Chinese Optics Letters, 2015, 13 (3): 032301, Published Online: Sep. 25, 2018
Highly efficient blue organic light-emitting diodes using various hole and electron confinement layers  Download: 890次
Download: 890次
230.3670 Light-emitting diodes 230.0230 Optical devices 230.4170 Multilayers 230.4205 Multiple quantum well (MQW) modulators 230.5590 Quantum-well, -wire and -dot devices
Abstract
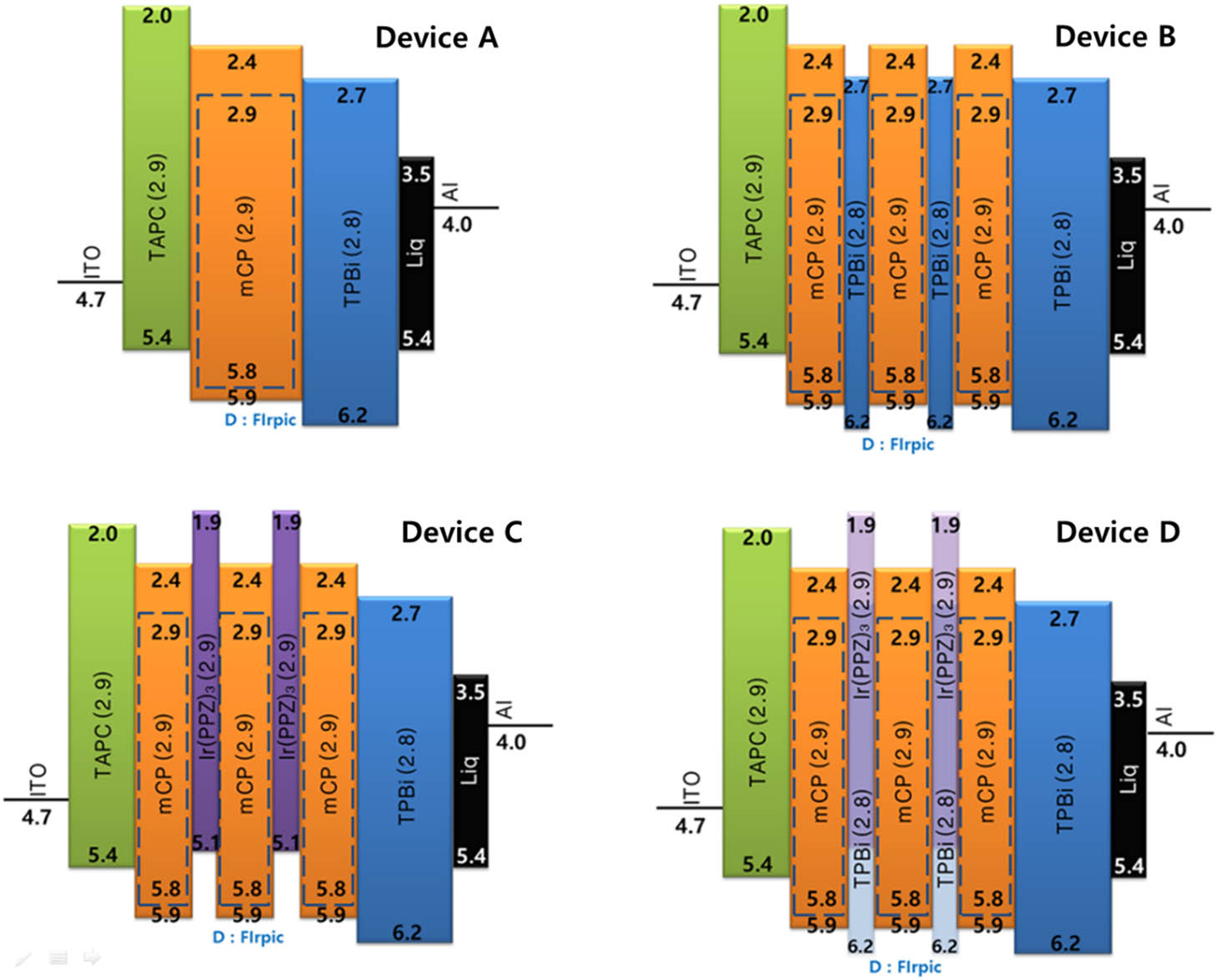
In this Letter, blue phosphorescence organic light-emitting diodes (PHOLEDs) employ structures for electron and/or hole confinement; 1,3,5-tris(N -phenylbenzimiazole-2-yl)benzene is used as a hole confinement layer and tris-(phenylpyrazole)iridium [Ir ( ppz ) 3 1500 cd / m 2 43.76 cd / A
Jin Sung Kang, Ju-An Yoon, Seung Il Yoo, Jin Wook Kim, Bo Mi Lee, Hyeong Hwa Yu, C.-B. Moon, Woo Young Kim. Highly efficient blue organic light-emitting diodes using various hole and electron confinement layers[J]. Chinese Optics Letters, 2015, 13(3): 032301.