短波紫外线的消杀机制与影响因素  下载: 540次
下载: 540次
The novel coronavirus pandemic has caused great concern in global public health. According to data released by the World Health Organization (WHO), the cumulative number of new confirmed coronavirus cases worldwide now exceeds 630 million and the number of deaths exceeds 6.62 million. The daily prevention of the spread of the virus has become an essential step in our lives. The coronaviruses plays an important role in transmission through aerosol transmission, so much research has focused on methods to disinfect the air to interrupt the spread of the virus.
Short-wave ultraviolet (UV) can reduce the incidence of airborne infectious diseases, effectively inactivate airborne active pathogens, and has non-toxic, non-polluting properties, providing an efficient, safe, and environmentally friendly epidemic prevention and control method. According to the New Coronavirus Pneumonia Prevention and Control Program, it is pointed out that the new coronavirus belongs to the beta genus coronavirus, and chemical reagents, such as ether, 75% ethanol, and chlorine-containing disinfectants can make the virus inactivate, and the new coronavirus is sensitive to ultraviolet light and heat, thus, chemical disinfection, ultraviolet disinfection, and high-temperature disinfection are effective methods for inactivating the virus. Currently, chemical disinfection is a common disinfection method, although it is effective, there are problems, such as consuming certain human resources and directly exposing disinfection personnel to danger; although the new coronavirus is sensitive to heat, high temperature inactivation has a narrow scope of application and is somewhat restrictive.
Unlike the above disinfection methods, short-wave UV disinfection is more effective and safer. With the advantages and characteristics of short-wave UV disinfection, it is widely used in medical, food, environmental health, and other areas. Compared with chemical disinfection, short-wave UV disinfection is a non-chemical process that does not produce chemical residues and does not require transportation, storage and subsequent treatment, and is simple to operate without human intervention; compared with thermal disinfection, short-wave UV disinfection has the advantages of being unaffected by temperature, wide range of application, and high sterilization efficiency. Therefore, short-wave UV disinfection has shown its unique advantages in epidemic prevention and control and has attracted much attention.
Recently, researchers at home and abroad have used different wavelengths of short-wave ultraviolet light to conduct experiments on the mechanics of different microorganisms as well as the effect of disinfection, exploring the mechanism of UV disinfection and the best disinfection plan. Some researchers have also conducted biosafety studies to bring short-wave UV into the market faster. Much progress has been made, but there is still a series of challenges in the mechanistic research and market feasibility. Therefore, it is important to understand the mechanism of short-wave UV killing, its influencing factors and biosafety research, for its research and application in epidemic prevention and control.
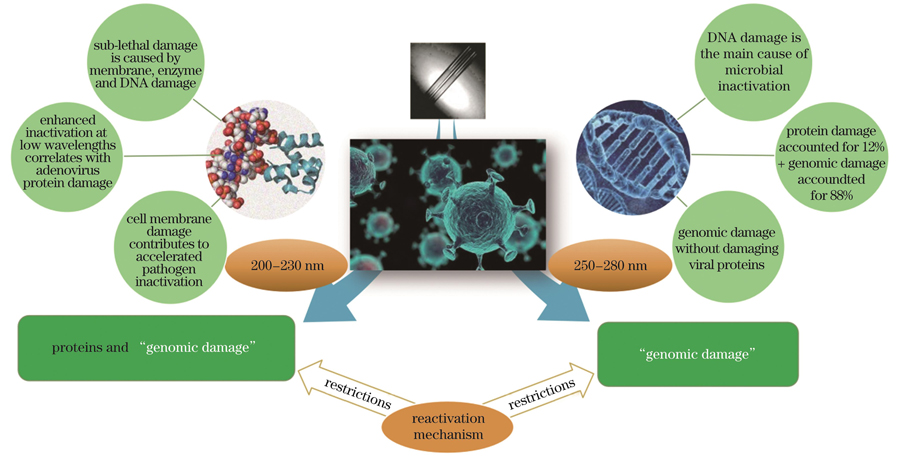
The research progress of short-wave UV in terms of the extinction mechanism, influencing factors and safety is summarized. Firstly, the extinction mechanism of short-wave UV was introduced, and the inactivation factors of microorganisms in two different wavelengths (200-230 nm and 250-280 nm) of short-wave UV were analyzed by comparing the differences in their extinction mechanisms (Table 2). According to previous research reports, the constraint mechanism of the short-wave UV extermination process is summarized, and this mechanism can be divided into light mechanism and dark mechanism. Secondly, the influencing factors of short-wave UV extermination were introduced, and the optimal operating parameters for extermination were summarized by analyzing the effects of UV wavelength, radiation dose, exterminating organisms, and extermination environment on the extermination efficiency. Thirdly, based on previous studies, it was found that the UV wavelengths of 254 nm and 222 nm were more meaningful for research, and the application of short-term low-dose radiation in health care using 254 nm UV was summarized (Table 3). This is followed by a summary of the findings of experimental studies related to long-term high-dose radiation using 222 nm UV, and an outlook on future research and development of short-wave UV (Fig. 5). Finally, the issues facing the field and the ongoing research trends are discussed, including the extinction mechanisms of different wavelengths of short-wave UV, the application studies of short-wave UV, and the investigation of the biosafety of short-wave UV.
With the new coronavirus pandemic, epidemic prevention has been gradually integrated into our lives. Compared with other disinfection methods, short-wave UV disinfection has the characteristics of fast sterilization, simple operation, and no chemical residue. Therefore, short-wave UV disinfection has a broad prospect in the future of the disinfection field. The disinfection mechanism of short-wave UV differs depending on the wavelength. The destruction of genetic material by UV in the 250-280 nm band is the main reason for the disinfection of microorganisms, while the damage to proteins by UV in the 200-230 nm band is the reason for its enhanced disinfection effect. The advantage of “human friendly” makes it a broader research value. The efficiency of disinfection in different environments is also determined by factors, such as UV wavelength and radiation illumination, so research on the application of short-wave UV should not be slackened, while research on the removal of stray light in the application of short-wave UV and application in public places are also current hot spots. In summary, the investigation of the mechanism, biosafety and application of short-wave UV is of great significance to its research and promotion, and still needs to be explored in depth and detail to promote the development of short-wave UV in academic and engineering aspects.
竹涛, 付顺江, 谢蔚, 徐欢. 短波紫外线的消杀机制与影响因素[J]. 中国激光, 2023, 50(9): 0907209. Tao Zhu, Shunjiang Fu, Wei Xie, Huan Xu. UVC Sterilization Mechanism and Influencing Factors[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2023, 50(9): 0907209.