2020, 18(8) Column
Chinese Optics Letters 第18卷 第8期
Soft-matter photonics (soft mattonics) is an emerging and active area that has attracted widespread attention in recent years. Compared with solid materials, soft matters exhibit inherent advantages such as excellent adjustability, high flexibility, scalable size, ease of manufacture, and environmental adaptation. This special issue focuses on various interesting optical properties and fantastic photonic applications of soft matters including different liquid crystal (LC) phases, stimuli-responsive polymers, and even silks. This special issue aims to present the impressive progresses on soft mattonics and promote developments of related applications.
Diffractive optical elements attract a considerable amount of attention, mainly due to their potential applications in imaging coding, optical sensing, etc. Application of ferroelectric liquid crystals (FLCs) with photo-alignment technology in diffractive optical elements results in a high efficiency and a fast response time. In this study we demonstrate a circular Dammann grating (CDG) with a diffraction efficiency of 84.5%. The achieved response time of 64 μs is approximately two orders of magnitude faster than the existing response time of nematic liquid crystal devices. By applying a low electric field (V = 6 V) to the FLC CDG, it is switched between the eight-order diffractive state and the transmissive diffraction-free state.
ferroelectric liquid crystals photo-alignment fast switching diffractive optical elements Photopatterned liquid crystal mediated terahertz Bessel vortex beam generator [Invited] Download:754次
Download:754次
 Download:754次
Download:754次In this Letter, we propose that the photopatterned liquid crystal (LC) can act as a broadband and efficient terahertz (THz) Bessel vortex beam (BVB) generator. The mechanism lies in the frequency-independent geometric phase modulation induced by the spatially variant LC directors. By adopting large birefringence LCs and optimizing the cell gap, the maximized mode conversion efficiency can be continuously adjusted in broadband. Furthermore, the LC patterns can be designed and fabricated at will, which enables the THz BVBs to carry various topological charges. Such a THz LC BVB generator may facilitate the advanced THz imaging and communication apparatus.
terahertz liquid crystal Bessel vortex beam photopatterning The growing demand of sustainable and biocompatible optical devices is stimulating the development of naturally derived biomaterials for optics and photonics. As a versatile biomaterial, silk provides excellent material characteristics that are favorable towards the generation of advanced optical systems. This review examines the use of silk as a material platform in optical applications. Recent advances in silk-based optical devices and multifunctional devices are summarized. The challenges and directions in further designing and fabricating silk optics are also discussed. We envision that silk will play a pivotal role in the future exploitation of sustainable, intelligent, wearable/implantable, and multifunctional optical devices.
silk biomaterials optical devices multifunctional devices The dynamic manipulation of the helicity in a cholesteric helical superstructure could enable precise control over its physical and chemical properties, thus opening numerous possibilities for exploring multifunctional devices. When cholesteric material satisfies the sufficiently small bending elastic effect, an electrically induced deformation named the cholesteric heliconical superstructure is formed. Through theoretical and numerical analysis, we systematically studied the tunable helicity of the heliconical superstructure, including the evolution of the corresponding oblique angle and pitch length. To further confirm the optical properties, Berreman’s 4 × 4 matrix method was employed to numerically analyze the corresponding structure reflection under the dual stimuli of chirality and electric field.
cholesteric liquid crystal heliconical superstructure tunable reflection band electro-optical materials The method for batch continuous production of polymerized cholesteric liquid crystal (PCLC) microdisks based on centrifugal microfluidics was proposed. The prototype centrifugal microfluidic chip was fabricated by the wet-etching technique with a series of ladder-like concentric ring channels whose depths decrease radially. Two types of dye-doped PCLC microdisks with different doping procedures were generated by this method, the tunable lasing properties were characterized, and corresponding potential applications in a micro-cavity laser and optical barcode were demonstrated. The method is also applicable to a broad range of other polymerized materials.
centrifugal microfluidics PCLC microdisks laser emission optical barcode We report holographic fabrication of nanoporous distributed Bragg reflector (DBR) films with periodic nanoscale porosity via a single-prism conuration. The nanoporous DBR films result from the phase separation in a material recipe, which consists of a polymerizable acrylate monomer and nonreactive volatile solvent. By changing the interfering angle of two laser beams, we achieve the nanoporous DBR films with highly reflective red, green, and blue colors. The reflection band of the nanoporous DBR films can be tuned by further filling different liquids into the pores inside the films, resulting in the color change accordingly. Experimental results show that such kinds of nanoporous DBR films could be potentially useful for many applications, such as color filters and refractive index sensors.
distributed Bragg reflector nanoporous reflection grating holographic fabrication phase separation refractive index sensing The generation of an autofocusing circular Airy beam (CAB) is realized via a liquid crystal (LC) geometric phase plate with a simple configuration. The fabrication of the LC plate is based on the photoalignment technology and dynamic exposure skill. A focal length of 74 cm is obtained, and the propagation dynamics are consistent with the simulations. Besides, a defocusing CAB is also generated, and the switch between the autofocusing and defocusing CABs can be achieved by controlling the input polarization state. This work provides a convenient and flexible approach to acquire CABs, which will promote the CAB-related applications and researches.
