活体小动物脓毒症肠道模型的光声内窥成像研究  下载: 578次
下载: 578次
Microcirculatory dysfunction may cause circulatory failure, insufficient oxygen delivery, and fatal risks. Microscopes are used to observe microcirculation, but they can only image superficial tissues. In addition, they can hardly provide functional information. In this study, we report a photoacoustic endoscope for in vivo imaging of the gastrointestinal microcirculation. The imaging probe is inserted into the rectum of a small animal for rotational-scanning endoscopic imaging. The vascular structures in the gastrointestinal wall can be visualized by detecting the ultrasound excited by the pulsed laser. Moreover, the blood oxygen saturation can be measured and imaged with a dual-wavelength excitation based on the difference in the optical absorption spectrum between oxy- and deoxygenated hemoglobin. We believe that this technology is capable of detecting the functional changes associated with microcirculation diseases with minimal invasion.
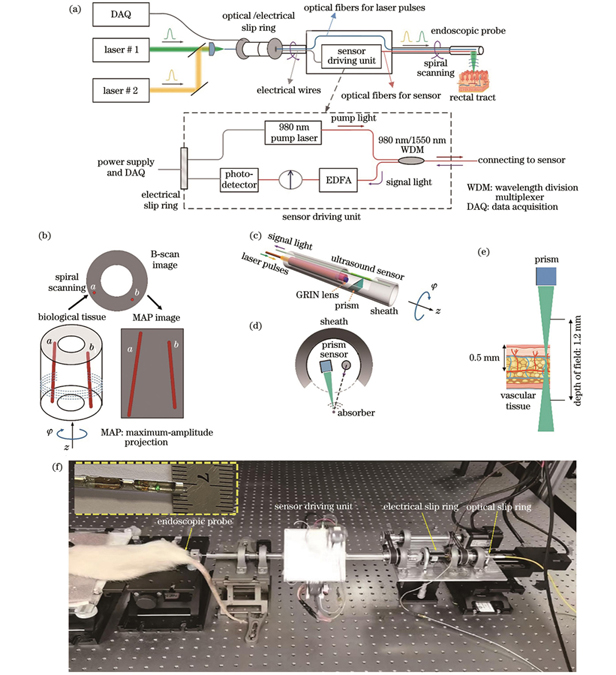
The imaging system consists of an endoscopic imaging probe, dual-wavelength pulsed laser source, rotary scanning device, and data acquisition and control module. First, we design an all-fiber endoscope probe containing two functional optical fibers as follows: one responsible for guiding and focusing the pulsed light and the other equipped with a laser ultrasonic sensor to detect the photoacoustic signal. Second, we design a rotational scanning device that rotates synchronously with the probe to achieve fast and unidirectional rotary scanning. This is achieved by miniaturizing the 980-nm pump laser, the optical amplifier, and the photodetector. Finally, we perform high-resolution in vivo endoscopic imaging of the rat rectum.
The endoscope probe has a diameter of 2.75 mm, a resolution of 12.5 μm, signal jitter root mean square of 2.5%, and a B-scan frequency of 1 Hz. The instrument is stable and provides spatial resolution in high-speed scanning and is suitable for small animal digestive tract endoscopic imaging. The functional imaging results of the rectum of healthy rats show that we achieve 360°scanning, obtain the three-dimensional imaging results of hemoglobin concentration distribution, and show the vascular structure of the inner wall of the rat rectum. Along with the spatial distribution of blood oxygen saturation, the images show the distributions of the artery and vein in the inner wall (Fig. 3). The imaging results of septic rats show the changes in microcirculation. According to the imaging result, the number of blood vessels in the intestine of rats gradually decreases, and the blood oxygen saturation also declines in 5 h (Fig. 4). The above results reflect the phenomenon of insufficient tissue perfusion caused by sepsis.
In summary, we develop a photoacoustic endoscope for in vivo rectal imaging. By using fiber optic ultrasound sensors, the endoscope can image the vascular structure and visualize the changes in oxygen saturation. By using this endoscope, we can visualize the gastrointestinal microcirculatory disorder caused by lesions. The structure, number, and blood oxygen saturation level of blood vessels are significantly changed. The experimental results show that this technology can provide functional imaging results with high spatial resolution and high contrast in the endoscopic imaging of narrow cavity structures, thus providing a feasible imaging method for the characterization of microcirculation status and the diagnosis and treatment of acute and severe diseases.
陈小龙, 梁贻智, 仲晓轩, 白雪, 金龙, 黄卫, 黄澄, 牛晓兵, 郭珊珊, 关柏鸥. 活体小动物脓毒症肠道模型的光声内窥成像研究[J]. 中国激光, 2023, 50(9): 0907103. Xiaolong Chen, Yizhi Liang, Xiaoxuan Zhong, Xue Bai, Long Jin, Wei Huang, Cheng Huang, Xiaobing Niu, Shanshan Guo, Baiou Guan. In Vivo Photoacoustic Endoscopy Imaging of Gastrointestinal Model of Septic Small-Animal[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2023, 50(9): 0907103.