硅酸镱环境障涂层抗熔盐腐蚀行为与机制研究
硅基非氧化物陶瓷及其复合材料具有低密度、高比强度、耐高温、抗氧化和优异的高温力学性能等特点, 可部分取代高温合金应用于航空发动机的热端部件[1]。在干燥环境中, 硅基非氧化物陶瓷材料与氧气发生反应生成SiO2保护层, 可以避免其继续氧化。然而, 航空发动机的服役环境包含多种腐蚀介质(如高温水蒸气、熔盐等), 会与SiO2保护层反应生成挥发性的Si(OH)4, 导致材料性能迅速退化[2-3]。环境障涂层(Environmental Barrier Coating, EBC)涂覆于硅基非氧化物陶瓷材料表面, 能够将基体与发动机中的腐蚀性介质隔离开来, 从而有效提高材料在发动机环境中的性能稳定性[4]。
稀土硅酸盐材料具有良好的相稳定性、优异的耐蚀性能、与基体匹配的热膨胀系数等特点, 是最具应用潜力的环境障涂层材料。王京阳等[5]结合第一性原理和实验表征系统研究了不同稀土硅酸盐块体材料的力学与热学性能。王一光等[6-7]针对稀土硅酸盐块体材料的耐蚀性能开展了相关研究工作, 发现X2-RE2SiO5比X1-RE2SiO5具有更好的耐蚀性能。近年来, 通过高熵化设计优化稀土硅酸盐材料的性能也引起了研究者的关注[8-9]。这些工作为EBC的选材和结构优化设计提供了可靠的理论依据。稀土硅酸盐用作涂层材料时, 其结构、性能与块体材料相比会产生差异。本研究团队[10⇓⇓⇓⇓-15]针对不同稀土硅酸盐涂层材料的显微结构、热学力学性能和耐蚀性能开展了系列研究, 发现稀土硅酸盐涂层在制备过程中易形成孔隙和裂纹等缺陷, 并分解产生氧化物第二相, 从而影响涂层的抗热震和耐蚀性能。为提高EBC的服役性能, 研究者[16-17]开发了稀土硅酸盐/Si和稀土硅酸盐/Mullite/Si等涂层体系。张小锋等[18⇓⇓-21]采用等离子喷涂-物理气相沉积技术(Plasma Spray-Physical Vapor Deposition, PS-PVD)制备了Yb2SiO5/Mullite/Si环境障涂层体系, 探讨了涂层沉积机制及其在高温环境下的显微结构演化过程, 并提出了通过表面镀Al来提高EBC耐蚀性的新方法。Hu等[22]设计了Lu2Si2O7- Lu2SiO5/Mullite双涂层体系, 该体系可有效提高服役温度(1450 ℃), 但热循环过程中因产生贯穿裂纹而失效。本研究团队[10,23]设计并制备了Yb2SiO5/ Yb2Si2O7/Si涂层体系, 发现该涂层体系各层之间化学相容性好, 具有良好的抗热震性能、抗裂纹扩展性能和抗CMAS(CaO-MgO-Al2O3- SiO2)腐蚀性能。
涡轮发动机在服役过程中会面临Na2SO4、NaCl等盐污染物引起的热腐蚀[24⇓-26]。Na2SO4主要由矿物燃料中硫的氧化产物(SO2/SO3)与大气中的NaCl气溶胶反应而形成。如果涡轮发动机在海洋环境中运行, NaCl会与发动机燃料中的SO3及水蒸气发生反应生成Na2SO4[27]。此外, 吸入的NaCl与Na2SO4的共晶混合物熔点较低(~620 ℃), 也会导致材料在低温下发生腐蚀[28]。EBC中硅黏结层的氧化产物SiO2与Na2SO4发生反应生成Na2SiO3和SO3, 进一步加剧了涂层性能的衰退[29]。因此, Na2SO4、NaCl等沉积物对EBC的腐蚀是值得引起重视的问题。
