Chinese Optics Letters, 2018, 16 (5): 050004, Published Online: Jul. 4, 2018
Mid-infrared superabsorbers based on quasi-periodic moiré metasurfaces  Download: 643次
Download: 643次
Figures & Tables
Fig. 1. (a) Fabrication procedure of MIM moiré superabsorbers with variable parameters (i.e., spacer thickness d , rotation angle θ
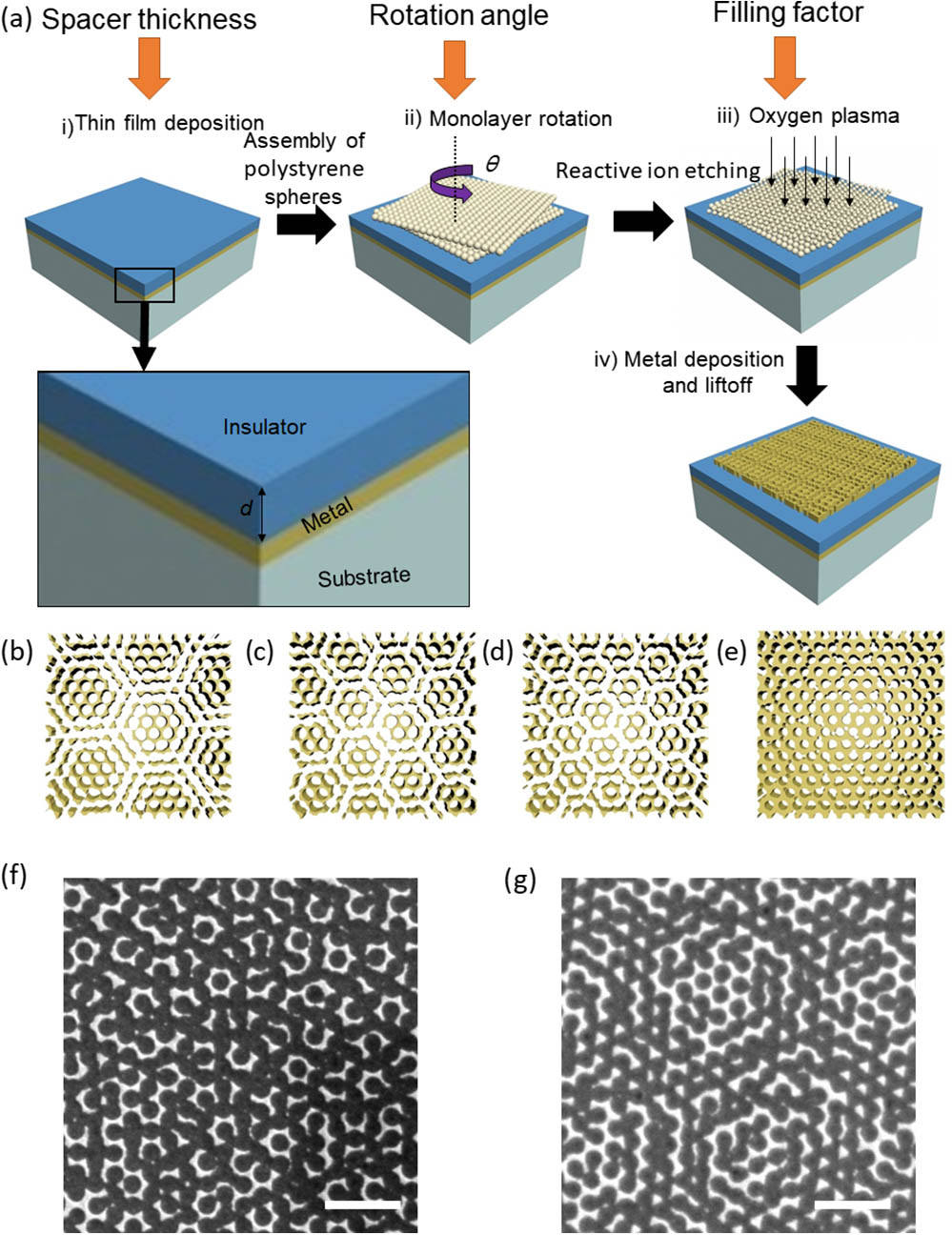
Fig. 2. (a) Unit vectors in the hexagonal hole array. (b) A rectangular area in the hexagonal hole array using V ( 5 , 8 ) V ′ ( 1 , 6 ) ∼ 15 ° ∼ 15 °

Fig. 3. (a) Cross-sectional view of r 12 ′ r 21 ′ t 12 ′ t 21 ′ r 12 ′ r 21 ′ t 12 ′ t 21 ′

Fig. 4. (a) Simulated (black dashed line) absorption for a 15° rotation angle pristine (no spacer) moiré metasurface; simulated (dashed red and blue line) and calculated (solid black line) results comparison for a 15° rotation angle moiré MIM structure with 800 nm spacer thickness. The PML boundary is applied in the simulation. (b) Simulated (dashed line) and calculated (solid line) results comparison for different rotation angles at 800 nm spacer thickness. The periodic boundary is applied in the simulation.

Fig. 5. (a) Calculated narrowband absorber with an optimized spacer thickness (1300 nm) at different rotation angles. (b) A calculated broadband absorber with an optimized spacer thickness (900 nm spacer for 10°, 800 nm spacer for 15°, and 700 nm spacer for 20°).

Fig. 6. (a) Simulated polarization-dependent broadband absorption for a 20° moiré MIM structure with an optimized spacer thickness. (b) Simulated polarization-dependent narrowband absorption for a 20° moiré MIM structure with an optimized spacer thickness.

Yaoran Liu, Zilong Wu, Eric H. Hill, Yuebing Zheng. Mid-infrared superabsorbers based on quasi-periodic moiré metasurfaces[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2018, 16(5): 050004.






