2021, 19(4) Column
Chinese Optics Letters 第19卷 第4期
This paper proposes a hybrid layered asymmetrically clipped optical (HLACO) single-carrier frequency-division multiplexing (SCFDM) scheme for dimmable visible light communication. It designs a signal structure that combines layered asymmetrically clipped optical (LACO)-SCFDM and negative LACO-SCFDM in proportion for improving the inherent weaknesses of orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM)-based dimmable schemes and further enhancing the system performance. Compared to the HLACO-OFDM-based dimming scheme, it obtains a lower bit error ratio and enables efficient communication over broader dimming range. Its spectral efficiency realizes 2.875 bit·s-1·Hz-1 within the dimming range of 30%–70%, and the attainable average spectral efficiency gains exceed at least 19.21% compared to other traditional dimmable schemes.
dimming control single-carrier frequency-division multiplexing visible light communication spectral efficiency complexity Enhancement of rapid lifetime determination for time-resolved fluorescence imaging in forensic examination Download:687次
Download:687次
 Download:687次
Download:687次An enhancement method of rapid lifetime determination is proposed for time-resolved fluorescence imaging to discriminate substances with approximate fluorescence lifetime in forensic examination. In the method, an image-exclusive-OR treatment with filter threshold adaptively chosen is presented to extract the region of interest from dual-gated fluorescence intensity images, and then the fluorescence lifetime image is reconstructed based on the rapid lifetime determination algorithm. Furthermore, a maximum and minimum threshold filtering is developed to automatically realize visualization enhancement of the lifetime image. In proof experiments, compared with traditional fluorescence intensity imaging and rapid lifetime determination method, the proposed method automatically distinguishes altered and obliterated documents written by two brands of highlighters with the same color and close fluorescence lifetime.
time-resolved fluorescence imaging fluorescence lifetime image visualization enhancement dual-gated intensity-correlation forensic examination Feedback ghost imaging by gradually distinguishing and concentrating onto the edge area Download:582次
Download:582次
 Download:582次
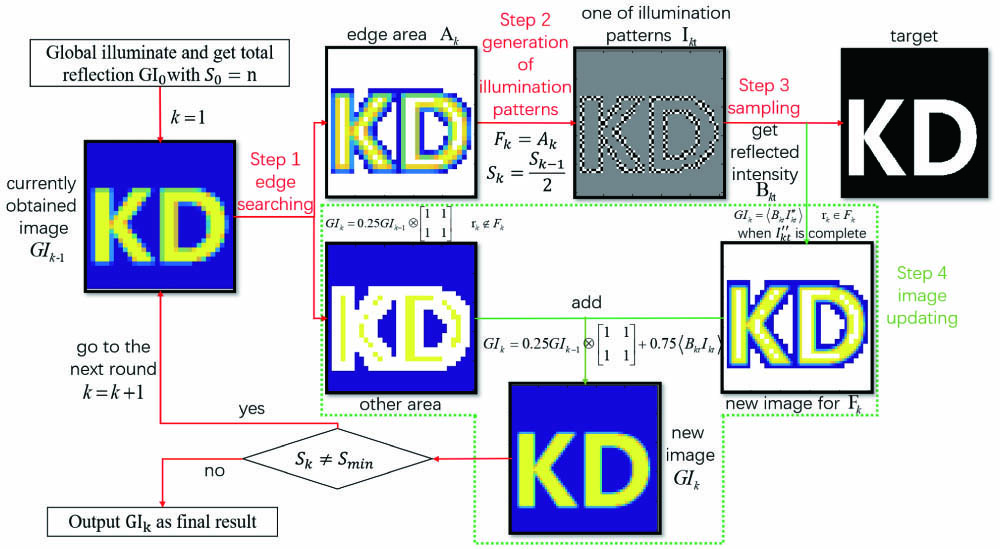
Download:582次Applications of ghost imaging are limited by the requirement on a large number of samplings. Based on the observation that the edge area contains more information thus requiring a larger number of samplings, we propose a feedback ghost imaging strategy to reduce the number of required samplings. The field of view is gradually concentrated onto the edge area, with the size of illumination speckles getting smaller. Experimentally, images of high quality and resolution are successfully reconstructed with much fewer samplings and linear algorithm.
computational ghost imaging adaptive imaging Influence of the sparsity of random speckle illumination on ghost imaging in a noise environment Download:694次
Download:694次
 Download:694次
Download:694次The influence of the sparsity of random speckle illumination on traditional ghost imaging (GI) and GI via sparsity constraint (GISC) in a noise environment is investigated. The experiments demonstrate that both GI and GISC obtain their best imaging quality when the sparsity of random speckle illumination is 0.5, which is also explained by some parameters such as detection of the signal to noise ratio and mutual coherence of the measurement matrix.
