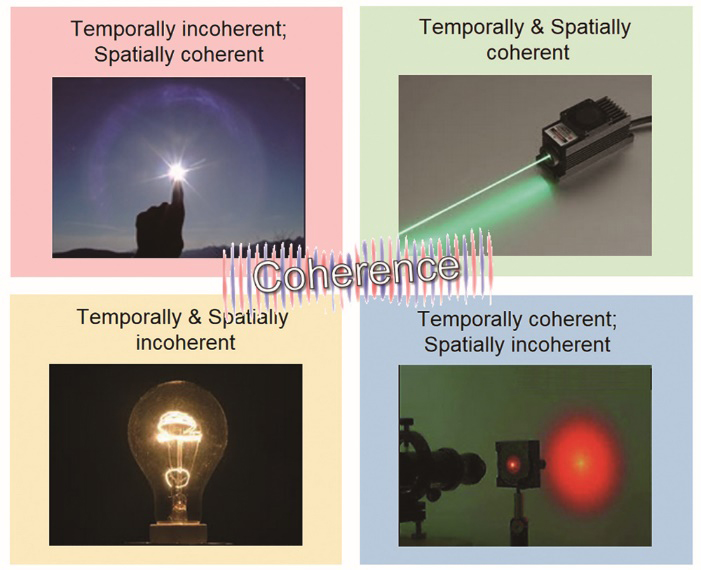
光场相干测量及其在计算成像中的应用  下载: 5987次内封面文章特邀综述
下载: 5987次内封面文章特邀综述
张润南, 蔡泽伟, 孙佳嵩, 卢林芃, 管海涛, 胡岩, 王博文, 周宁, 陈钱, 左超. 光场相干测量及其在计算成像中的应用[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2021, 58(18): 1811003.
Runnan Zhang, Zewei Cai, Jiasong Sun, Linpeng Lu, Haitao Guan, Yan Hu, Bowen Wang, Ning Zhou, Qian Chen, Chao Zuo. Optical-Field Coherence Measurement and Its Applications in Computational Imaging[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2021, 58(18): 1811003.
[1] Maiman T H. Stimulated optical radiation in ruby[J]. Nature, 1960, 187(4736): 493-494.
[2] Abramovici A, Althouse W E, Drever R W, et al. LIGO: the laser interferometer gravitational-wave observatory[J]. Science, 1992, 256(5055): 325-333.
[3] Abbott B P, Abbott R, Abbott T, et al. Observation of gravitational waves from a binary black hole merger[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2016, 116(6): 061102.
[4] Cuche E, Bevilacqua F, Depeursinge C. Digital holography for quantitative phase-contrast imaging[J]. Optics Letters, 1999, 24(5): 291-293.
[5] Schnars U, Jüptner W P O. Digital recording and numerical reconstruction of holograms[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2002, 13(9): R85-R101.
[6] Cuche E, Marquet P, Depeursinge C. Simultaneous amplitude-contrast and quantitative phase-contrast microscopy by numerical reconstruction of Fresnel off-axis holograms[J]. Applied Optics, 1999, 38(34): 6994-7001.
[7] Cuche E, Marquet P, Depeursinge C. Spatial filtering for zero-order and twin-image elimination in digital off-axis holography[J]. Applied Optics, 2000, 39(23): 4070-4075.
[8] SchnarsU, FalldorfC, WatsonJ, et al. Digital holography[M] //Digital holography and wavefront sensing, Heidelberg: Springer, 2014: 39- 68.
[9] Roddier F, Roddier C, Roddier N. Curvature sensing: a new wavefront sensing method[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 1988, 0976: 203-209.
[10] Roddier F. Curvature sensing and compensation: a new concept in adaptive optics[J]. Applied Optics, 1988, 27(7): 1223-1225.
[11] Roddier F. Wavefront sensing and the irradiance transport equation[J]. Applied Optics, 1990, 29(10): 1402-1403.
[12] Roddier N A. Algorithms for wavefront reconstruction out of curvature sensing data[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 1991, 1542: 120-129.
[13] Giewekemeyer K, Thibault P, Kalbfleisch S, et al. Quantitative biological imaging by ptychographic X-ray diffraction microscopy[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of USA, 2010, 107(2): 529-534.
[14] Maiden A M, Morrison G R, Kaulich B, et al. Soft X-ray spectromicroscopy using ptychography with randomly phased illumination[J]. Nature Communications, 2013, 4: 1669.
[15] Thibault P, Elser V, Jacobsen C, et al. Reconstruction of a yeast cell from X-ray diffraction data[J]. Acta Crystallographica Section A Foundations of Crystallography, 2006, 62(4): 248-261.
[16] Rodenburg J M, Hurst A C, Cullis A G, et al. Hard-X-ray lensless imaging of extended objects[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2007, 98(3): 034801.
[17] Rodenburg J M, Hurst A C, Cullis A G. Transmission microscopy without lenses for objects of unlimited size[J]. Ultramicroscopy, 2007, 107(2/3): 227-231.
[19] Hüe F, Rodenburg J M, Maiden A M, et al. Wave-front phase retrieval in transmission electron microscopy via ptychography[J]. Physical Review B, 2010, 82(12): 121415.
[20] Allman B E, McMahon P J, Nugent K A, et al. Phase radiography with neutrons[J]. Nature, 2000, 408(6809): 158-159.
[21] McMahon P J, Allman B E, Jacobson D L, et al. Quantitative phase radiography with polychromatic neutrons[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2003, 91(14): 145502.
[22] Young T. An account of some cases of the production of colours, not hitherto described[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, 1802, 92: 387-397.
