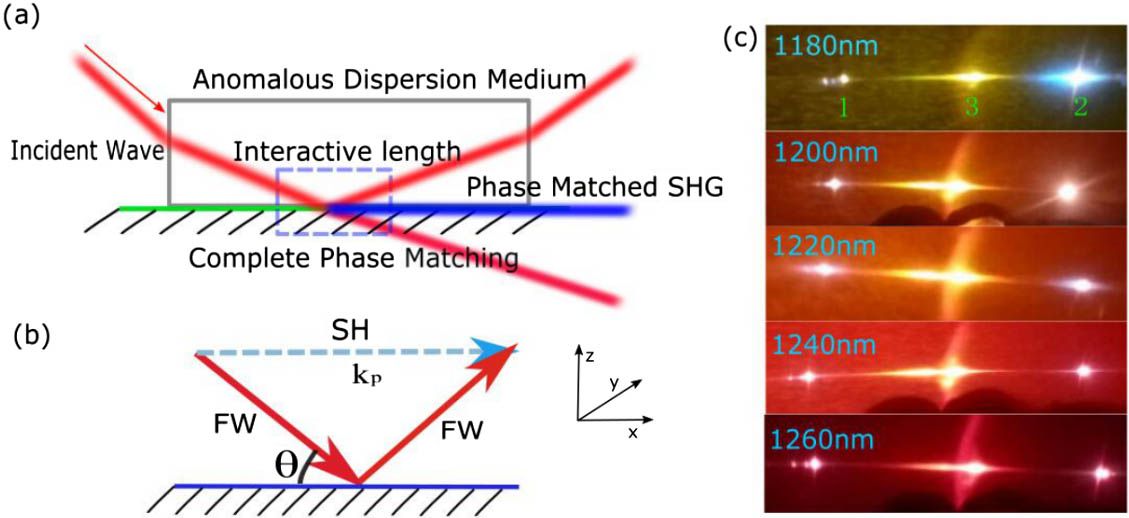
190.4400 Nonlinear optics, materials 160.4236 Nanomaterials 190.5970 Semiconductor nonlinear optics including MQW 020.4180 Multiphoton processes Interactive length of fundamental wave and second harmonic generated on the surface of anomalous dispersion medium Download:580次
Download:580次
 Download:580次
Download:580次In this Letter, a new method is presented to calculate the interactive length between the fundamental wave and second harmonic generation (SHG) for the configuration of total internal reflection on the inner surface of a nonlinear crystal. Three independent experiments are designed to measure the bandwidths of this second harmonic wave. The theoretical expression of the intensity of SHG is obtained through a nonlinear coupled wave equation. The interactive length of this phase-matched SHG can be calculated mathematically by utilizing the measured bandwidths and the intensity equation. There is no existing method to obtain the interactive length either from theoretical calculations or by experimental measurement. This method can be applied to estimate the extremely short interactive volume in nonlinear processes.
190.4410 Nonlinear optics, parametric processes 190.2620 Harmonic generation and mixing The diffraction of a dielectric microline pair is optimized by numerical simulations to generate an efficient focusing pattern with a micron-scale footprint. Microlines separated by 1.12 μm are fabricated by two-photon polymerization on a glass substrate, and their diffraction pattern is characterized by three-dimensional wide-field transmission microscopy. A line pair, having a width W = 0.40 μm H = 0.80 μm
220.3630 Lenses 220.4000 Microstructure fabrication Angle tolerant transmissive subtractive color filters incorporating a metasurface exploiting hydrogenated amorphous silicon nanopillars (NPs) on a glass substrate were proposed and demonstrated. The achieved transmission efficiency ranged from 75% to 95% at off-resonance wavelengths. For an NP resonator, electric and magnetic-field distributions in conjunction with absorption cross-sections were investigated to confirm a resonant transmission dip, which is primarily governed by the absorption resulting from simultaneous excitation of magnetic and electric dipoles via Mie scattering. The proposed devices exhibit higher angular tolerance and lower crosstalk for the absorption spectra and, therefore, are applicable with photodetectors, image sensors, and imaging/display devices.
230.7408 Wavelength filtering devices 230.0040 Detectors Design of an all-optical logic sequence generator based on polarization holographic gratings Download:728次
Download:728次
 Download:728次
Download:728次In this Letter, an all-optical logic sequence generator based on two different polarization holographic gratings has been proposed and demonstrated, which has one input port and four output ports. The polarization state of input light signal determines logic output signals. It can produce four kinds of logic sequence output signals: 1000, 0100, 0010, and 0001, corresponding to the input light signal of four different polarization states: the p-linear, s-linear, left-handed circular, and right-handed circular. The two polarization gratings have been fabricated, and the working principle of the logic sequence generator has been proved by diffraction pattern analysis of polarization gratings.