Sun等[30]研究了γ-Y2Si2O7的Na2SO4腐蚀行为和机制, 发现其在950 ℃环境下腐蚀20 h生成条形的磷灰石相NaY9Si6O26和富硅层, 腐蚀产物在高温下易熔融形成液相, 可填充涂层内部孔隙, 有利于延缓腐蚀。Fan等[31]发现在950 ℃、Na2SO4+V2O5熔盐环境下, γ-Y2Si2O7腐蚀20 h会生成NaY9Si6O26相。Opila等[27]对Yb2Si2O7/Si涂层体系的Na2SO4腐蚀行为研究发现, 经1316 ℃腐蚀不足1 h, Yb2Si2O7全部反应; 涂层体系失效的原因是热生长氧化物(Thermally Grown Oxide, TGO)的生成以及无定型硅酸钠的渗透与迁移。目前未发现文献报道Yb2O3-SiO2-Na2O的相图, 但Yb2O3-SiO2-Na2O化合物的合成研究已证明存在钠磷灰石相NaYb9Si6O26以及Na3YbSi2O7和NaYbSiO4相[32-33]。
Yb2SiO5/Yb2Si2O7/Si涂层体系具有良好的高温性能, 但其在Na2SO4热腐蚀环境中的腐蚀行为和机制尚无系统研究。本工作以Yb2SiO5/Yb2Si2O7/Si涂层体系为研究对象, 探究该体系在900 ℃、Na2SO4+25% NaCl熔盐环境中的腐蚀行为, 明确不同腐蚀时间的涂层体系中各层的显微结构变化及失效机制。这些结果将为稀土硅酸盐环境障涂层的设计和性能优化提供科学依据。
1 实验方法
1.1 涂层制备
采用固相反应法合成Yb2SiO5和Yb2Si2O7, 喷涂粉体的具体合成方法参考团队前期工作[12,15]。以尺寸为ϕ25.4 mm×3 mm的SiC陶瓷作为基体, 采用真空等离子喷涂技术(VPS, A-2000; Oerlikon Metco, Switzerland)分别将Si、Yb2Si2O7和Yb2SiO5粉体依次喷涂在基体上, 最终获得Yb2SiO5/Yb2Si2O7/Si涂层体系。制备的样品用无水乙醇超声清洗3次, 烘干、备用。真空等离子喷涂参数见
表 1. 真空等离子喷涂参数
Table 1. Operating parameters used for vacuum plasma spraying
|
1.2 腐蚀实验
研究采用马弗炉进行热腐蚀实验。模拟的熔盐腐蚀环境为900 ℃空气环境, 熔盐成分为Na2SO4+ 25% NaCl。首先以去离子水为分散剂, 将熔盐粉体均匀分散, 涂覆于涂层表面。随后在120 ℃干燥箱中干燥15 min, 反复涂覆, 使表面熔盐浓度达6 mg/cm2。将样品放入马弗炉中, 设置并启动升温程序, 以10 ℃/min升温至900 ℃并保温10 h, 然后取出样品并在其表面重新涂覆6 mg/cm2的熔盐粉体, 此为一个循环。观察样品形貌, 实验循环进行至涂层开始出现剥落为止。
1.3 样品表征
采用光学显微镜(OM, E3CMOS, 宁波舜宇仪器有限公司, 中国)观察样品实验前后的宏观形貌。采用X射线衍射仪(XRD, RAX-10, Rigaku, 日本)表征不同腐蚀时间的涂层物相。根据衍射峰强度, 通过RIR值法计算腐蚀后涂层表面的物相含量(Jade 6.5)。采用场发射扫描电子显微镜(SEM, Magellan 400, FEI, 美国)分析涂层的表面和截面等微观结构。分析截面样品前, 需要进行金相抛光处理, 后经无水乙醇超声清洗并烘干。采用电子顺磁共振仪(EPR, A300-10, Bruker, 德国)表征涂层中的氧空位浓度。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 喷涂态涂层显微结构分析
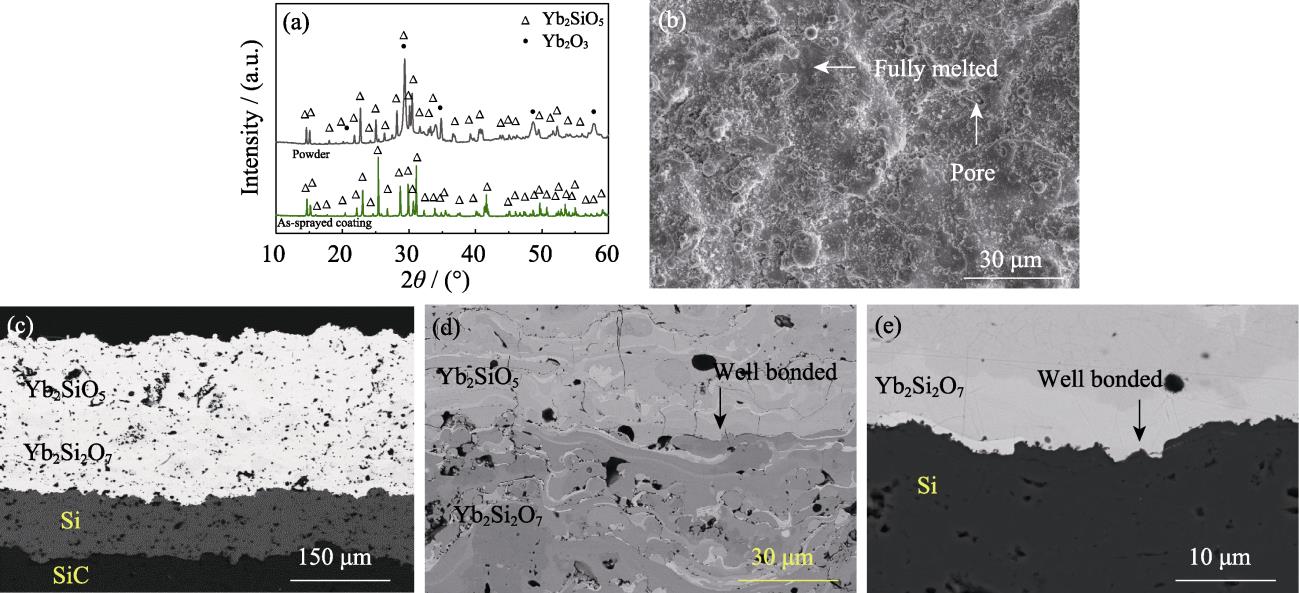
图 1. 喷涂态Yb2SiO5/Yb2Si2O7/Si涂层的XRD图谱和显微结构
Fig. 1. XRD patterns and SEM morphologies of as-sprayed Yb2SiO5/Yb2Si2O7/Si coating
2.2 熔盐腐蚀行为研究