[23] Young T I. Experiments and calculations relative to physical optics[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London, 1804, 94: 1-16.
[24] Crease R P. The most beautiful experiment[J]. Physics World, 2002, 15(9): 19-20.
[25] van Cittert P H. Die wahrscheinliche schwingungsverteilung in einer von einer lichtquelle direkt Oder mittels einer linse beleuchteten ebene[J]. Physica, 1934, 1(1/2/3/4/5/6): 201-210.
[26] Zernike F. The concept of degree of coherence and its application to optical problems[J]. Physica, 1938, 5(8): 785-795.
[27] Wolf E. Optics in terms of observable quantities[J]. Il Nuovo Cimento, 1954, 12(6): 884-888.
[28] Hopkins H H. Applications of coherence theory in microscopy and interferometry[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1957, 47(6): 508-526.
[29] Hopkins H H, Thomson G P. The concept of partial coherence in optics[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series: A Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 1951, 208(1093): 263-277.
[30] Hopkins H H, Mott N F. On the diffraction theory of optical images[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London Series: A Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 1953, 217(1130): 408-432.
[31] Mandel L. Concept of cross-spectral purity in coherence theory[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1961, 51(12): 1342-1350.
[32] Mandel L, Wolf E. Spectral coherence and the concept of cross-spectral purity[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1976, 66(6): 529-535.
[33] Wolf E. New theory of partial coherence in the space-frequency domain part II: steady-state fields and higher-order correlations[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1986, 3(1): 76-85.
[34] MandelL, WolfE. Optical coherence and quantum optics[M]. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1995.
[35] Gori F, Santarsiero M, Vicalvi S, et al. Beam coherence-polarization matrix[J]. Pure and Applied Optics: Journal of the European Optical Society Part A, 1998, 7(5): 941-951.
[36] Gori F. Matrix treatment for partially polarized, partially coherent beams[J]. Optics Letters, 1998, 23(4): 241-243.
[37] Wolf E. Unified theory of coherence and polarization of random electromagnetic beams[J]. Physics Letters A, 2003, 312(5/6): 263-267.
[38] Testorf ME, Hennelly BM, Ojeda-CastañedaJ. Phase-space optics: fundamentals and applications[M]. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2010.
[39] Wigner E P. On the quantum correction for thermodynamic equilibrium[J]. Physical Review, 1932, 40(5): 749-759.
[41] Walther A. Radiometry and coherence[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1968, 58(9): 1256-1259.
[42] Walther A. Radiometry and coherence[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1973, 63(12): 1622-1623.
[43] Walther A. Propagation of the generalized radiance through lenses[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1978, 68(11): 1606-1610.
[44] Bastiaans M J. A frequency-domain treatment of partial coherence[J]. Optica Acta: International Journal of Optics, 1977, 24(3): 261-274.
[45] Bastiaans M J. The Wigner distribution function applied to optical signals and systems[J]. Optics Communications, 1978, 25(1): 26-30.
[46] Bastiaans M J. The Wigner distribution function and Hamilton’s characteristics of a geometric-optical system[J]. Optics Communications, 1979, 30(3): 321-326.
[47] Bastiaans M J. Transport equations for the Wigner distribution function[J]. Optica Acta: International Journal of Optics, 1979, 26(10): 1265-1272.
[48] Bastiaans M J. Wigner distribution function and its application to first-order optics[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1979, 69(12): 1710-1716.
[49] Bastiaans M J. Transport equations for the Wigner distribution function in an inhomogeneous and dispersive medium[J]. Optica Acta: International Journal of Optics, 1979, 26(11): 1333-1344.
[50] Bastiaans M J. The Wigner distribution function of partially coherent light[J]. Optica Acta: International Journal of Optics, 1981, 28(9): 1215-1224.
[51] Bastiaans M J. Application of the Wigner distribution function to partially coherent light[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1986, 3(8): 1227-1238.
[52] Zhang ZY, LevoyM. Wigner distributions and how they relate to the light field[C] //2009 IEEE International Conference on Computational Photography (ICCP), April 16-17, 2009, San Francisco, CA, USA.New York: IEEE Press, 2009: 1- 10.
[53] Pu J X, Zhang H H, Nemoto S. Spectral shifts and spectral switches of partially coherent light passing through an aperture[J]. Optics Communications, 1999, 162(1/2/3): 57-63.
[54] Pu J X, Cai C, Nemoto S. Spectral anomalies in Young’s double-slit interference experiment[J]. Optics Express, 2004, 12(21): 5131-5139.
[55] 陈斐楠, 陈晶晶, 赵琦, 等. 高阶贝塞尔高斯光束在非柯尔莫哥诺夫大气中的传输特性[J]. 中国激光, 2012, 39(9): 0913001.
[56] 陈延如, 赵琦. 随机分布粒子侧向散射光特性的实验研究[J]. 光学学报, 2003, 23(9): 1110-1114.
[57] 郭旭岳, 李冰洁, 樊鑫豪, 等. 基于电介质超表面的光场复振幅调制及应用[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2020, 49(9): 20201031.
[58] Guo X Y, Li P, Zhong J Z, et al. Tying polarization-switchable optical vortex knots and links via holographic all-dielectric metasurfaces[J]. Laser & Photonics Reviews, 2020, 14(3): 1900366.
[59] 陆延青. 液晶光子学研究进展[J]. 光学与光电技术, 2017, 15(1): 9-12.
[60] 陈鹏, 徐然, 胡伟, 等. 基于光取向液晶的光场调控技术[J]. 光学学报, 2016, 36(10): 1026005.
