2016, 4(6) Column
Photonics Research 第4卷 第6期
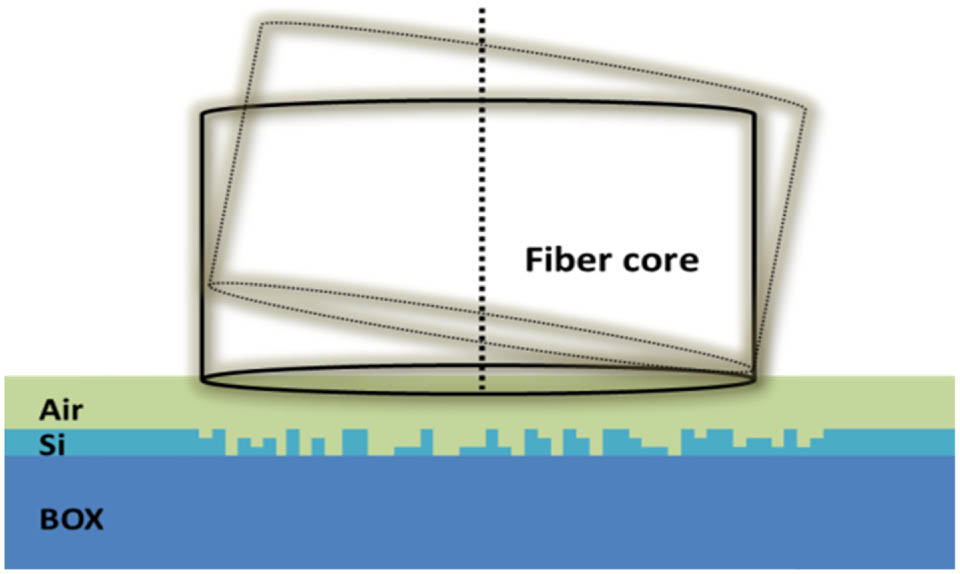
A barcode-like waveguide nanostructure with discretized multilevel pixel lines is designed and optimized by a nonlinear search algorithm. We obtain the design of a one-dimensional multilevel nanostructure with ?1.04 dB efficiency for surface normal coupling to a standard single-mode fiber. Another design is achieved from the automatic optimization process, which enables polarization-independent coupling to a single-mode fiber. The optimum coupling efficiency is simulated to be ?2.83 dB for TE and ?3.49 for TM polarization centered near the 1550 nm wavelength. Polarization-dependent loss of less than 1 dB over 45.3 nm is achieved.
Integrated optics devices Integrated optics devices Diffraction gratings Diffraction gratings Thermal and luminescent properties of 2 μm emission in thulium-sensitized holmium-doped silicate-germanate glass Download:1409次
Download:1409次
 Download:1409次
Download:1409次In this paper, we present the luminescent properties of Tm3+∕Ho3+ co-doped new glass. A series of silicategermanate glass was prepared by the conventional melt-quenching method. In the Tm3+∕Ho3+ co-doped silicategermanate glass, a strong emission of 2 μm originating from the Ho3+:5I7 → 5I8 transition can be observed under conventional 808 nm pumping. The characteristic temperatures, structure, and absorption spectra have been measured. The radiative properties of Ho33+ in the prepared glass were calculated. The emission cross section of Ho33+ ions transition can reach 4.78 × 10?21 cm2 around 2 μm, and the FWHM is as high as 153 nm. The energy transfer efficiency between Ho3+ and Tm3+ has a large value (52%), which indicates the Tm3+∕Ho3+ co-doped silicategermanate glass is a suitable candidate for the 2 μm laser. Moreover, the energy transfer mechanism between Tm3+ and Ho3+ ions was investigated.(61370049, 61308090, 61405182, 51172252, 51372235, 51472225); International Science & Technology Cooperation Program of China (2013DFE63070); Public TechnicalInternational Cooperation Project of the Science Technology Department of Zhejiang Province (2015c340009).
Laser materials Laser materials Optical materials Optical materials Glass and other amorphous materials Glass and other amorphous materials Spectroscopy Spectroscopy infrared infrared Strip-loaded waveguide-based optical phase shifter for high-efficiency silicon optical modulators Download:802次
Download:802次
 Download:802次
Download:802次We propose a novel silicon optical phase shifter structure based on heterogeneous strip-loaded waveguides on a photonic silicon on insulator (SOI) platform. The features of an etchless SOI layer and loaded strip would enhance the performance and uniformity of silicon optical modulators on a large-scale wafer. We implemented the phase shifter by loading an amorphous silicon strip onto an SOI layer with a vertical PN diode structure. Compared to the conventional lateral PN phase shifter based on half-etched rib waveguides, this phase shifter shows a >1.5 times enhancement of modulation efficiency and provides >20 GHz high-speed operation.