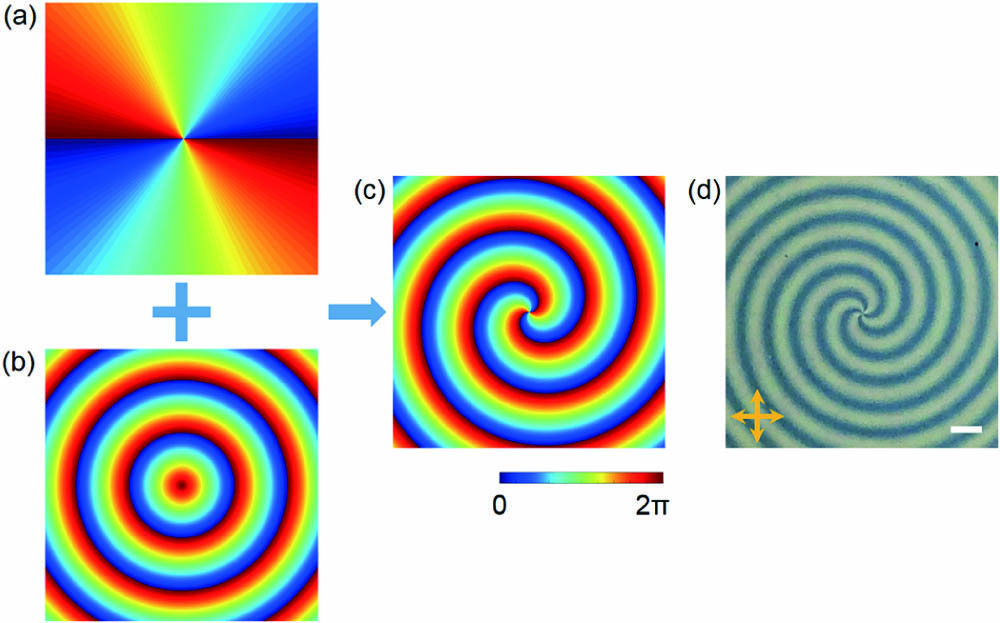
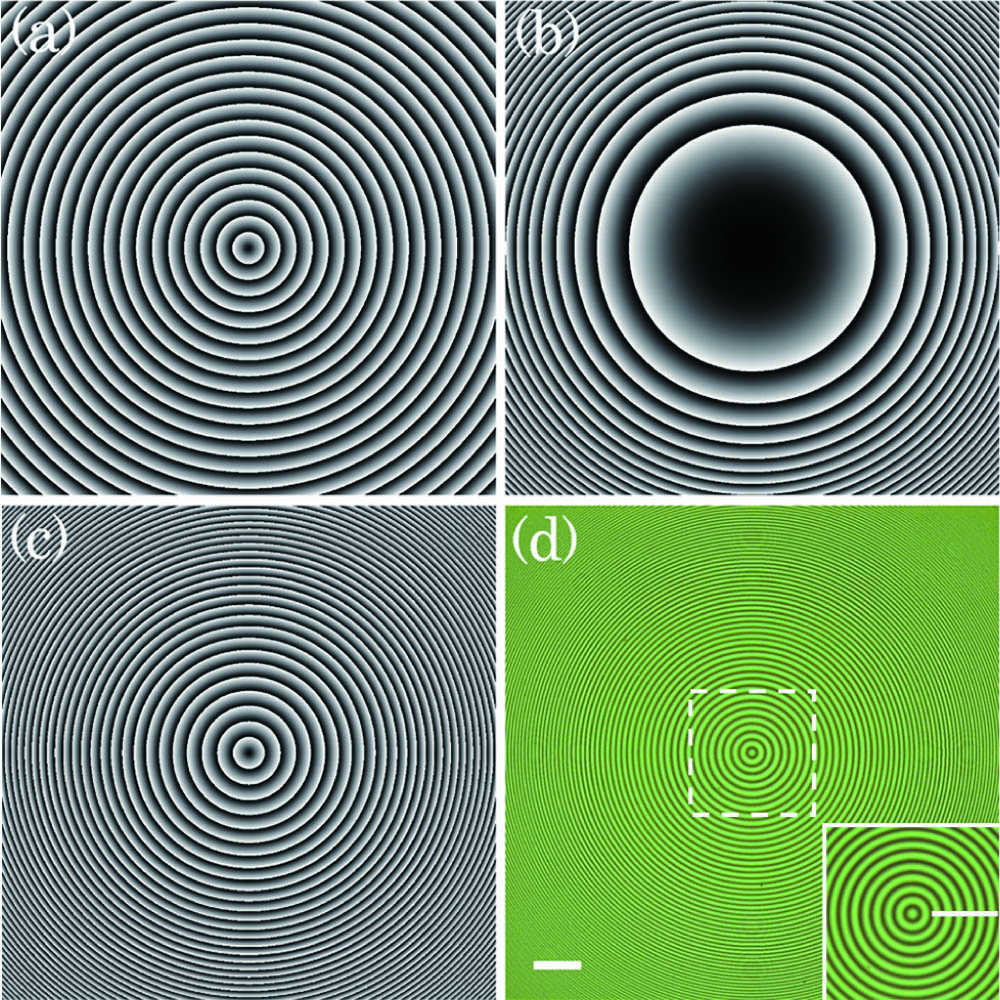
circular Airy beam autofocusing liquid crystal photoalignment technique The nitrogen vacancy (NV) center in diamond has been well applied in quantum sensing of electromagnetic field and temperature, where the sensitivity can be enhanced by the number of NV centers. Here, we used electron beam irradiation to increase the generation rate of NV centers by nearly 22 times. We systematically studied the optical and electronic properties of the NV center as a function of an electron irradiation dose, where the detection sensitivity of magnetic fields was improved. With such samples with dense NV centers, a sub-pico-Tesla sensitivity in magnetic fields detection can be achieved with optimal controls and detections.
quantum sensing nitrogen vacancy center generation electron irradiation Self-copy-shift-based differential phase extracting method for fiber distributed acoustic sensing Download:925次
Download:925次
 Download:925次
Download:925次A differential phase extracting method based on self-copy-shift for distributed acoustic sensing is proposed. Heterodyne and optical hybrids are used to realize high signal-to-noise ratio in-phase and quadrature-phase (IQ) signal measurement. The measured signals are self-copied and shifted for certain data points, and then they are digitally mixed with the original signals to construct the differential phase. The four produced signals are then combined to carry out IQ demodulation. An experiment with strain having an amplitude modulation waveform is carried out. The results showed that waveform information can be recovered well, and the signal-to-noise ratio achieves 32.8 dB.
optical fiber sensing phase extraction coherent OTDR distributed sensing Hybrid calibration method of a wide-view-angle Mueller polarimeter for hyper-numerical-aperture imaging systems Download:872次
Download:872次
 Download:872次