[61] 袁小聪, 贾平, 雷霆, 等. 光学旋涡与轨道角动量光通信[J]. 深圳大学学报(理工版), 2014, 31(4): 331-346.
Yuan X C, Jia P, Lei T, et al. Optical vortices and optical communication with orbital angular momentum[J]. Journal of Shenzhen University Science and Engineering, 2014, 31(4): 331-346.
[62] Lei T, Zhang M, Li Y R, et al. Massive individual orbital angular momentum channels for multiplexing enabled by Dammann gratings[J]. Light: Science & Applications, 2015, 4(3): e257.
[63] Zhan Q W. Cylindrical vector beams: from mathematical concepts to applications[J]. Advances in Optics and Photonics, 2009, 1(1): 1-57.
[64] 陈建, 詹其文. 矢量光场与激光焦场定制[J]. 光学学报, 2019, 39(1): 0126002.
[65] 李占成, 刘文玮, 程化, 等. 基于光学人工微结构的光场调控研究[J]. 物理实验, 2019, 39(12): 1-10, 14.
Li Z C, Liu W W, Cheng H, et al. Manipulating optical waves based on artificial nanostructures[J]. Physics Experimentation, 2019, 39(12): 1-10, 14.
[66] Li J X, Chen S Q, Yang H F, et al. Simultaneous control of light polarization and phase distributions using plasmonic metasurfaces[J]. Advanced Functional Materials, 2015, 25(5): 704-710.
[67] Cai Y J, Lu X H, Lin Q. Hollow Gaussian beams and their propagation properties[J]. Optics Letters, 2003, 28(13): 1084-1086.
[68] Cai Y J, He S L. Propagation of various dark hollow beams in a turbulent atmosphere[J]. Optics Express, 2006, 14(4): 1353-1367.
[69] Zhao C L, Cai Y J. Trapping two types of particles using a focused partially coherent elegant Laguerre-Gaussian beam[J]. Optics Letters, 2011, 36(12): 2251-2253.
[70] 卢兴园, 赵承良, 蔡阳健. 部分相干照明下的相位恢复方法及应用研究进展[J]. 中国激光, 2020, 47(5): 0500016.
[71] 万玉红, 满天龙, 陶世荃. 非相干全息术成像特性及研究进展[J]. 中国激光, 2014, 41(2): 0209004.
[72] 方璐, 戴琼海. 计算光场成像[J]. 光学学报, 2020, 40(1): 0111001.
Fang L, Dai Q H. Computational light field imaging[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2020, 40(1): 0111001.
[73] Wu J M, Lu Z, Jiang D, et al. Iterative tomography with digital adaptive optics permits hour-long intravital observation of 3D subcellular dynamics at millisecond scale[J]. Cell, 2021, 184(12): 3318-3332.
[74] Li H Y, Guo C L, Kim-Holzapfel D, et al. Fast, volumetric live-cell imaging using high-resolution light-field microscopy[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2019, 10(1): 29-49.
[75] Zhang Z K, Bai L, Cong L, et al. Imaging volumetric dynamics at high speed in mouse and zebrafish brain with confocal light field microscopy[J]. Nature Biotechnology, 2021, 39(1): 74-83.
[76] Cai Z W, Liu X L, Peng X, et al. Structured light field 3D imaging[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(18): 20324-20334.
[77] Santarsiero M, Borghi R. Measuring spatial coherence by using a reversed-wavefront young interferometer[J]. Optics Letters, 2006, 31(7): 861-863.
[78] González A I, Mejía Y. Nonredundant array of apertures to measure the spatial coherence in two dimensions with only one interferogram[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, Optics, Image Science, and Vision, 2011, 28(6): 1107-1113.
[79] Marks D L, Stack R A, Brady D J, et al. Visible cone-beam tomography with a lensless interferometric camera[J]. Science, 1999, 284(5423): 2164-2166.
[80] Iaconis C, Walmsley I A. Direct measurement of the two-point field correlation function[J]. Optics Letters, 1996, 21(21): 1783-1785.
[81] Itoh K, Ohtsuka Y. Fourier-transform spectral imaging: retrieval of source information from three-dimensional spatial coherence[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1986, 3(1): 94-100.
[82] Mendlovic D, Shabtay G, Lohmann A W, et al. Display of spatial coherence[J]. Optics Letters, 1998, 23(14): 1084-1086.
[83] Alonso M A. Diffraction of paraxial partially coherent fields by planar obstacles in the Wigner representation[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, Optics, Image Science, and Vision, 2009, 26(7): 1588-1597.
[84] Cho S, Alonso M A, Brown T G. Measurement of spatial coherence through diffraction from a transparent mask with a phase discontinuity[J]. Optics Letters, 2012, 37(13): 2724-2726.
[85] Raymer M G, Beck M, McAlister D. Complex wave-field reconstruction using phase-space tomography[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1994, 72(8): 1137-1140.
[86] McAlister D F, Beck M, Clarke L, et al. Optical phase retrieval by phase-space tomography and fractional-order Fourier transforms[J]. Optics Letters, 1995, 20(10): 1181-1183.
[87] Nugent K A. Wave field determination using three-dimensional intensity information[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1992, 68(15): 2261-2264.
[88] Hazak G. Comment on “Wave field determination using three-dimensional intensity information”[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1992, 69(19): 2874.
[89] Gori F, Guattari G, Santarsiero M. Coherence and the spatial distribution of intensity[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1993, 10(4): 673-679.