Waveguide modulators Waveguide modulators Modulators Modulators Waveguide superlattices, a special type of waveguide arrays, can be designed to achieve very low cross talk at submicrometer/subwavelength pitches. The theoretical framework and design rationales for such waveguide superlattices will be presented in depth. Waveguide sidewall roughness can help to deter the coherent coupling between identical waveguides in nearby supercells, but it also induces random fluctuation of transmission. Statistical behavior of the transmission due to roughness in a waveguide superlattice is systematically treated. Complex transmission characteristics due to spectral oscillation and random roughness will be presented, and their evolution with the superlattice length will be analyzed.Institutions.
Waveguides Waveguides Multiplexing Multiplexing Integrated optics Integrated optics Optical interconnects Optical interconnects In this paper, we propose a ghost imaging scheme with fast Walsh–Hadamard transform, named GIFWHT. In the scheme, Walsh–Hadamard pattern pairs are used to illuminate an object to generate pairs of detection results, and the corresponding differential detection result is used as the result as that from the conventional bucket detector. By performing the fast Walsh–Hadamard transform on 2k (k is a positive integer) differential detection results, the image of the object can be recovered. The experimental and numerical simulation results show that the reconstruction time of GIFWHT is greatly reduced, and the quality of the recovered image is noticeably improved. In addition, GIFWHT is robust against interference from environmental illumination and could savememory.Network Technology, Ministry of Education (NYKL2015011).
Computational imaging Computational imaging Image reconstruction techniques Image reconstruction techniques Image formation theory Image formation theory All-optical two-channel polarization-multiplexing format conversion from QPSK to BPSK signals in a silicon waveguide Download:1075次
Download:1075次
 Download:1075次
Download:1075次All-optical two-channel format conversion is proposed and experimentally demonstrated from a 40 Gbit/s polarization multiplexing (Pol-MUX) non-return-to-zero quadrature phase-shift keying (QPSK) signal to Pol-MUX binary phase-shift keying (BPSK) signals by using phase-doubled four-wave mixing effects with two polarization-angled pumps in a silicon waveguide. The eye diagrams and constellation diagrams of the original QPSK sequences and the converted BPSK sequences of each channel are clearly observed on the two polarization states. Moreover, the bit error rates (BERs) of the two converted idlers are measured. The power penalties of all these converted BPSK sequences on both X and Y polarization states are less than 3.4 dB at a BER of 3.8 × 10?3.(20130101110089); Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (LY14F050006).
Phase modulation Phase modulation Nonlinear optical signal processing Nonlinear optical signal processing Nonlinear optics Nonlinear optics four-wave mixing four-wave mixing Nonlinear optics Nonlinear optics integrated optics integrated optics Light-emitting diode (LED)-based visible light communication (VLC) has become a potential candidate for nextgeneration ultra-high-speed indoor wireless communication. In this paper, four special-shaped 8-quadrature amplitude modulation (QAM) constellations are investigated in a single-carrier VLC system. It is numerically verified and experimentally demonstrated that circular (7,1) shows obvious superiority in the performance of the dynamic range of signal voltage peak-to-peak (vpp) value and bit error rate (BER). Next best is rectangular, followed by triangular; circular (4,4) has the worst performance. A data rate of 1.515 Gbit/s is successfully achieved by circular (7,1) employing a red chip LED over 0.5 m indoor free space transmission below a BER threshold of 3.8 × 10?3. Compared with circular (4,4), the traditional 8-QAM constellation, circular (7,1) provides a wider dynamic range of signal vpp, a higher data rate, and a longer transmission distance. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first investigation into the performance differences of special-shaped 8-QAM constellations in a highspeed, single-carrier VLC system, and the results comprehensively demonstrate that circular (7,1) is the optimal option.