ghost imaging sparsity speckle illumination noise environment A fiber-optic sensor for the simultaneous measurement of strain and temperature is proposed and experimentally demonstrated based on Fabry–Pérot (FP) interference and the antiresonance (AR) mechanism. The sensor was implemented using a single-mode fiber (SMF)–hollow-core fiber–SMF structure. A temperature sensitivity of 21.11 pm/°C was achieved by tracing the troughs of the envelope caused by the AR mechanism, and a strain sensitivity of 2 pm/με was achieved by detecting the fine fringes caused by the FP cavity. The results indicate that the dual-parameter sensor is stable and reliable.
fiber-optic sensor Fabry–Pérot interference antiresonance Highly sensitive torsion sensor based on triangular-prism-shaped long-period fiber gratings Download:671次
Download:671次
 Download:671次
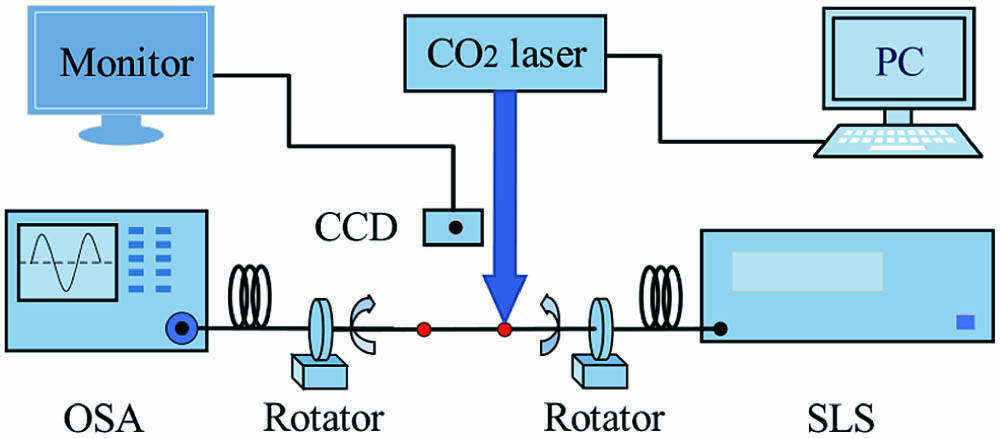
Download:671次We propose and investigate a compact optical fiber sensor that aims to measure the torsion in both amount and direction with high sensitivity. This sensor is configured by a triangular-prism-shaped long-period fiber grating, which is fabricated by the high frequency
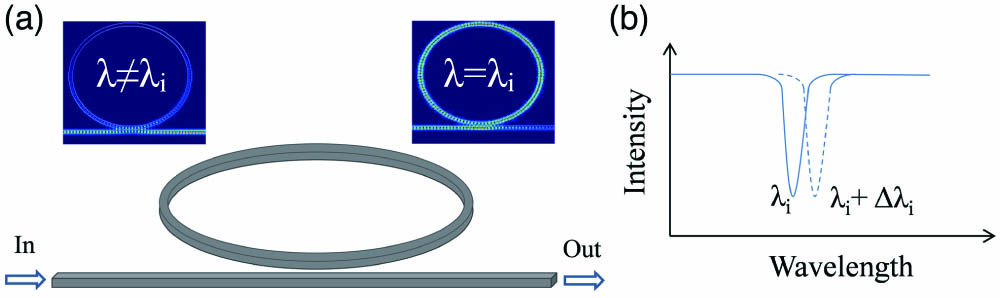
long-period fiber grating torsion sensor CO2 laser etched method Electro-optic (EO) ring resonator modulators have a number of communications and scientific applications, including analog optical links, optical signal processing, and frequency comb generation. Among the EO materials used to fabricate ring modulators, the EO polymer has many promising characteristics, including a high EO coefficient of 100–200 pm/V (3–7 times larger than that of
electro-optic polymer ring resonator high-bandwidth modulator Wavelength-flexible all-polarization-maintaining self-sweeping fiber laser based on intracavity loss tuning Download:678次
Download:678次
 Download:678次
Download:678次We reported a wavelength-flexible all-polarization-maintaining self-sweeping fiber laser based on the intracavity loss tuning brought by the bent optical fiber. The bidirectional cavity structure achieved the self-sweeping effect due to the appearance of the dynamic grating in the active fiber with the spatial hole burning effect. Under this, a section of fiber was bent into a circle for adjusting the loss of the cavity. With a descending diameter of bent fiber circle, the sweeping range moves to the shorter wavelength and covers a wide range from 1055.6 to 1034.6 nm eventually. Both the initial wavelength of self-sweeping regime and the threshold of the fiber laser show exponential correlation with the diameter of the circular fiber. Our work provides a compact and low-cost way to achieve the broad wavelength-flexible self-sweeping operation.