[90] Tran C Q, Peele A G, Paterson D, et al. Phase space density measurement of interfering X-rays[J]. Journal of Electron Spectroscopy and Related Phenomena, 2005, 144/145/146/147: 947-951.
[91] Agarwal G S, Simon R. Reconstruction of the Wigner transform of a rotationally symmetric two-dimensional beam from the Wigner transform of the beam’s one-dimensional sample[J]. Optics Letters, 2000, 25(18): 1379-1381.
[92] Dragoman D. Can the Wigner transform of a two-dimensional rotationally symmetric beam be fully recovered from the Wigner transform of its one-dimensional approximation?[J]. Optics Letters, 2000, 25(5): 281-283.
[94] Bartelt H O, Brenner K H, Lohmann A W. The Wigner distribution function and its optical production[J]. Optics Communications, 1980, 32(1): 32-38.
[97] Stoklasa B, Motka L, Rehacek J, et al. Wavefront sensing reveals optical coherence[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5: 3275.
[98] Hartmann J. Bemerkungen uber den bau und die justirung von spektrographen[J]. Zt. Instrumentenkd, 1990, 20(47): 17-27.
[99] Platt B C, Shack R. History and principles of Shack-Hartmann wavefront sensing[J]. Journal of Refractive Surgery, 2001, 17(5): S573-S577.
[100] Shack R V, Platt B. Production and use of a lenticular Hartmann screen[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1971, 656.
[102] Zhang Z, Chen Z, Rehman S, et al. Factored form descent: a practical algorithm for coherence retrieval[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(5): 5759-5780.
[103] Bao C L, Barbastathis G, Ji H, et al. Coherence retrieval using trace regularization[J]. SIAM Journal on Imaging Sciences, 2018, 11(1): 679-706.
[104] Liang CK, Lin TH, Wong BY, et al.Programmable aperture photography: multiplexed light field acquisition[C] //ACM SIGGRAPH 2008 papers on-SIGGRAPH’08, August 11-15, 2008, Los Angeles, California. New York: ACM Press, 2008: 10.
[105] Levin A, Fergus R, Durand F, et al. Image and depth from a conventional camera with a coded aperture[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2007, 26(3): 70.
[106] Zuo C, Sun J S, Feng S J, et al. Programmable aperture microscopy: a computational method for multi-modal phase contrast and light field imaging[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2016, 80: 24-31.
[107] AntipaN, NeculaS, NgR, et al.Single-shot diffuser-encoded light field imaging[C] //2016 IEEE International Conference on Computational Photography (ICCP), May 13-15, 2016, Evanston, IL, USA.New York: IEEE Press, 2016: 1- 11.
[109] Liu C, Qiu J, Jiang M. Light field reconstruction from projection modeling of focal stack[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(10): 11377-11388.
[110] WilburnB, JoshiN, VaishV, et al.High performance imaging using large camera arrays[C] //ACM SIGGRAPH 2005 Papers on-SIGGRAPH’05, July 31-August 4, 2005, Los Angeles, California.New York: ACM Press, 2005: 765- 776.
[111] LevoyM, NgR, AdamsA, et al.Light field microscopy[C] //ACM SIGGRAPH 2006 Papers on - SIGGRAPH’06, July 30-August 3, 2006, Boston, Massachusetts.New York: ACM Press, 2006: 924- 934.
[113] Guo C L, Liu W H, Hua X W, et al. Fourier light-field microscopy[J]. Optics Express, 2019, 27(18): 25573-25594.
[114] Rosen J, Brooker G. Fresnel incoherent correlation holography (FINCH): a review of research[J]. Advanced Optical Technologies, 2012, 1(3): 151-169.
[115] Vijayakumar A, Kashter Y, Kelner R, et al. Coded aperture correlation holography-a new type of incoherent digital holograms[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(11): 12430-12441.
[116] Kumar M, Vijayakumar A, Rosen J. Incoherent digital holograms acquired by interferenceless coded aperture correlation holography system without refractive lenses[J]. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 11555.
[117] Vijayakumar A, Rosen J. Interferenceless coded aperture correlation holography: a new technique for recording incoherent digital holograms without two-wave interference[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(12): 13883-13896.
[118] Rosen J, Brooker G. Non-scanning motionless fluorescence three-dimensional holographic microscopy[J]. Nature Photonics, 2008, 2(3): 190-195.
[120] Rai M R, Vijayakumar A, Rosen J. Non-linear adaptive three-dimensional imaging with interferenceless coded aperture correlation holography (I-COACH)[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(14): 18143-18154.
[121] Wolf E. New theory of partial coherence in the space-frequency domain part I: spectra and cross spectra of steady-state sources[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1982, 72(3): 343-351.
[122] Zernike F. Diffraction and optical image formation[J]. Proceedings of the Physical Society, 1948, 61(2): 158-164.
[123] Dragoman D. Phase-space interferences as the source of negative values of the Wigner distribution function[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, Optics, Image Science, and Vision, 2000, 17(12): 2481-2485.
[124] Gershun A. The light field[J]. Journal of Mathematics and Physics, 1939, 18(1/2/3/4): 51-151.
[125] Adelson E H, Bergen J R. The plenoptic function and the elements of early vision[J]. Computational Models of Visual Processing, 1991: 3-20.
[126] LevoyM, HanrahanP. Light field rendering[C] //Proceedings of the 23rd annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques-SIGGRAPH’96, August 4-9, 1996, New Orleans, LA, USA.New York: ACM Press, 1996: 31- 42.