Free-space optical communication Free-space optical communication Optical communications Optical communications Light-emitting diodes Light-emitting diodes Hybrid silicon slotted photonic crystal waveguides: how does third order nonlinear performance scale with slow light Download:825次
Download:825次
 Download:825次
Download:825次We investigate in this paper the influence of slow light on the balance between the Kerr and two-photon absorption (TPA) processes in silicon slotted hybrid nonlinear waveguides. Three typical silicon photonic waveguide geometries are studied to estimate the influence of the light slow-down factor on the mode field overlap with the silicon region, as well as on the complex effective nonlinear susceptibility. It is found that slotted photonic crystal modes tend to focalize in their hollow core with increasing group index (nG) values. Considering a hybrid integration of nonlinear polymers in such slotted waveguides, a relative decrease of the TPA process by more factor of 2 is predicted from nG 10 to nG 50. As a whole, this work shows that the relative influence of TPA decreases for slotted waveguides operating in the slow light regime, making them a suitable platform for third-order nonlinear optics.
Photonic crystals Photonic crystals Photonic crystal waveguides Photonic crystal waveguides Nonlinear optical devices Nonlinear optical devices Nonlinear optics Nonlinear optics integrated optics integrated optics Ultrasensitive biosensors based on long-range surface plasmon polariton and dielectric waveguide modes Download:1974次
Download:1974次
 Download:1974次
Download:1974次An ultrasensitive biosensor based on hybrid structure and composed of long-range surface plasmon polariton (LRSPP) and dielectric planar waveguide (PWG) modes is proposed. Both PWG and LRSPP modes have strong resonances to form strong coupling between the two modes, and the two modes can couple to enhance sensitivityof sensors. In the hybrid structure, PWG is composed of cytop–Si–cytop multilayers and the LRSPP configuration is composed of cytop–metal–sensing medium multilayer slabs. The highest imaging sensitivities of 2264 and 3619 RIU?1 were realized in the proposed sensors based on Au and Al-monolayer graphene, respectively, which are nearly 1.2 and 1.9 times larger than the 1910 RIU?1 sensitivity of the conventional LRSPR sensor (LRSPP sensor). Moreover, it is demonstrated that the PWG-coupled LRSPP biosensor is applicable to the sensing medium, with refractive index in the vicinity of 1.34.of Guangdong Province (2016B050501005); Science and Technology Project of Shenzhen (JCYJ20140828163633996, JCYJ20150324141711667); Natural Science Foundation ofSZU (201452, 201517, 827-000051, 827-000052, 827-000059).
Remote sensing and sensors Remote sensing and sensors Sensors Sensors Remote sensing and sensors Remote sensing and sensors Biological sensing and sensors Biological sensing and sensors Optical sensing and sensors Optical sensing and sensors Surface plasmons Surface plasmons High-peak-power passivelyQ-switched Nd:YAG/Cr4+:YAG composite laser with multiple-beam output Download:856次
Download:856次
 Download:856次
Download:856次We report on the design, realization, and output performance of a diode-pumped high-peak-power passively Q-switched Nd:YAG∕Cr4:YAG composite medium onolithic laser with four-beam output. The energy of a laser pulse was higher than 3 mJ with duration of 0.9 ns. The proposed system has the ability to choose independently the focus of each beam. Such a laser device can be used for multipoint ignition of an automobile gasoline engine, but could also be of interest for ignition in space propulsion or in turbulent conditions specific to aeronautics.
Lasers Lasers solid-state solid-state Lasers Lasers neodymium neodymium Lasers Lasers Q-switched Q-switched Pumping Pumping Low cross-talk, deep subwavelength plasmonic metal/insulator/metal waveguide intersections with broadband tunability Download:941次
Download:941次
 Download:941次
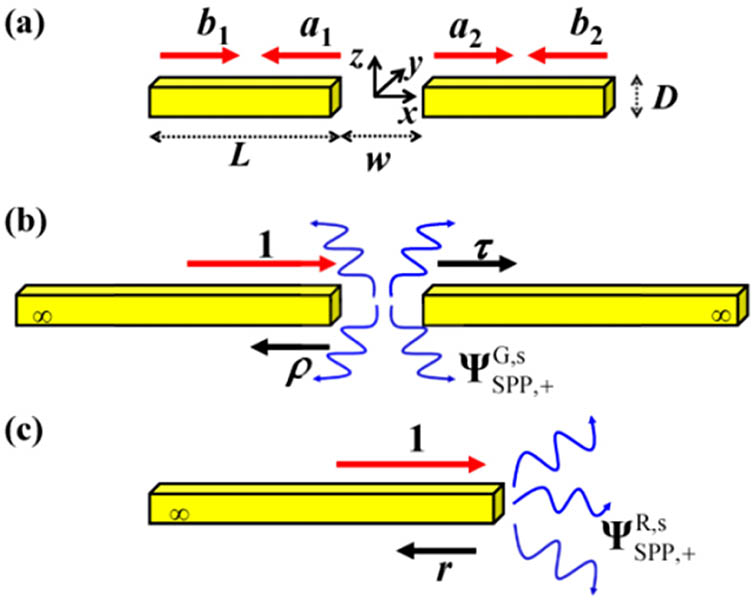
Download:941次We suggest a low cross-talk plasmonic cross-connector based on a metal/insulator/metal cavity and waveguides. We separately investigate the isolated cavity mode, the waveguide mode, and the combination of cavity and waveguide modes using a finite-different time-domain method. Due to resonant tunneling and the cutoff frequency of the odd waveguide mode, our proposed structure achieves a high throughput transmission ratio and eliminates cross-talk. Furthermore, the proposed structure has a broadband tunability of 587 nm, which can be achieved by modulating the cavity air gap thickness. This structure enables the miniaturization of photonic integrated circuits and sensing applications.
