High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 2020, 8 (2): 02000e16, Published Online: May. 8, 2020
Generation mechanism of 100 MG magnetic fields in the interaction of ultra-intense laser pulse with nanostructured target
Figures & Tables
Fig. 1. Schematic diagram of the initial electron density for the partial nanolayered target.
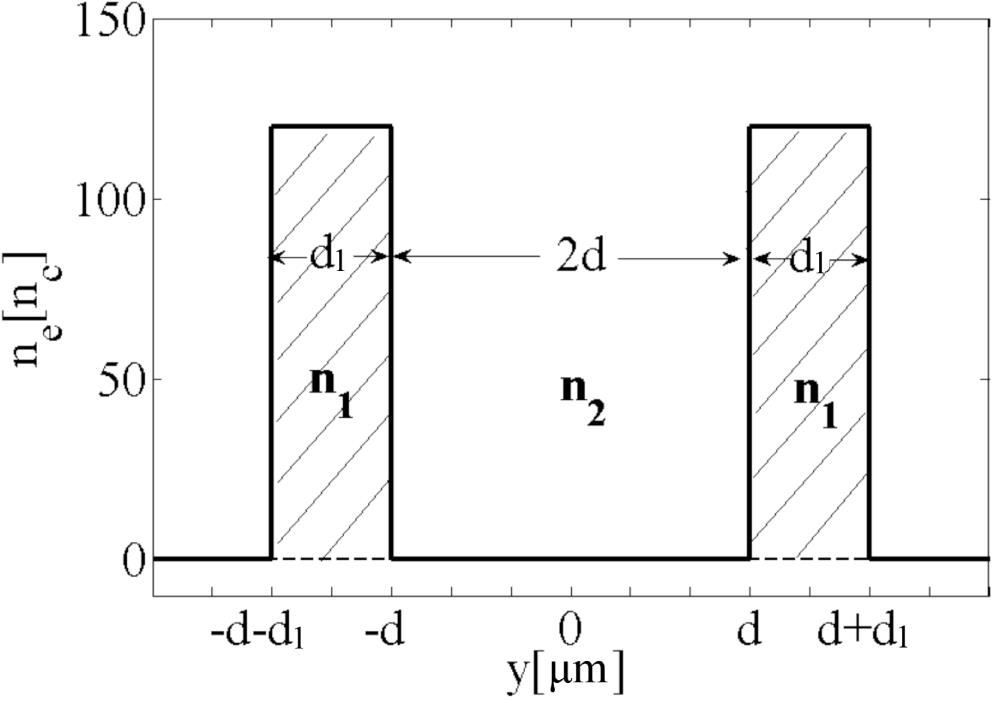
Fig. 2. The magnetic field generated in the nanolayered target (a) with different electron density of  and (b) with different fast electron current density of
and (b) with different fast electron current density of  . The initial plasma density of the nanolayers is
. The initial plasma density of the nanolayers is  . The other parameters are
. The other parameters are  and
and  . The unit of the magnetic field here is
. The unit of the magnetic field here is  MG.
MG.

Fig. 3. (a) The distribution of the magnetostatic field  at time
at time  . (b) The transverse distributions of self-generated magnetic fields at
. (b) The transverse distributions of self-generated magnetic fields at  and
and  are plotted. The blue solid curve is for the simulation result and the black dot curve is for the analytical result.
are plotted. The blue solid curve is for the simulation result and the black dot curve is for the analytical result.

J. M. Tian, H. B. Cai, W. S. Zhang, E. H. Zhang, B. Du, S. P. Zhu. Generation mechanism of 100 MG magnetic fields in the interaction of ultra-intense laser pulse with nanostructured target[J]. High Power Laser Science and Engineering, 2020, 8(2): 02000e16.
 MG. The blue dashed line stands for the simulation results and the black solid line stands for the theoretical analysis result.
MG. The blue dashed line stands for the simulation results and the black solid line stands for the theoretical analysis result.