[127] CamahortE, LeriosA, FussellD. Uniformly sampled light fields[M] //Drettakis G, Max N. Rendering techniques’98. Vienna: Springer, 1998: 117- 130.
[128] Zuo C, Chen Q, Tian L, et al. Transport of intensity phase retrieval and computational imaging for partially coherent fields: the phase space perspective[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2015, 71: 20-32.
[129] Ng R. Fourier slice photography[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2005, 24(3): 735-744.
[130] BornM, WolfE. Principles of optics: electromagnetic theory of propagation, interference and diffraction of light[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2013.
[131] Kirchhoff G. Zur theorie der lichtstrahlen[J]. Annalen Der Physik, 1883, 254(4): 663-695.
[132] Goodman JW. Introduction to Fourier optics[M]. Colorado: Roberts and Company Publishers, 2005.
[133] Teague M R. Deterministic phase retrieval: a Green’s function solution[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1983, 73(11): 1434-1441.
[134] Streibl N. Phase imaging by the transport equation of intensity[J]. Optics Communications, 1984, 49(1): 6-10.
[136] Gori F. Directionality and spatial coherence[J]. Optica Acta: International Journal of Optics, 1980, 27(8): 1025-1034.
[137] Wolf E. New spectral representation of random sources and of the partially coherent fields that they generate[J]. Optics Communications, 1981, 38(1): 3-6.
[138] Starikov A, Wolf E. Coherent-mode representation of Gaussian Schell-model sources and of their radiation fields[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1982, 72(7): 923-928.
[139] Kemper B, Langehanenberg P, von Bally G. Digital holographic microscopy[J]. Optik & Photonik, 2007, 2(2): 41-44.
[140] Kim MK. Digital holographic microscopy[M] //Digital holographic microscopy. Springer series in materials science. New York: Springer, 2011, 162: 149- 190.
[141] Kemper B, von Bally G. Digital holographic microscopy for live cell applications and technical inspection[J]. Applied Optics, 2008, 47(4): A52-A61.
[142] Marquet P, Rappaz B, Magistretti P J, et al. Digital holographic microscopy: a noninvasive contrast imaging technique allowing quantitative visualization of living cells with subwavelength axial accuracy[J]. Optics Letters, 2005, 30(5): 468-470.
[143] Ragazzoni R. Pupil plane wavefront sensing with an oscillating prism[J]. Journal of Modern Optics, 1996, 43(2): 289-293.
[144] Esposito S, Riccardi A. Pyramid wavefront sensor behavior in partial correction adaptive optic systems[J]. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2001, 369(2): L9-L12.
[145] Ragazzoni R, Diolaiti E, Vernet E. A pyramid wavefront sensor with no dynamic modulation[J]. Optics Communications, 2002, 208(1/2/3): 51-60.
[146] Neil M A A, Booth M J, Wilson T. New modal wave-front sensor: a theoretical analysis[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 2000, 17(6): 1098-1107.
[147] Booth M J. Wave front sensor-less adaptive optics: a model-based approach using sphere packings[J]. Optics Express, 2006, 14(4): 1339-1352.
[148] Schäfer B, Mann K. Determination of beam parameters and coherence properties of laser radiation by use of an extended Hartmann-Shack wave-front sensor[J]. Applied Optics, 2002, 41(15): 2809-2817.
[149] Schäfer B, Lübbecke M, Mann K. Hartmann-Shack wave front measurements for real time determination of laser beam propagation parameters[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2006, 77(5): 053103.
[150] Pfund J, Lindlein N, Schwider J, et al. Absolute sphericity measurement: a comparative study of the use of interferometry and a Shack-Hartmann sensor[J]. Optics Letters, 1998, 23(10): 742-744.
[151] Greivenkamp J E, Smith D G, Gappinger R O, et al. Optical testing using Shack-Hartmann wavefront sensors[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2001, 4416: 260-263.
[152] Ricklin J C, Davidson F M. Atmospheric turbulence effects on a partially coherent Gaussian beam: implications for free-space laser communication[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 2002, 19(9): 1794-1802.
[153] Dayton D, Gonglewski J, Pierson B, et al. Atmospheric structure function measurements with a Shack-Hartmann wave-front sensor[J]. Optics Letters, 1992, 17(24): 1737-1739.
[154] Booth M J. Adaptive optics in microscopy[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 2007, 365(1861): 2829-2843.
[155] Cha J W, Ballesta J, So P T C. Shack-Hartmann wavefront-sensor-based adaptive optics system for multiphoton microscopy[J]. Journal of Biomedical Optics, 2010, 15(4): 046022.
[156] Liang J, Grimm B, Goelz S, et al. Objective measurement of wave aberrations of the human eye with the use of a Hartmann-Shack wave-front sensor[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, Optics, Image Science, and Vision, 1994, 11(7): 1949-1957.
[157] Moreno-Barriuso E, Navarro R. Laser ray tracing versus Hartmann-Shack sensor for measuring optical aberrations in the human eye[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 2000, 17(6): 974-985.
[158] KohnenT, Koch DD. Cataract and refractive surgery[M]. Heidelberg: Springer, 2006.
[159] Gerchberg R W. A practical algorithm for the determination of phase from image and diffraction plane pictures[J]. Optik, 1972, 35: 237-250.
[160] Allen L J, Oxley M P. Phase retrieval from series of images obtained by defocus variation[J]. Optics Communications, 2001, 199(1/2/3/4): 65-75.
[161] Bauschke H H, Combettes P L, Luke D R. Phase retrieval, error reduction algorithm, and fienup variants: a view from convex optimization[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 2002, 19(7): 1334-1345.