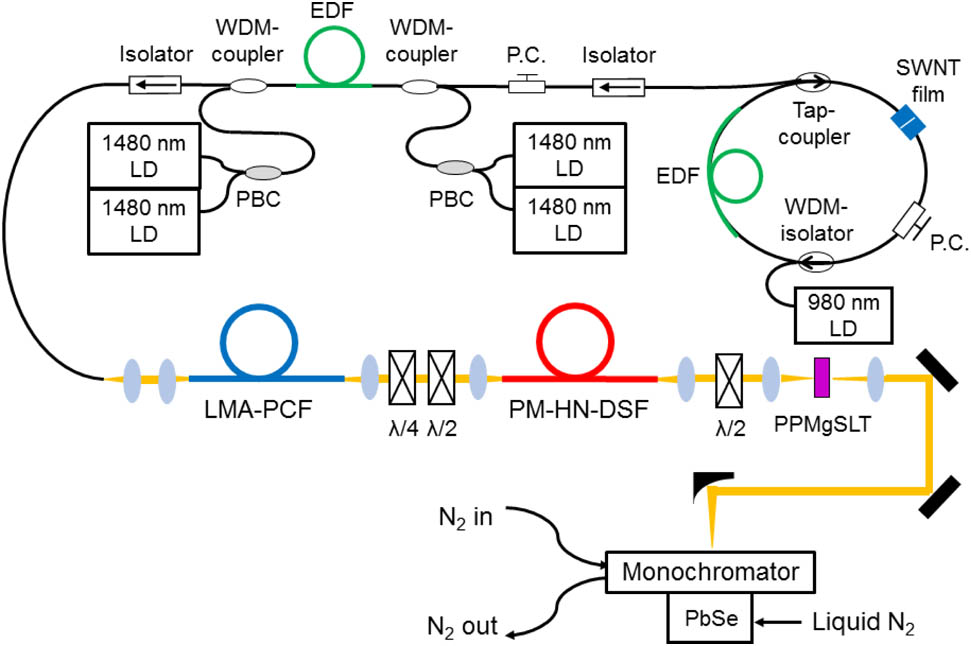
Plasmonics Plasmonics Surface plasmons Surface plasmons Resonators Resonators Waveguides Waveguides Power-scaled dissipative soliton using double-claddingpumped Yb-doped all-fiber amplifier Download:988次
Download:988次
 Download:988次
Download:988次We report on an all-fiber oscillator followed by an all-fiber amplifier to produce as short as 382 fs laser pulses with up to 0.9Waverage power. The oscillator is an all-normal-dispersion all-fiber dissipative soliton laser operating at 1030 nm, and operating in dissipative soliton mode. The amplifier stage is mainly based on a double-cladding 20 μm radius ytterbium-doped fiber pumped by an up to 2.5WCWlaser source. The optical-to-optical conversion amplifier efficiency is around 40%. To our knowledge, this is the first report of an all-fiber mode-locked fiber laser oscillator amplified by an all-fiber amplifier.