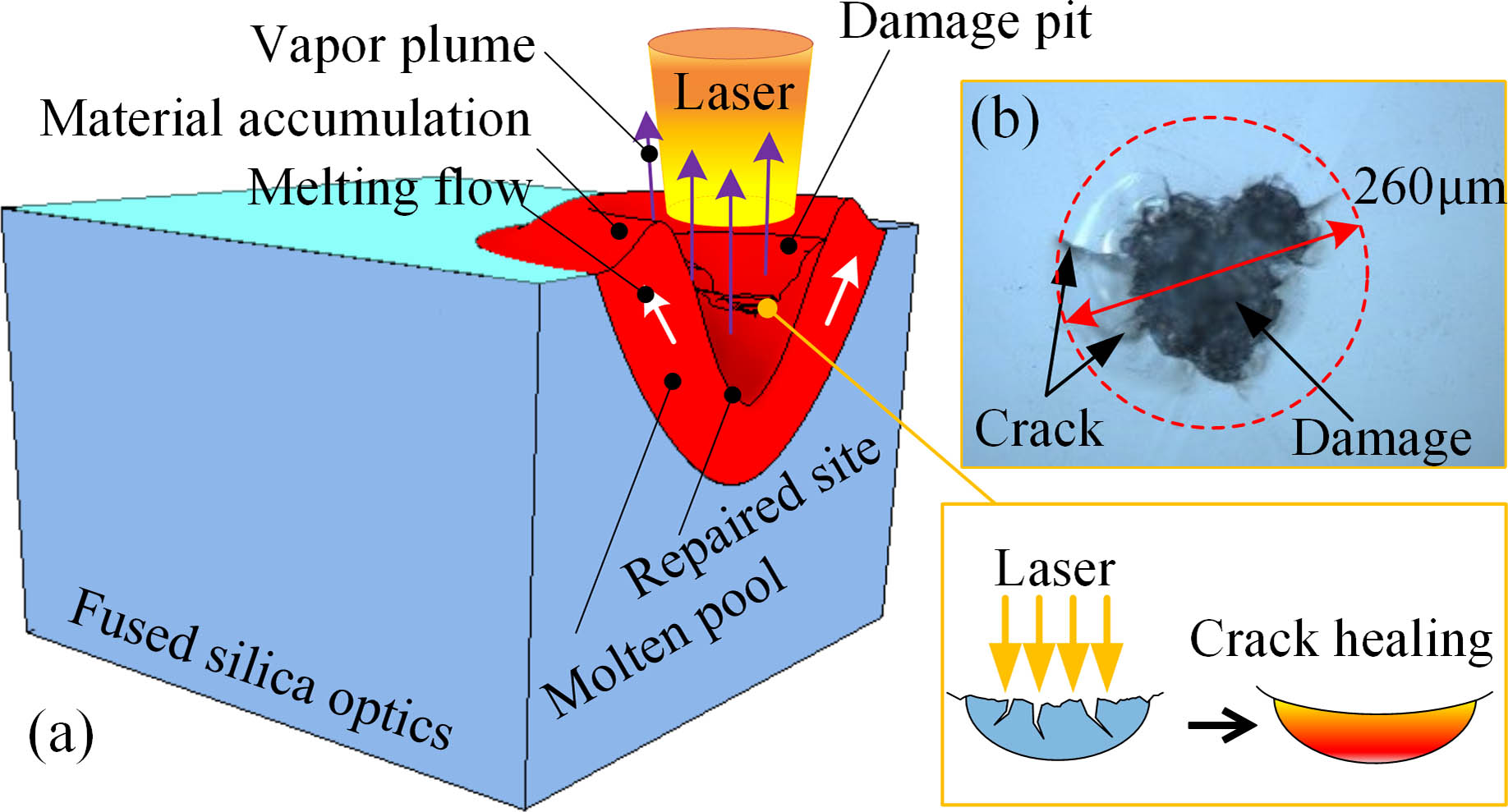
fiber laser self-sweeping effect bidirectional cavity flexible wavelength all-polarization maintaining In order to reveal the evolution mechanism of repaired morphology and the material’s migration mechanism on the crack surface in the process of
CO2 laser repairing fused silica crack healing surface evolution High-power, ultra-broadband supercontinuum source based upon 1/1.5 µm dual-band pumping Download:713次
Download:713次
 Download:713次
Download:713次We experimentally demonstrate an all-fiber supercontinuum source that covers the spectral region ranging from visible to mid-infrared. The ultra-broadband supercontinuum is realized by pumping a cascaded photonic crystal fiber and a highly nonlinear fiber with a 1/1.5 μm dual-band pump source. A maximum output power of 9.01 W is achieved using the system, which is the highest power ever achieved from a supercontinuum source spanning from the visible to mid-infrared.