[162] Bauschke H H, Combettes P L, Luke D R. Hybrid projection-reflection method for phase retrieval[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, Optics, Image Science, and Vision, 2003, 20(6): 1025-1034.
[163] Elser V. Phase retrieval by iterated projections[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 2003, 20(1): 40-55.
[164] Luke D R. Relaxed averaged alternating reflections for diffraction imaging[J]. Inverse Problems, 2005, 21(1): 37-50.
[165] Faulkner H M L, Rodenburg J M. Movable aperture lensless transmission microscopy: a novel phase retrieval algorithm[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2004, 93(2): 023903.
[166] Faulkner H M L, Rodenburg J M. Error tolerance of an iterative phase retrieval algorithm for moveable illumination microscopy[J]. Ultramicroscopy, 2005, 103(2): 153-164.
[168] Zuo C, Li J J, Sun J S, et al. Transport of intensity equation: a tutorial[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2020, 135: 106187.
[169] Hamilton D K, Sheppard C J R. Differential phase contrast in scanning optical microscopy[J]. Journal of Microscopy, 1984, 133(1): 27-39.
[170] Hamilton D K, Sheppard C J R, Wilson T. Improved imaging of phase gradients in scanning optical microscopy[J]. Journal of Microscopy, 1984, 135(3): 275-286.
[171] Zheng G A, Shen C, Jiang S W, et al. Concept, implementations and applications of Fourier ptychography[J]. Nature Reviews Physics, 2021, 3(3): 207-223.
[172] 左超, 陈钱, 孙佳嵩, 等. 基于光强传输方程的非干涉相位恢复与定量相位显微成像: 文献综述与最新进展[J]. 中国激光, 2016, 43(6): 0609002.
[173] 孙佳嵩, 张玉珍, 陈钱, 等. 傅里叶叠层显微成像技术: 理论、发展和应用[J]. 光学学报, 2016, 36(10): 1011005.
[174] 范瑶, 陈钱, 孙佳嵩, 等. 差分相衬显微成像技术发展综述[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2019, 48(6): 0603014.
[175] Pan A, Zuo C, Yao B. High-resolution and large field-of-view Fourier ptychographic microscopy and its applications in biomedicine[J]. Reports on Progress in Physics. Physical Society, 2020, 83(9): 096101.
[176] 潘兴臣, 刘诚, 陶华, 等. Ptychography相位成像及其关键技术进展[J]. 光学学报, 2020, 40(1): 0111010.
[177] Mejía Y, González A I. Measuring spatial coherence by using a mask with multiple apertures[J]. Optics Communications, 2007, 273(2): 428-434.
[178] Tu J H, Tamura S. Wave field determination using tomography of the ambiguity function[J]. Physical Review E, 1997, 55(2): 1946-1949.
[179] Dragoman D, Dragoman M, Brenner K H. Tomographic amplitude and phase recovery of vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers by use of the ambiguity function[J]. Optics Letters, 2002, 27(17): 1519-1521.
[180] Dragoman D, Dragoman M, Brenner K H. Amplitude and phase recovery of rotationally symmetric beams[J]. Applied Optics, 2002, 41(26): 5512-5518.
[181] Liu X, Brenner K H. Reconstruction of two-dimensional complex amplitudes from intensity measurements[J]. Optics Communications, 2003, 225(1/2/3): 19-30.
[182] Testorf M E, Semichaevsky A. Phase retrieval and phase-space tomography from incomplete data sets[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2004, 5562: 38-49.
[183] Lohmann A W. Image rotation, Wigner rotation, and the fractional Fourier transform[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1993, 10(10): 2181-2186.
[184] Lohmann A W, Soffer B H. Relationships between the Radon-Wigner and fractional Fourier transforms[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1994, 11(6): 1798-1801.
[185] Zhang ZY, BarbastathisG. Regularizers for coherence retrieval and their physical interpretation[C] //Computational Optical Sensing and Imaging 2014, June 22-26, 2014, Kohala Coast, Hawaii, United States. Washington, D.C.: OSA, 2014: CW4C. 4.
[186] Banaszek K, Wódkiewicz K. Direct probing of quantum phase space by photon counting[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1996, 76(23): 4344-4347.
[187] Chapman H N. Phase-retrieval X-ray microscopy by Wigner-distribution deconvolution[J]. Ultramicroscopy, 1996, 66(3/4): 153-172.
[189] Lin X, Wu J M, Zheng G A, et al. Camera array based light field microscopy[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2015, 6(9): 3179-3189.
[190] Perwass C, Wietzke L. Single lens 3D-camera with extended depth-of-field[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 2012, 8291: 829108.
[191] VeeraraghavanA, RaskarR, AgrawalA, et al.Dappled photography: mask enhanced cameras for heterodyned light fields and coded aperture refocusing[C] //ACM SIGGRAPH 2007 papers on-SIGGRAPH’07, August 5-9, 2007, San Diego, California. New York: ACM Press, 2007: 69.
[192] Marwah K, Wetzstein G, Bando Y, et al. Compressive light field photography using overcomplete dictionaries and optimized projections[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2013, 32(4): 1-12.
[193] Chen N, Ren Z, Lam E Y. High-resolution Fourier hologram synthesis from photographic images through computing the light field[J]. Applied Optics, 2016, 55(7): 1751-1756.
[194] Yin X W, Wang G J, Li W T, et al. Iteratively reconstructing 4D light fields from focal stacks[J]. Applied Optics, 2016, 55(30): 8457-8463.
[195] Chen N, Zuo C, Lam E, et al. 3D imaging based on depth measurement technologies[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(11): 3711.