Lasers and laser optics Lasers and laser optics Nonlinear optics Nonlinear optics Lasers Lasers ytterbium ytterbium Ultrafast lasers Ultrafast lasers Nonlinear optics Nonlinear optics fibers fibers Ultrafast nonlinear optics Ultrafast nonlinear optics The features of the characteristic matrix used in linear intensity correlation reconstruction methods are directly related to the quality of ghost imaging. In order to suppress the noise caused by the off-diagonal elements in the characteristic matrix, we propose a reconstruction method for ghost imaging called scalar-matrix-structured ghost imaging (SMGI). The characteristic matrix is made to approximate a scalar matrix by modifying the measurement matrix. Experimental results show that SMGI improves the peak signal-to-noise ratio of the object reconstruction significantly compared with differential ghost imaging, even in the case of a nonzero two-arm longitudinal difference, which is a promising result for practical applications.of China (2013AA122901); National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (61571427); Youth Innovation Promotion Association of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (2013162).
Image formation theory Image formation theory Coherence imaging Coherence imaging Speckle Speckle Ultrafast nonlinear absorption and nonlinear refraction in few-layer oxidized black phosphorus Download:1448次
Download:1448次
 Download:1448次
Download:1448次We experimentally investigated the nonlinear optical response in few-layer oxidized black phosphorus (OBP) by the femtosecond Z-scan measurement technique, and found that OBP not only possesses strong ultrafast saturable absorption but also a nonlinear self-defocusing effect that is absent in black phosphorus (BP). The saturable absorption property originates mainly from the direct band structure, which is still maintained in OBP. The emergence of self-defocusing might originate from the combined consequences of the oxygen-induced defects in BP. Our experimental findings might constitute the first experimental evidence on how to dynamically tuneits nonlinear property, offering an inroad in tailoring its optical properties through chemical modification (oxidation, introducing defects, etc.). The versatile ultrafast nonlinear optical properties (saturable absorption and self-defocusing) imply a significant potential of the layered OBP in the development of unprecedentedoptoelectronic devices, such as mode lockers, optical switches, laser beam shapers, and wavelength converters.China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2015M580731); Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province (2016B050501005).
Nonlinear optics Nonlinear optics Optical devices Optical devices Ultrafast optics Ultrafast optics Understanding localized surface plasmon resonance with propagative surface plasmon polaritons in optical nanogap antennas Download:1186次
Download:1186次
 Download:1186次
