1 暨南大学 光子技术研究院 广东省光纤传感与通信技术重点实验室,广东 广州 511443
2 中国科学院理化技术研究所 仿生智能界面科学中心 有机纳米光子学实验室,北京 100190
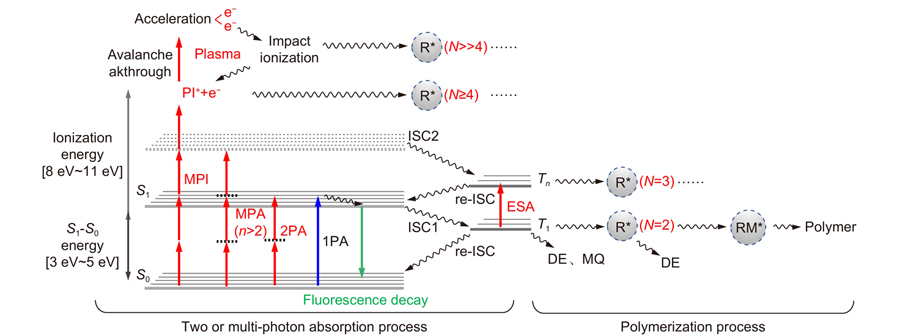
Overview: Femtosecond laser two-photon polymerization (TPP) micro-nanofabrication technology is a new type of three-dimensional lithography technology that integrates nonlinear optics, ultra-fast pulsed laser, microscopic imaging, ultra-high-precision positioning, three-dimensional (3D) graphics CAD modeling, and photochemical materials. It has the characteristics of simplicity, low cost, high resolution, true 3D, and so on. Different from the technical route of shortening the wavelength of the traditional lithography, this TPP technology breaks through the optical diffraction limit using the ultrafast laser in the near-infrared and the nonlinear optical effect of the interaction between the laser and the material. TPP can achieve true 3D fabrication of complex 3D structures. After the femtosecond pulse laser is tightly focused in space, photopolymerization is initiated by the two-photon absorption(TPA), which can limit the fabrication area in the center of the focus. The interaction time of the ultrashort pulse with the material is much lower than the thermal relaxation of the material, avoiding the photothermal effect. The lateral linewidth can be reduced to about 100 nm due to the strong threshold characteristics of the two-photon absorption process. Thus, TPP is an ideal fabrication method in the field of 3D micro-nanostructure. Since 2001, Kawata’s team has used a near-infrared femtosecond laser with a wavelength of 780 nm to fabricate a "nanobull" with the size of red blood cells. It fully demonstrated the advantages of TPP in the preparation of three-dimensional micro-nano structures. At the same time, a polymer nanodot with a size of 120 nm was fabricated, which was only 1/7 of the laser wavelength, breaking the optical diffraction limit in this study. Since then, scientists from various countries have improved the line width, resolution, and other parameters of 3D structure by continuously improving the materials, structure, processing technology and light field control, and other aspects. At the same time, with the continuous development and improvement of the 3D nanostructure fabrication technology, the advantages of TPP technology are also reflected in some application fields, such as micro-optical devices, integrated optical devices, micro-electromechanical systems, and biomedical devices. This paper will systematically introduce the femtosecond laser TPP micro-nanofabrication technology, including the fabricating principle, the development of fabricating methods, and its research overview in many application fields. Finally, its existing problems and future development and application prospects are discussed.