图 2. Yb2SiO5/Yb2Si2O7/Si涂层熔盐腐蚀不同时间的宏观形貌
Fig. 2. Macro-photographs of Yb2SiO5/Yb2Si2O7/Si coating after molten salt corrosion for different time
Yb2SiO5/Yb2Si2O7/Si涂层经不同时间腐蚀后的XRD图谱如

图 3. Yb2SiO5/Yb2Si2O7/Si涂层经熔盐腐蚀不同时间的XRD图谱
Fig. 3. XRD patterns of Yb2SiO5/Yb2Si2O7/Si coating after molten salt corrosion for different time

图 4. Yb2SiO5/Yb2Si2O7/Si涂层经熔盐腐蚀不同时间的低倍和高倍形貌及其不同位置元素分析
Fig. 4. Surface morphologies of Yb2SiO5/Yb2Si2O7/Si coating after molten salt corrosion for different time and correponding EDS analyses of different areas
Yb2SiO5/Yb2Si2O7/Si涂层经900 ℃熔盐腐蚀不同时间后Yb2SiO5层的截面形貌如

图 5. Yb2SiO5 面层经熔盐腐蚀不同时间的截面形貌及其元素面分析
Fig. 5. Cross-sectional morphologies and corresponding element analyses of Yb2SiO5 top layer after molten salt corrosion for different time

图 6. Yb2SiO5/Yb2Si2O7/Si涂层经熔盐腐蚀不同时间的截面形貌及其EDS元素面分析
Fig. 6. Cross-sectional morphologies and corresponding EDS element mappings of Yb2SiO5/Yb2Si2O7/Si EBCs after molten salt corrosion for different time

图 7. 经Na2SO4+25% NaCl熔盐腐蚀不同时间的涂层体系Yb2Si2O7中间层渗透区高倍截面形貌及EDS元素面分析
Fig. 7. High-magnification cross-sectional morphologies and corresponding EDS mappings of infiltration zone in Yb2Si2O7 interlayer after molten salt corrosion for different time
表 2. 图7 中标记区域的EDS元素组成/%(原子分数)
Table 2. EDS elemental compositions of the marked regions in Fig. 7 /%(in atom)
|
2.3 熔盐腐蚀机制分析