fiber lasers supercontinuum generation nonlinear optics After the three-dimensional self-affine fractal random surface simulation, we use the optical scattering theory to calculate the deep Fresnel region speckle (DFRS) under consideration of the more strict shadowing effect. The evolution of DFRS with the scattering distance and the intensity probability distribution are studied. It is found that the morphology of the scatterer has an antisymmetric relationship with the intensity distribution of DFRS, and the effect of micro-lenses on the scattering surface causes the intensity probability distribution of DFRS to deviate from the Gaussian speckle in the high light intensity area.
speckle simulation shadowing effect deep Fresnel region The anisotropy of thermal property in an
anisotropy thermal property tunable laser Yb,Nd:Sc2SiO5 crystal Gas sensing for measurement of gas components, concentrations, and other parameters plays an important role in many fields. In this Letter, a micro-ring resonator laser used for gas sensing is experimentally demonstrated. The multi-quantum-wells micro-ring laser based on whispering-gallery modes with an annular resonator and an output waveguide was fabricated. A single-mode laser with a wavelength of 1746.4 nm was fabricated for the first time, to the best of our knowledge, experimentally. The output power of 1.65 mW under 40 mA injection current was obtained with a side-mode suppression ratio over 33 dB.
gas sensing whispering-gallery mode micro-ring resonator laser Floquet spectrum and optical behaviors in dynamic Su–Schrieffer–Heeger modeled waveguide array Download:742次
Download:742次
 Download:742次
Download:742次Floquet topological insulators (FTIs) have been used to study the topological features of a dynamic quantum system within the band structure. However, it is difficult to directly observe the dynamic modulation of band structures in FTIs. Here, we implement the dynamic Su–Schrieffer–Heeger model in periodically curved waveguides to explore new behaviors in FTIs using light field evolutions. Changing the driving frequency produces near-field evolutions of light in the high-frequency curved waveguide array that are equivalent to the behaviors in straight arrays. Furthermore, at modest driving frequencies, the field evolutions in the system show boundary propagation, which are related to topological edge modes. Finally, we believe curved waveguides enable profound possibilities for the further development of Floquet engineering in periodically driven systems, which ranges from condensed matter physics to photonics.
topological photonics insulator waveguide array Floquet In this work, inspired by advances in twisted two-dimensional materials, we design and study a new type of optical bi-layer metasurface system, which is based on subwavelength metal slit arrays with phase-gradient modulation, referred to as metagratings (MGs). It is shown that due to the found reversed diffraction law, the interlayer interaction that can be simply adjusted by the gap size can produce a transition from optical beam splitting to high-efficiency asymmetric transmission of incident light from two opposite directions. Our results provide new physics and some advantages for designing subwavelength optical devices to realize efficient wavefront manipulation and one-way propagation.
asymmetric transmission high efficiency bi-layer metagratings abrupt phase control We present a velocity-gauge model for the generation of even-order high harmonics, and reveal that the even-order harmonics originate from the multiple-step transitions among the energy bands in momentum space, while the odd-order harmonics are mainly from direct transitions. The lower valence band is found vital for the generation of even harmonics. Relative intensity of even-order harmonics versus the odd orders is calculated and shows a growing trend as the laser field amplitude increases.
solid high-harmonic generation inversion asymmetry even-order harmonics 动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 | 经典导波与拓扑单向波间的高效转换动态信息 丨 2024-04-19
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 主编推荐 | 单片集成硅基灵活栅格MWSS为突破“容量危机”提供新策略动态信息 丨 2024-04-10
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 封面 |构造任意自相似类贝塞尔光束构造新方法动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
COL Highlight (Vol. 22, Iss. 2): 主编推荐 |声光调制的干涉增强效应,助力光学量子信息技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
COL 封面故事 (Vol. 22, Iss. 1): 基于时空耦合效应的超宽带频率转换技术激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