飞秒激光 双光子聚合 光学衍射极限 加工分辨力 加工效率 femtosecond laser two-photon polymerization optical diffraction limit resolution efficiency
暨南大学光子技术研究院,广东省光纤传感与通信技术重点实验室,广东 广州 511443
光聚合微纳3D打印作为一种微纳尺度的增材制造技术,在高精度、复杂三维微纳结构的制造方面具有显著优势,已被广泛应用于微机电系统、微纳光子器件、微流体器件、生物工程领域。本文首先介绍了光聚合微纳3D打印技术的光物理/光化学原理,重点对所涉及的各种类型的打印工艺及其应用领域进行综述;然后讨论了一些前沿性的微纳3D打印方法,通过回顾和比较这些最新的技术,阐明了打印分辨率与打印效率之间的关系,以及串行扫描、并行扫描、面投影和体投影的打印模式对微纳3D打印性能的影响;最后对微纳3D打印技术进行全面总结与概述,并对其未来的发展趋势和应用前景予以展望。
中国激光
2022, 49(10): 1002703
暨南大学光子技术研究院,广东省光纤传感与通信技术重点实验室,广东 广州 511443
现有主流光刻技术与设备变得越来越复杂的原因之一在于其仍然囿于线性光学光刻范畴,未能突破光学衍射极限,是衍射极限附近的光刻技术。采用紫外、可见或近红外等长波长光源进行纳米光刻,必须突破光学衍射极限,实现超衍射光刻,研究和发展激光超衍射纳米光刻技术具有十分重要的科学意义和应用价值。本文从光学衍射极限的基本概念出发,系统阐述各类超衍射光刻原理与方法,重点回顾激光远场超衍射光刻相关研究成果与最新进展,并对其现存的问题和发展方向进行评述。
激光与光电子学进展
2022, 59(9): 0922029
上海交通大学机械与动力工程学院,上海 200240
光场相机作为新一代的成像设备,能够同时捕获光线的空间位置和入射角度,然而其记录的光场存在空间分辨率和角度分辨率之间的制约关系,尤其子孔径图像有限的空间分辨率在一定程度上限制了光场相机的应用场景。因此本文提出了一种融合多尺度特征的光场图像超分辨网络,以获取更高空间分辨率的光场子孔径图像。该基于深度学习的网络框架分为三大模块:多尺度特征提取模块、全局特征融合模块和上采样模块。网络首先通过多尺度特征提取模块学习4D光场中固有的结构特征,然后采用融合模块对多尺度特征进行融合与增强,最后使用上采样模块实现对光场的超分辨率。在合成光场数据集和真实光场数据集上的实验结果表明,该方法在视觉评估和评价指标上均优于现有算法。另外本文将超分辨后的光场图像用于深度估计,实验结果展示出光场图像空间超分辨率能够增强深度估计结果的准确性。
超分辨 光场 深度学习 多尺度特征提取 特征融合 super-resolution light-field deep learning multi-scale feature extraction feature fusion
1 中国科学院理化技术研究所仿生智能界面科学中心, 北京 100190
2 中国科学院大学未来技术学院, 北京 100049
3 中国科学院重庆绿色智能技术研究院, 重庆 401122
研究了一种基于数字微镜器件 (DMD)的数字掩模投影光刻 (DMPL)技术,以400 nm飞秒激光作为光源, 结合高缩放比投影系统,来缩小光刻胶与光子束的反应区域,通过调控不同DMD像素投影光场强度分布,将投影光刻的线宽分辨率推进至亚微米 尺度,实现了具有跨尺度加工能力(单次曝光面积在百微米以上,曝光精度在百纳米)的DMPL技术,同时详细对比分析了DMPL 中存在的几何和 物理光学模型,阐明了像素个数与加工结构尺寸的关系,并进一步基于物理光学模型分析了DMPL中极限分辨率的关键科学问题。
激光技术 仪器数字掩模投影光刻 数字微镜器件 跨尺度 飞秒激光 分辨率 laser technology instrument digital-mask projective lithography digital micromirror device cross-scale femtosecond laser resolution
1 湘潭大学 信息工程学院, 湖南 湘潭 411105
2 湘潭大学 智能计算与信息处理教育部重点实验室, 湖南 湘潭 411105
可靠、有效的视盘分割对自动眼底病变诊断分析具有重要意义。提出了一种基于平滑滤波和CV模型的视盘分割算法。在利用投影法定位出视盘中心后, 首先采用Gabor滤波技术提取并移除视盘局部区域的主血管, 然后利用邻域信息通过插值运算填充被移除血管区域的像素, 采用边缘保留平滑滤波对视盘区域进行平滑, 最后利用基于区域信息的CV水平集模型分割出视盘的边界。该方法在MESSIDOR数据库上进行了测试, 平均分割准确率为0.83, 表现出了良好的分割性能。
眼底图像 视盘分割 平滑滤波 CV水平集模型 retinal fundus image optic disc segmentation smoothing filtering CV model of level sets
1 湘潭大学 信息工程学院, 湖南 湘潭 411105
2 智能计算与信息处理教育部重点实验室(湘潭大学), 湖南 湘潭 411105
可靠、有效的视盘定位对自动眼底病变分析具有重要意义。本文提出一种快速自动定位视盘方法, 首先基于梯度和亮度信息提取视盘的候选区域点; 然后利用血管在视盘区域分布非常集中并且沿垂直方向延伸,对候选点进行匹配滤波最终定位视盘点。本文方法在五个公开的眼底图像数据库1 540 幅图像上进行了测试, 其中1 514幅眼底图像定位成功, 准确率达到了98.3%, STARE 图像平均处理时间为6.3 s, 在所有正常和病变眼底图像测试中表现出良好的鲁棒性。
眼底图像 视盘检测 滤波 retinal fundus image optic disc detection filtering





