腔道肿瘤光动力诊疗内窥技术的发展及临床应用现状  下载: 600次
下载: 600次
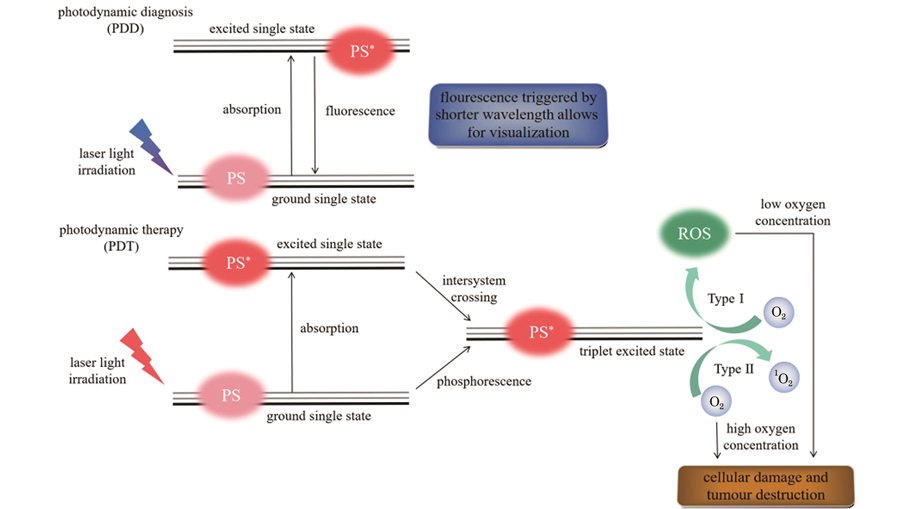
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a novel cancer treatment technique based on the local or systemic application of a photosensitizer that selectively accumulates within tumor cells and peaks after a certain time. The photosensitizer can then be activated by light of an appropriate wavelength, leading to generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). There are three main processes by which ROS contribute to tumor destruction in PDT: direct cellular damage, indirect vascular shutdown, and activation of immune responses against tumor cells. For deep luminal tumors, the PDT approach involves the passage of a flexible optical fiber that can follow the naturally curving orifice of the human body to deliver the laser directly to the target tumor through the operating channel of a flexible endoscope. Endoscopic photodynamic therapy has a good selective killing effect on tumors, resulting in a strong curative effect. Endoscopic PDT is also minimally invasive, making it suitable for treating gastrointestinal and respiratory tumors. PDT spares vital organ function while effectively removing tumor cells after treatment; therefore, it is a standard treatment option for esophageal cancer and central lung cancers.
During PDT for luminal tumors, the endoscope, an important auxiliary device, can accurately identify the lesion tissue preoperatively, provide a high-definition view in real time perioperatively, guide optical fibers to emit light toward the lesion, and detect postoperative lesion response to evaluate treatment efficacy. However, conventional endoscopes display technical deficiencies in achieving the above functions. Hence, it is important and necessary to summarize existing specific problems and the application status of endoscopic technology in PDT to guide the development of photodynamic diagnosis and treatment technologies.
Conventional endoscopes have some limitations and problems, such as invisible targets resulting from lens exposure under the laser, deviations between treatment light and the observation field, leakage, and tumor tissue misdiagnosis. Here we analyze the specific causes of these problems by briefly describing the basic principles of electronic endoscopy. We comprehensively introduce the laser visualization endoscope during PDT, coaxial laser endoscope, and fluorescence diagnostic endoscopes and describe the combination of the endoscopic systems of photodynamic diagnosis (PDD) and PDT, which were earlier separated and now developed into integrated systems. We further introduce the integrated endoscope used for PDD and PDT.
Using the laser visualization endoscope during PDT avoids charge-coupled device (CCD) exposure resulting from intense laser light and, therefore, whiteout; however, the real picture of the tumor can be restored. Prior studies have reported that simultaneous imaging endoscopes are highly suitable for PDT. A coaxial laser endoscope, which couples the laser fiber and optical image fiber on the same axis with the same view field and laser irradiation field, improves laser positioning accuracy. Fluorescence diagnostic endoscopes include autofluorescence endoscopes and PDD-based endoscopes, in which the tumor and normal tissue are labeled with different fluorescent colors. These have a higher diagnostic sensitivity than white light detection endoscopes. Photodynamic diagnosis and therapy all-in-one endoscopes can realize PDD and PDT simultaneously, avoiding the inconvenience caused by switching endoscopes, detect photosensitizer consumption, and judge the treatment effect. These new all-in-one endoscopes can be used for PDT and PDD. The innovation of endoscopic devices plays an important role in the clinical practice of PDT, reducing technical difficulty and operation time.
The endoscopy technology for the clinical application of PDD and PDT in luminal tumors has gradually adapted to the disease characteristics. PDD is used to diagnose gastric cancer, allowing an objective diagnosis and not completely relying on the endoscopist’s clinical experience. Thus, it is a promising tool for diagnosing early peritoneal metastases in gastric cancer. Moreover, the simultaneous video endoscopy systems can image tumor sites in greater detail, improving PDD and PDT accuracy. PDT for unresectable cholangiocarcinoma is usually performed with duodenoscopy guided by endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) and percutaneous transhepatic cholangioscopy (PTCS). Transoral digital cholangioscopy can shorten fluoroscopy time and reduce patient and physician radiation exposure. Regarding central lung cancer, PDT can be assisted by bronchoscopy and autofluorescence bronchoscopy. In peripheral lung cancer cases, the optical fiber can be placed under computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging guidance. Furthermore, a new small-diameter laser probe, the composite-type optical fiberscope, was recently developed to enable non-invasive treatment. Blue-light cystoscopy assists in the diagnosis of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer and has been recognized clinically to resolve the problem of residual tumors after transurethral resection. In conclusion, these new endoscopic devices make PDT and PDD more efficient, minimally invasive, and safe.
Here we summarize the clinical application status of PDT for luminal tumors. With the increasing clinical demand for PDT, endoscopic technology will be continuously optimized for luminal tumors, featuring improving device intelligence, minimally invasive usage, and modernization. The integration of emerging technologies will allow the products to perform more powerful functions, making PDT more diverse and further improving its surgical quality.
赵萌, 王荣峰, 路倚文, 张晓刚, 吴荣谦, 吕毅, 庞利辉. 腔道肿瘤光动力诊疗内窥技术的发展及临床应用现状[J]. 中国激光, 2023, 50(9): 0907202. Meng Zhao, Rongfeng Wang, Yiwen Lu, Xiaogang Zhang, Rongqian Wu, Lü Yi, Lihui Pang. Development and Clinical Application of Endoscopic Techniques in Photodynamic Therapy for Luminal Tumors[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2023, 50(9): 0907202.