Download:1186次The plasmonic nanogap antenna is an efficient radiating or receiving optical device. The resonance behavior of optical antennas is commonly attributed to the excitation of a localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR), which can be theoretically defined as the quasi-normal mode (QNM). To clarify the physical origin of the LSPR, we build up an analytical model of the LSPR by considering a multiple scattering process of propagative surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) on the antenna arms. The model can comprehensively reproduce the complex eigenfrequency and the field distribution of QNMs of the antenna, unveiling that the LSPR arises from a Fabry–Perot resonance of SPPs. By further applying the complex pole expansion theorem of meromorphic functions, the field of the antenna under illumination by a nearby dipole emitter can be analytically expanded with QNMs, which well predicts the frequency response of the enhancement factor of radiation. The present model establishes explicit relations between the concepts of the LSPR and the propagative SPP and integrates the advantages of the Fabry–Perot and QNM formalisms of nanogap antennas.
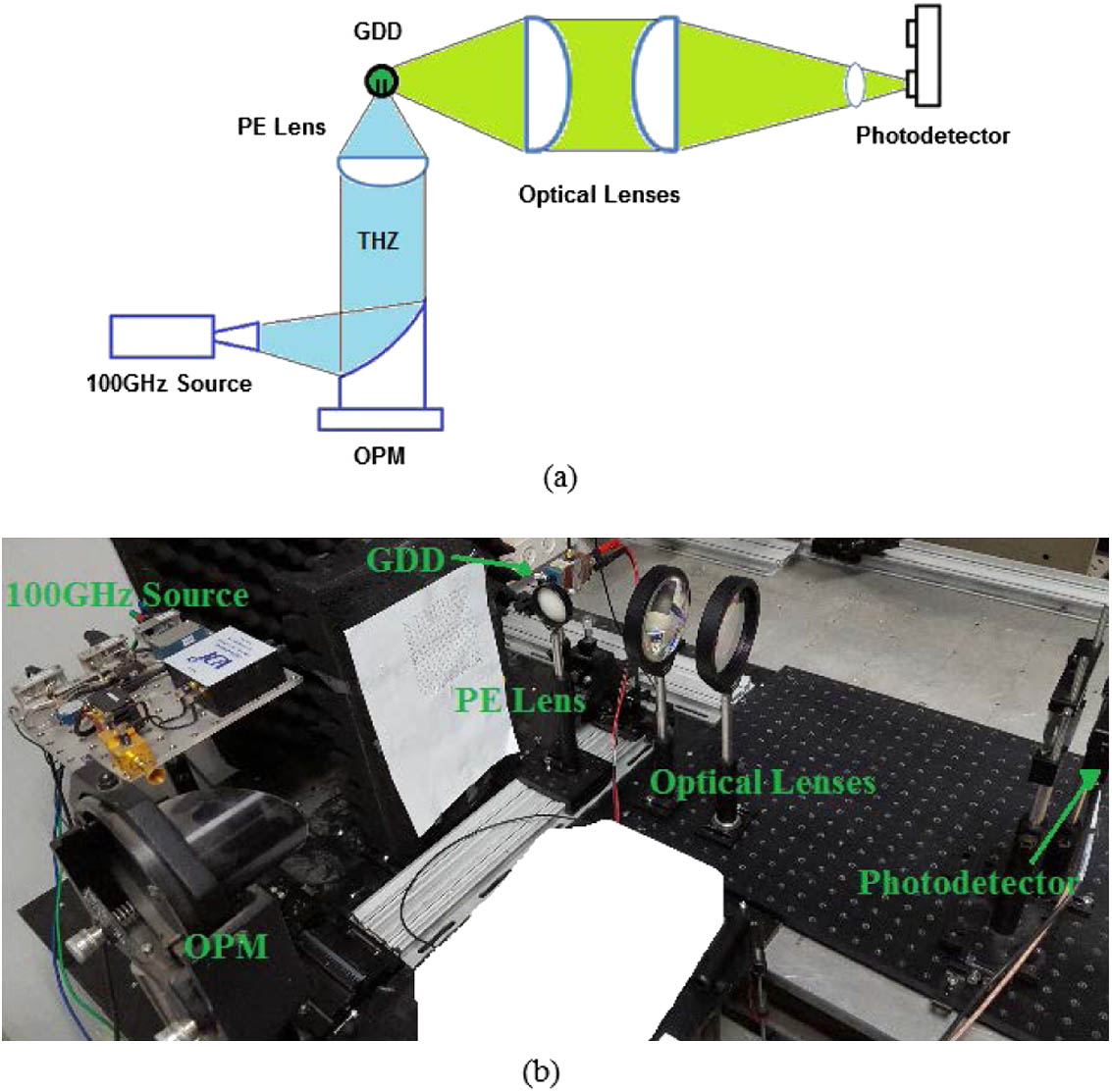
Surface plasmons Surface plasmons Resonance Resonance Subwavelength structures Subwavelength structures We present an inexpensive technique to obtain a three-dimensional (3D) millimeter wave (MMW) and terahertz (THz) image using upconversion. In this work we describe and demonstrate a method for upconversion of MMW/THz radiation to the visual band using a very inexpensive miniature glow discharge detector (GDD) and a silicon photodetector. We present MMW/THz upconversion images based on measuring the visual light emitting from the GDD rather than its electrical current. The results show better response time and better sensitivity compared to the electronic detection performed previously. Furthermore, in this work we perform frequency modulation continuous wave (FMCW) radar detection based on this method using a GDD lamp, with a photodetector to measure GDD light emission. By using FMCW detection, the range in addition to the intensity at each pixel can be obtained, thus yielding the 3D image. The GDD acts as a heterodyne mixer not only electronically but also optically. Thesuggested 3D upconversion technique using the GDD is simple and inexpensive and has better performance compared to other MMW/THz imaging systems suggested in the literature. This method provides minimum detectable signal power that is about 6 orders of magnitude better than similar plasma systems due to the very largeinternal signal gain deriving from the much smaller electrode separation and resulting in much higher plasma electric field.
Imaging systems Imaging systems Terahertz imaging Terahertz imaging Three-dimensional image acquisition Three-dimensional image acquisition Detectors Detectors Upconversion Upconversion Photodetectors Photodetectors We demonstrated stable midinfrared (MIR) optical frequency comb at the 3.0 μm region with difference frequency generation pumped by a high power, Er-doped, ultrashort pulse fiber laser system. A soliton mode-locked 161 MHz high repetition rate fiber laser using a single wall carbon nanotube was fabricated. The output pulse was amplified in an Er-doped single mode fiber amplifier, and a 1.1–2.2 μm wideband supercontinuum (SC) with an average power of 205 mW was generated in highly nonlinear fiber. The spectrogram of the generated SC was examined both experimentally and numerically. The generated SC was focused into a nonlinear crystal, and stable generation of MIR comb around the 3 μm wavelength region was realized.(AMED).