[196] 陈妮, 左超, Lee B. 基于深度测量的三维成像技术[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2019, 48(6): 0603013.
[197] Orth A, Crozier K B. Light field moment imaging[J]. Optics Letters, 2013, 38(15): 2666-2668.
[199] Liu J D, Xu T F, Yue W R, et al. Light-field moment microscopy with noise reduction[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(22): 29154-29162.
[200] Levoy M, Zhang Z. McDowall I. Recording and controlling the 4D light field in a microscope using microlens arrays[J]. Journal of Microscopy, 2009, 235(2): 144-162.
[201] Barone-Nugent E D, Barty A, Nugent K A. Quantitative phase-amplitude microscopy I: optical microscopy[J]. Journal of Microscopy, 2002, 206(3): 194-203.
[202] Jenkins M H, Gaylord T K. Quantitative phase microscopy via optimized inversion of the phase optical transfer function[J]. Applied Optics, 2015, 54(28): 8566-8579.
[203] Chakraborty T, Petruccelli J C. Source diversity for transport of intensity phase imaging[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(8): 9122-9137.
[204] Kou S S, Waller L, Barbastathis G, et al. Quantitative phase restoration by direct inversion using the optical transfer function[J]. Optics Letters, 2011, 36(14): 2671-2673.
[205] Sung Y, Choi W, Fang-Yen C, et al. Optical diffraction tomography for high resolution live cell imaging[J]. Optics Express, 2009, 17(1): 266-277.
[206] Gureyev T E, Davis T J, Pogany A, et al. Optical phase retrieval by use of first Born- and Rytov-type approximations[J]. Applied Optics, 2004, 43(12): 2418-2430.
[207] Lu L P, Fan Y, Sun J S, et al. Accurate quantitative phase imaging by the transport of intensity equation: a mixed-transfer-function approach[J]. Optics Letters, 2021, 46(7): 1740-1743.
[208] Gabor D. A new microscopic principle[J]. Nature, 1948, 161(4098): 777-778.
[209] Takeda M, Wang W, Duan Z H, et al. Coherence holography[J]. Optics Express, 2005, 13(23): 9629-9635.
[210] Naik D N, Ezawa T, Miyamoto Y, et al. 3-D coherence holography using a modified Sagnac radial shearing interferometer with geometric phase shift[J]. Optics Express, 2009, 17(13): 10633-10641.
[211] Naik D N, Ezawa T, Miyamoto Y, et al. Real-time coherence holography[J]. Optics Express, 2010, 18(13): 13782-13787.
[212] Naik D N, Ezawa T, Miyamoto Y, et al. Phase-shift coherence holography[J]. Optics Letters, 2010, 35(10): 1728-1730.
[213] Naik D N, Singh R K, Ezawa T, et al. Photon correlation holography[J]. Optics Express, 2011, 19(2): 1408-1421.
[214] Rosen J, Brooker G. Digital spatially incoherent Fresnel holography[J]. Optics Letters, 2007, 32(8): 912-914.
[215] Naik D N, Pedrini G, Osten W. Recording of incoherent-object hologram as complex spatial coherence function using Sagnac radial shearing interferometer and a Pockels cell[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(4): 3990-3995.
[217] Kim S G, Lee B, Kim E S. Removal of bias and the conjugate image in incoherent on-axis triangular holography and real-time reconstruction of the complex hologram[J]. Applied Optics, 1997, 36(20): 4784-4791.
[218] Pedrini G, Li H, Faridian A, et al. Digital holography of self-luminous objects by using a Mach-Zehnder setup[J]. Optics Letters, 2012, 37(4): 713-715.
[219] Kang S, Jeong S, Choi W, et al. Imaging deep within a scattering medium using collective accumulation of single-scattered waves[J]. Nature Photonics, 2015, 9(4): 253-258.
[220] van der Horst J, Trull A K, Kalkman J. Deep-tissue label-free quantitative optical tomography[J]. Optica, 2020, 7(12): 1682-1689.
[221] Huang D, Swanson E A, Lin C P, et al. Optical coherence tomography[J]. Science, 1991, 254(5035): 1178-1181.
[222] Wang L, Ho P P, Liu C, et al. Ballistic 2-D imaging through scattering walls using an ultrafast optical Kerr gate[J]. Science, 1991, 253(5021): 769-771.
[223] Tyson RK. Principles of adaptive optics[M]. Boston: CRC Press, 2015.
[224] Webb R H. Confocal optical microscopy[J]. Reports on Progress in Physics, 1996, 59(3): 427-471.
[225] Yaqoob Z, Psaltis D, Feld M S, et al. Optical phase conjugation for turbidity suppression in biological samples[J]. Nature Photonics, 2008, 2(2): 110-115.
[227] Papadopoulos I N, Jouhanneau J S, Poulet J F, et al. Scattering compensation by focus scanning holographic aberration probing (F-SHARP)[J]. Nature Photonics, 2017, 11(2): 116-123.
[228] Vellekoop I M, Mosk A P. Focusing coherent light through opaque strongly scattering media[J]. Optics Letters, 2007, 32(16): 2309-2311.
[229] Vellekoop I M. Feedback-based wavefront shaping[J]. Optics Express, 2015, 23(9): 12189-12206.
[231] Popoff S M, Lerosey G, Fink M, et al. Controlling light through optical disordered media: transmission matrix approach[J]. New Journal of Physics, 2011, 13(12): 123021.
[232] Katz O, Ramaz F, Gigan S, et al. Controlling light in complex media beyond the acoustic diffraction-limit using the acousto-optic transmission matrix[J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 717.