Download:872次Polarization aberration of hyper-numerical-aperture projection optics should be measured accurately in order to control it exactly and ensure favorable imaging performance. A hybrid calibration method combining the Fourier analysis method and the eigenvalue calibration method is proposed. A wide-view-angle Mueller polarimeter (WMP) is exemplified to demonstrate the capability of the proposed calibration method, which can calibrate the polarimeter and determine the error budget of polarizing elements in the polarimeter. In addition, an experimental setup and a WMP are developed in-house to implement the hybrid calibration method.
polarimetric imaging measurement calibration We investigate femtosecond laser trapping dynamics of two-photon absorbing hollow-core nanoparticles with different volume fractions and two-photon absorption (TPA) coefficients. Numerical simulations show that the hollow-core particles with low and high-volume fractions can easily be trapped and bounced by the tightly focused Gaussian laser pulses, respectively. Further studies show that the hollow-core particles with and without TPA can be identified, because the TPA effect enhances the radiation force, and subsequently the longitudinal force destabilizes the trap by pushing the particle away from the focal point. The results may find direct applications in particle sorting and characterizing the TPA coefficient of single nanoparticles.
laser trapping multiphoton processes ultrafast nonlinear optics Chromatic dispersion manipulation based on metasurface devices in the mid-infrared region Download:1014次
Download:1014次
 Download:1014次
Download:1014次The chromatic aberration of metasurfaces limits their application. How to cancel or utilize the large chromatic dispersion of metasurfaces becomes an important issue. Here, we design Si-based metasurfaces to realize flexible chromatic dispersion manipulation in mid-infrared region. We demonstrate the broadband achromatic metalens and achromatic gradient metasurface to cancel the chromatic aberration over a continuous bandwidth (8–12 μm). In contrast, the metalens and gradient metasurface with enhanced chromatic dispersion have also been realized, where the focal length and deflection angle with different wavelengths vary more significantly than the conventional devices designed with geometric phase. These demonstrations indicate promising potential applications.
