光谱学与光谱分析, 2021, 41 (9): 2759, 网络出版: 2021-10-29
近红外光谱的通用聚苯乙烯牌号在线识别方法
In-Line Identification of Different Grades of GPPS Based on Near-Infrared Spectroscopy
近红外光谱 牌号识别 通用聚苯乙烯 偏最小二乘判别分析 随机森林 Near-infrared spectroscopy Grade identification General purpose polystyrene Partial least square-discriminant analysis Random forest
摘要
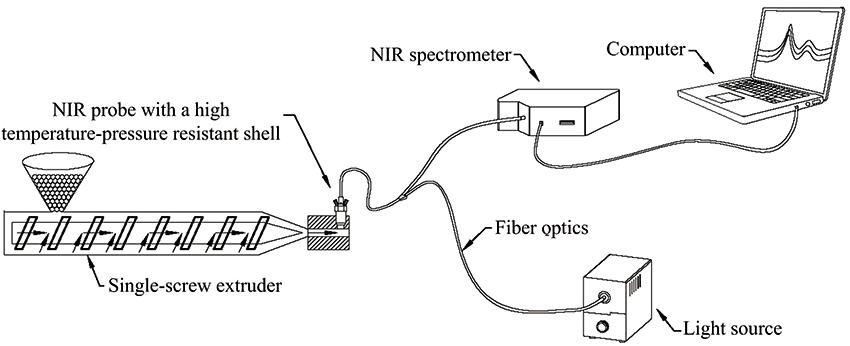
在聚合物加工过程中, 如果在同一生产线上混用不同牌号的原材料, 可能会影响产品性能, 降低产品合格率。 然而采用传统方法识别相同类型不同牌号的聚合物往往耗时长且具有滞后性, 目前还缺乏一种快速实时的牌号识别方法。 因此, 以5种不同牌号的通用聚苯乙烯(GPPS)为研究对象, 利用自主开发的安装于挤出机上的在线近红外光谱测量系统, 将近红外光谱与化学计量学、 机器学习算法相结合, 实现对挤出过程中GPPS牌号的快速在线识别。 首先利用在线近红外光谱测量系统实时采集5种不同牌号GPPS熔体的在线近红外光谱, 波长范围为900~1 700 nm。 经过谱图分析后, 利用主成分分析结合K均值聚类算法验证在线近红外光谱数据对于不同牌号的可分性。 最后采用偏最小二乘判别分析和随机森林两种算法分别建立GPPS牌号识别模型并进行对比。 结果表明: ①经过基线校正、 最大最小归一化、 7点移动平均平滑预处理后, 在线近红外光谱在1 207, 1 388, 1 407和1 429 nm处的特征峰峰值会随着牌号的变化呈阶梯状改变, 以前3个主成分得分作为K均值聚类的输入变量得到聚类正确率为88%, 说明了不同牌号GPPS在线近红外光谱数据的可分性; ②所建立的两种预测模型均能够对GPPS牌号有效识别, 最佳主因子数为3的偏最小二乘判别分析模型对验证集的分类正确率为90.4%, 以前5个主成分得分作为输入变量建立的随机森林模型对验证集的分类正确率达95.6%, 所以随机森林模型的牌号识别性能更好。 因此, 在线近红外光谱测量系统结合化学计量学、 机器学习算法可以实现GPPS牌号的快速在线识别, 为在生产线上利用近红外光谱识别同种聚合物的不同牌号提供参考。
Abstract
Misusing the wrong grades polymer during the polymer processing in the same production line may lead to poorer product performance and a lower qualification ratio. The traditional methods identifying the grades from same kind of polymer are usually time consuming and hysteretic. There has not yet been discovered a fast and real time method for grade identification. In this work, 5 different grades of GPPS were the research object. An in-line near-infrared spectral measurement system installed on the extruder was developed. Near-infrared spectroscopy was combined with chemometrics and machine learning algorithms. The different grades of GPPS could be fast and in-line identified during the extrusion process. First, the in- line near-infrared spectra of GPPS melts of 5 different grades were collected in real time by the developed system with a spectral range of 900~1 700 nm. After spectrum analysis, a K-means clustering algorithm in combination with PCA was performed to verify the distinguishability of in-line near-infrared spectra for different grades. Last, PLS-DA and RF algorithm were used to establish the grade identification models respectively, and the identification ability of these two models was compared. The results show that: ①After baseline correction, maximum and minimum normalization, and 7-point moving average smoothing, the characteristic peak values at 1 207, 1 388, 1 407, 1 429 nm of the in-line near-infrared spectra change in a step-like manner with the change of grades. With the first three principal components scores as input variables, the clustering accuracy by K-means can reach 88%. It shows the distinguishability of the in-line near-infrared spectral data of different grades of GPPS; ②The two prediction models established by PLS-DA and RF can both effectively identify the grades of GPPS. The classification accuracy on the validation set of the PLS-DA model with the optimal principal components of 3 can reach 90.4%. The classification accuracy on the validation set of the RF model with the first five principal components as input variables can reach 95.6%. The RF model shows better grade identification performance than that of the PLS-DA model. Therefore, combined with chemometrics and machine learning algorithms, the in-line near-infrared spectral measurement system can realize the rapid and in-line identification of GPPS grades. It provides a reference for the in-line identification of different grades of the same kind of polymer by near-infrared spectroscopy in a production line.
方圆, 何张平, 朱世超, 梁显荣, 晋刚. 近红外光谱的通用聚苯乙烯牌号在线识别方法[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2021, 41(9): 2759. Yuan FANG, Zhang-ping HE, Shi-chao ZHU, Xian-rong LIANG, Gang JIN. In-Line Identification of Different Grades of GPPS Based on Near-Infrared Spectroscopy[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2021, 41(9): 2759.