图 8. Yb2SiO5/Yb2Si2O7/Si涂层经900 ℃、Na2SO4+25% NaCl熔盐腐蚀示意图
Fig. 8. Schematic diagrams of Yb2SiO5/Yb2Si2O7/Si coating under Na2SO4+25% NaCl molten salt corrosion at 900 ℃
随着腐蚀时间延长, Yb2SiO5涂层中Yb2O3含量逐渐减少, 这主要由于Yb2O3与Na2SO4反应生成了Yb2(SO4)3(反应式(1))。而Yb2(SO4)3易从涂层表面脱落, 因此XRD中没有检测出该物相[35]。当熔盐渗透至中间层时, 与Yb2Si2O7反应生成条状稀土钠磷灰石NaYb9Si6O26(反应式(2)), 同时在Na元素富集的黑色衬度区可能形成由Yb2O3-SiO2-Na2O组成的化合物。随着腐蚀循环次数增加, 在热应力的作用下, 表层涂层出现贯穿裂纹, 熔盐进一步渗透, 且渗透区增大, 渗透深度增加, 促使生成更多的NaYb9Si6O26。NaCl中的Cl-会与O2发生反应生成Cl2, 同时Na2SO4与硅酸盐发生反应生成SO2等挥发性气体, 随着腐蚀时间延长, 生成的气体更多, 从而导致涂层变得疏松多孔, 这为腐蚀介质提供通道, 加速了涂层失效。
通过EPR测试Yb2SiO5和Yb2Si2O7涂层的氧空位浓度, 如
3 结论
研究采用真空等离子喷涂技术制备了Yb2SiO5/Yb2Si2O7/Si涂层体系, 研究了涂层在900 ℃空气环境中的熔盐(Na2SO4+25% NaCl)腐蚀行为与机制, 得出以下结论:
1)Yb2SiO5/Yb2Si2O7/Si涂层结构较为致密, 各层之间结合良好。腐蚀过程中, Na2SO4+25% NaCl熔盐渗透多层体系中的Yb2SiO5涂层, 在Yb2Si2O7中间层发生富集, 但并未渗透至硅黏结层。结果显示该涂层体系具有良好耐熔盐腐蚀性能。
2)Yb2SiO5涂层中Yb2O3第二相会与熔盐发生反应生成Yb2(SO4)3和Na2O。随着腐蚀时间延长, Yb2O3含量减少。Yb2Si2O7与Na2SO4反应生成NaYb9Si6O26磷灰石相, 并产生Cl2、SO2等气体, 导致涂层孔隙增加, 从而影响其服役寿命。
[15] ZHONGX, ZHUT, NIUY R, et al.Effect of microstructure evolution and crystal structure on thermal properties for plasma- sprayed RE2SiO5 (RE=Gd, Y, Er) environmental barrier coatings. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2021, 85:141-151.
[19] WANGC, ZHANGX F, ZHOUK S, et al.Nano-composite structured environmental barrier coat-ings prepared by plasma spray- physical vapor deposition and their thermal cycle performance. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2019, 48(11):3455-3462
[23] LIUP P, ZHONGX, NIUY R, et al.Reaction behaviors and mechanisms of tri-layer Yb2SiO5/Yb2Si2O7/Si environmental barrier coatings with molten calcium-magnesium-alumino-silicate. Corrosion Science, 2022: 110069.
[35] 蒋凤瑞.B1-xSxAS及稀土硅酸盐环境障碍涂层热腐蚀性能研究. 西安: 西北工业大学博士学位论文, 2017.
刘平平, 钟鑫, 张乐, 李红, 牛亚然, 张翔宇, 李其连, 郑学斌. 硅酸镱环境障涂层抗熔盐腐蚀行为与机制研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(12): 1267. Pingping LIU, Xin ZHONG, Le ZHANG, Hong LI, Yaran NIU, Xiangyu ZHANG, Qilian LI, Xuebin ZHENG. Molten Salt Corrosion Behaviors and Mechanisms of Ytterbium Silicate Environmental Barrier Coating[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(12): 1267.