Infrared and far-infrared lasers Infrared and far-infrared lasers Fiber optics amplifiers and oscillators Fiber optics amplifiers and oscillators A mode-locked thulium-doped fiber laser (TDFL) based on nonlinear polarization rotation (NPR) with different net anomalous dispersion is demonstrated. When the cavity dispersion is ?1.425 ps2, the noise-like (NL) pulse with coherence spike width of 406 fs and pulse energy of 12.342 nJ is generated at a center wavelength of 2003.2 nm with 3 dB spectral bandwidth of 23.20 nm. In the experimental period of 400 min, the 3 dB spectral bandwidth variation, the output power fluctuation, and the central wavelength shift are less than 0.06 nm, 0.04 dB, and 0.4 nm, respectively, indicating that the NPR-based TDFL operating in the NL regime holds good long-term stability.
Infrared and far-infrared lasers Infrared and far-infrared lasers Lasers Lasers pulsed pulsed Ultrafast lasers Ultrafast lasers Fiber loop ring-down cavity integrated U-bent single-mode-fiber for magnetic field sensing Download:1073次
Download:1073次
 Download:1073次
Download:1073次A novel magnetic field sensing system based on the fiber loop ring-down technique is proposed in this paper. In the fiber loop, a U-bent single-mode-fiber structure coated with magnetic fluid (MF) serves as the sensing head, and an erbium-doped fiber amplifier (EDFA) is introduced to compensate for the intrinsic loss of the cavity. The ring-down time of the system varies with the change of applied magnetic field due to the tunable absorption coefficient and refractive index of the MF. Therefore, measurement of the magnetic field can be realized by monitoring the ringdown time. The experimental results show that the performance of the system is extremely dependent on the interrogation wavelength, because both the gain of the EDFA and the loss of the sensing head are wavelength dependent. We found that at the optimal wavelength, the ratio of the gain to loss attained its maximum. The sensing system was experimentally demonstrated and a sensitivity of ?0.5951 μs∕Oe was achieved.61107035).
Fiber optics Fiber optics Fiber optics sensors Fiber optics sensors Magneto-optical materials Magneto-optical materials Spectroscopy Spectroscopy time-resolved time-resolved Self-starting passively mode-locked all fiber laser based on carbon nanotubes with radially polarized emission Download:874次
Download:874次
 Download:874次
Download:874次We demonstrate an all fiber passively mode-locked laser emitting a radially polarized beam by using a few-mode fiber Bragg grating to achieve mode selection and spectrum filtering. An offset splicing of single-mode fiber with four-mode fiber is utilized as a mode coupler in the laser cavity. Carbon nanotubes are introduced into the laser cavity as the saturable absorber to achieve self-start mode locking. The laser operates at 1547.5 nm with a narrow spectrum width of 0.3 nm at 30 dB. The emitted mode-locked pulses have a duration of 22.73 ps and repetition of 10.61 MHz. A radially polarized beam has been obtained with high mode purity by adjusting the polarization in the laser cavity.
Fibers Fibers erbium erbium Lasers Lasers fiber fiber Fiber Bragg gratings Fiber Bragg gratings Mode-locked lasers Mode-locked lasers Nanomaterials Nanomaterials 公告
动态信息
动态信息 丨 2024-04-25
PR Highlight (Vol. 12, Iss. 2): 封面|超紧凑片上偏振控制器动态信息 丨 2024-04-11
PR Highlight (Vol. 11, Iss. 12): 亮点 | 十亿像素级、高通量的无透镜偏振编码叠层成像技术动态信息 丨 2024-03-29
PR 封面故事 (Vol. 12, Iss. 3): 封面 | 基于时空编码神经网络的像差感知超分辨成像动态信息 丨 2024-03-25
PR 封面故事 (Vol. 12, Iss. 1) 光涡旋与手性器件微纳3D打印动态信息 丨 2024-03-14
PR Highlight (Vol. 12, Iss. 1): 同步双脉冲激光烧蚀中的气泡相互作用效应激光评论微信公众号

点击菜单“联系编辑”即可添加期刊编辑为好友啦