metasurfaces chromatic dispersion manipulation achromatic metalenses super dispersion We employ quantum state and process tomography with time-bin qubits to benchmark a city-wide metropolitan quantum communication system. Over this network, we implement real-time feedback control systems for stabilizing the phase of the time-bin qubits and obtain a 99.3% quantum process fidelity to the ideal channel, indicating the high quality of the whole quantum communication system. This allows us to implement a field trial of high-performance quantum key distribution using coherent one way protocol with an average quantum bit error rate and visibility of 0.25% and 99.2% during 12 h over 61 km. Our results pave the way for the high-performance quantum network with metropolitan fibers.
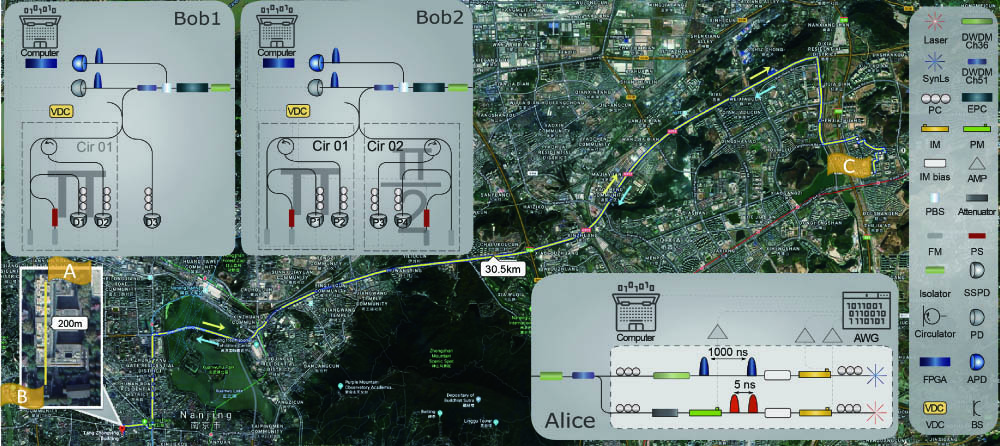
quantum process tomography quantum networks quantum communication quantum key distribution Carbon is hard to be sensitively detected in laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS). The optical emission can be significantly enhanced by resonantly exciting CN radicals in the plasma center using LIBS assisted with laser-induced fluorescence (LIBS-LIF). However, the nitrogen source for CN formation is provided by ambient gas. Therefore, we propose a new approach of periphery excitation in plasma to improve CN fluorescence. The optical and spatial characteristics of CN radicals in plasma were discussed. A fluorescence map was established by combining focal point location and fluorescent intensity, demonstrating that plasma periphery had 4.2 times stronger fluorescence than the center.
laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy laser-induced fluorescence carbon The plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) technique is well suited for fabricating optical filters with continuously variable refractive index profiles; however, it is not clear how the optical and structural properties of thin films differ when deposited on different substrates. Herein, silicon nitride films were deposited on silicon, fused silica, and glass substrates by PECVD, using silane and ammonia, to investigate the effects of the substrate used on the optical properties and structures of the films. All of the deposited films were amorphous. Further, the types and amounts of Si-centered tetrahedral Si–SivN4-v bonds formed were based upon the substrates used; Si–N4 bonds with higher elemental nitrogen content were formed on Si substrates, which lead to obtaining higher refractive indices, and the Si–SiN3 bonds were mainly formed on glass and fused silica substrates. The refractive indices of the films formed on the different substrates had a maximum difference of 0.05 (at 550 nm), the refractive index of SiNx films formed on silicon substrates was 1.83, and the refractive indices of films formed on glass were very close to those formed on fused silica. The deposition rates of these SiNx films are similar, and the extinction coefficients of all the films were lower than 10?4.
thin films plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition optical properties structural properties substrate materials 动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 | 经典导波与拓扑单向波间的高效转换动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 主编推荐 | 单片集成硅基灵活栅格MWSS为突破“容量危机”提供新策略动态信息 丨 2024-04-10
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 封面 |构造任意自相似类贝塞尔光束构造新方法动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 |声光调制的干涉增强效应,助力光学量子信息技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 基于时空耦合效应的超宽带频率转换技术激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