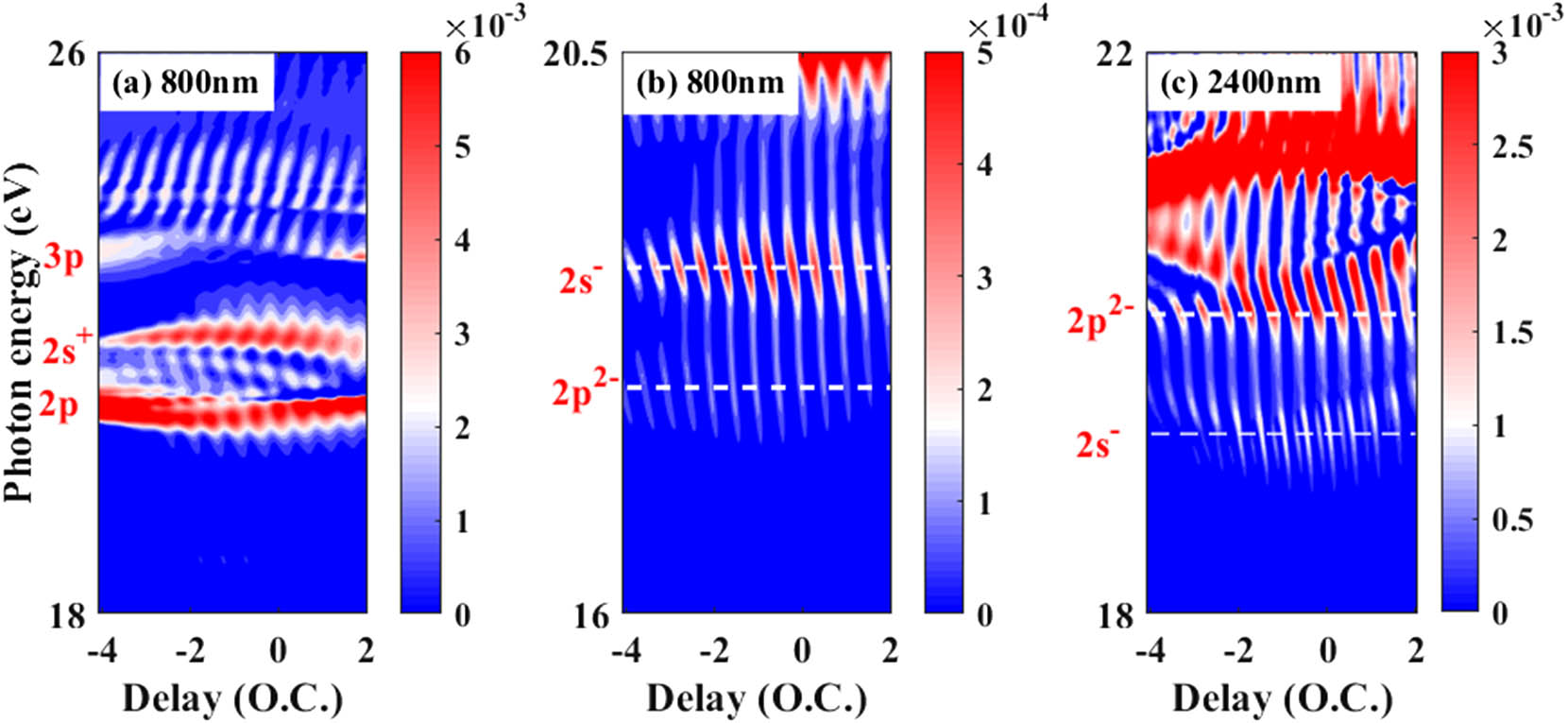
230.1150 All-optical devices 230.3750 Optical logic devices 050.2770 Gratings Multiple-fringe structure of attosecond transient absorption spectrum driven by mid-infrared laser Download:878次
Download:878次
 Download:878次
Download:878次We theoretically investigate the delay-dependent attosecond transient absorption spectra in the helium atom dressed by an infrared laser pulse in the wavelength range of 800–2400 nm. By numerically solving the three-dimensional time-dependent Schr dinger equation, we find that the absorption spectrogram exhibits a multiple-fringe structure for using the mid-infrared dressing pulse. The quantitative calculation of the transition matrix between different Floquet states provides direct evidence on the origin of the multiple-fringe structure. Our result shows that the wavelength of the dressing pulse is an important parameter and the unique feature of attosecond transient absorption spectroscopy can be induced in the mid-infrared regime.
260.3090 Infrared, far 300.1030 Absorption 340.7480 X-rays, soft x-rays, extreme ultraviolet (EUV) 动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 | 经典导波与拓扑单向波间的高效转换动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 主编推荐 | 单片集成硅基灵活栅格MWSS为突破“容量危机”提供新策略动态信息 丨 2024-04-10
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 封面 |构造任意自相似类贝塞尔光束构造新方法动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 |声光调制的干涉增强效应,助力光学量子信息技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 基于时空耦合效应的超宽带频率转换技术激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