High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 2018, 6 (2): 02000e21, Published Online: Jul. 5, 2018
EMP control and characterization on high-power laser systems  Download: 651次
Download: 651次
high energy density physics high-power laser related laser components laser plasmas interaction target design and fabrication.
Abstract
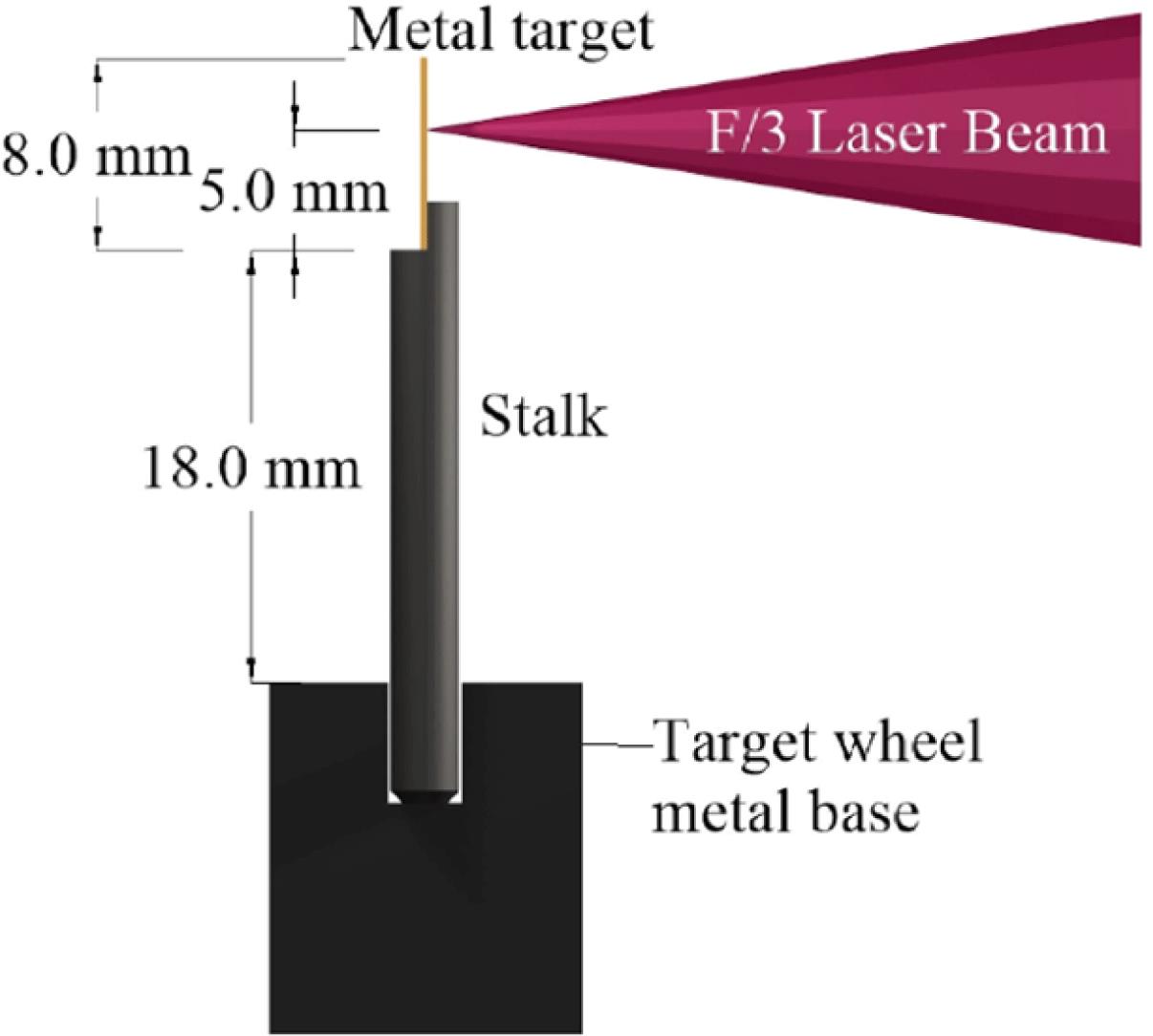
Giant electromagnetic pulses (EMP) generated during the interaction of high-power lasers with solid targets can seriously degrade electrical measurements and equipment. EMP emission is caused by the acceleration of hot electrons inside the target, which produce radiation across a wide band from DC to terahertz frequencies. Improved understanding and control of EMP is vital as we enter a new era of high repetition rate, high intensity lasers (e.g. the Extreme Light Infrastructure). We present recent data from the VULCAN laser facility that demonstrates how EMP can be readily and effectively reduced. Characterization of the EMP was achieved using B-dot and D-dot probes that took measurements for a range of different target and laser parameters. We demonstrate that target stalk geometry, material composition, geodesic path length and foil surface area can all play a significant role in the reduction of EMP. A combination of electromagnetic wave and 3D particle-in-cell simulations is used to inform our conclusions about the effects of stalk geometry on EMP, providing an opportunity for comparison with existing charge separation models.
P. Bradford, N. C. Woolsey, G. G. Scott, G. Liao, H. Liu, Y. Zhang, B. Zhu, C. Armstrong, S. Astbury, C. Brenner, P. Brummitt, F. Consoli, I. East, R. Gray, D. Haddock, P. Huggard, P. J. R. Jones, E. Montgomery, I. Musgrave, P. Oliveira, D. R. Rusby, C. Spindloe, B. Summers, E. Zemaityte, Z. Zhang, Y. Li, P. McKenna, D. Neely. EMP control and characterization on high-power laser systems[J]. High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 2018, 6(2): 02000e21.