[233] Li Y Z, Xue Y J, Tian L. Deep speckle correlation: a deep learning approach toward scalable imaging through scattering media[J]. Optica, 2018, 5(10): 1181-1190.
[234] Barbastathis G, Ozcan A, Situ G H. On the use of deep learning for computational imaging[J]. Optica, 2019, 6(8): 921-943.
[235] Mahalati R N, Gu R Y, Kahn J M. Resolution limits for imaging through multi-mode fiber[J]. Optics Express, 2013, 21(2): 1656-1668.
[236] Freund I, Rosenbluh M, Feng S. Memory effects in propagation of optical waves through disordered media[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1988, 61(20): 2328-2331.
[239] 朱磊, 邵晓鹏. 散射成像技术的研究进展[J]. 光学学报, 2020, 40(1): 0111005.
[240] 陈子阳, 陈丽, 范伟如, 等. 基于相关全息原理的散射成像技术及其进展[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2021, 58(2): 0200001.
[241] Kendrick RL, DuncanA, OgdenC, et al. Segmented planar imaging detector for EO reconnaissance[C] //Computational Optical Sensing and Imaging 2013, June 23-27, 2013, Arlington, Virginia, United States. Washington, D.C.: OSA, 2013: CM4C. 1.
[243] Katz B, Rosen J. Super-resolution in incoherent optical imaging using synthetic aperture with Fresnel elements[J]. Optics Express, 2010, 18(2): 962-972.
[244] Charrière F, Marian A, Montfort F, et al. Cell refractive index tomography by digital holographic microscopy[J]. Optics Letters, 2006, 31(2): 178-180.
[245] Buzug TM. Computed tomography[M] //Kramme R, Hoffmann K P, Pozos R S. Springer handbook of medical technology. Springer handbooks. Heidelberg: Springer, 2011: 311- 342.
[246] Choi W, Fang-Yen C, Badizadegan K, et al. Tomographic phase microscopy[J]. Nature Methods, 2007, 4(9): 717-719.
[248] Feldkamp L A, Davis L C, Kress J W. Practical cone-beam algorithm[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, 1984, 1(6): 612-619.
[249] Tuy H K. An inversion formula for cone-beam reconstruction[J]. SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, 1983, 43(3): 546-552.
[251] Pégard N C, Liu H Y, Antipa N, et al. Compressive light-field microscopy for 3D neural activity recording[J]. Optica, 2016, 3(5): 517-524.
[252] Skocek O, Nöbauer T, Weilguny L, et al. High-speed volumetric imaging of neuronal activity in freely moving rodents[J]. Nature Methods, 2018, 15(6): 429-432.
[255] Siegel N, Lupashin V, Storrie B, et al. High-magnification super-resolution FINCH microscopy using birefringent crystal lens interferometers[J]. Nature Photonics, 2016, 10(12): 802-808.
[257] Kelner R, Rosen J. Parallel-mode scanning optical sectioning using digital Fresnel holography with three-wave interference phase-shifting[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(3): 2200-2214.
[258] 肖相国, 王忠厚, 孙传东, 等. 基于光场摄像技术的对焦测距方法的研究[J]. 光子学报, 2008, 37(12): 2539-2543.
Xiao X G, Wang Z H, Sun C D, et al. A range focusing measurement technology based on light field photography[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2008, 37(12): 2539-2543.
[259] VaishV, GargG, TalvalaE, et al.Synthetic aperture focusing using a shear-warp factorization of the viewing transform[C] //2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’05)-Workshops, September 21-23, 2005, San Diego, CA, USA.New York: IEEE Press, 2005: 129.
[260] Rosen J, Brooker G. Fluorescence incoherent color holography[J]. Optics Express, 2007, 15(5): 2244-2250.
[261] Tran C Q, Peele A G, Roberts A, et al. Synchrotron beam coherence: a spatially resolved measurement[J]. Optics Letters, 2005, 30(2): 204-206.
[262] Tran C Q, Peele A G, Roberts A, et al. X-ray imaging: a generalized approach using phase-space tomography[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, Optics, Image Science, and Vision, 2005, 22(8): 1691-1700.
[263] Tran C Q, Williams G J, Roberts A, et al. Experimental measurement of the four-dimensional coherence function for an undulator X-ray source[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2007, 98(22): 224801.
[264] Cámara A, Alieva T, Rodrigo J A, et al. Phase space tomography reconstruction of the Wigner distribution for optical beams separable in cartesian coordinates[J]. Journal of the Optical Society of America A, Optics, Image Science, and Vision, 2009, 26(6): 1301-1306.
[265] Cámara A, Alieva T, Rodrigo J A, et al. Phase-space tomography with a programmable Radon-Wigner display[J]. Optics Letters, 2011, 36(13): 2441-2443.
[266] Cámara A, Alieva T, Castro I, et al. Phase-space tomography for characterization of rotationally symmetric beams[J]. Journal of Optics, 2014, 16(1): 015705.
[268] Pan S H, Ma J, Zhu R H, et al. Real-time complex amplitude reconstruction method for beam quality M2 factor measurement[J]. Optics Express, 2017, 25(17): 20142-20155.
[269] Whitehead L W, Williams G J, Quiney H M, et al. Diffractive imaging using partially coherent X rays[J]. Physical Review Letters, 2009, 103(24): 243902.
[272] Tian L, Li X, Ramchandran K, et al. Multiplexed coded illumination for Fourier Ptychography with an LED array microscope[J]. Biomedical Optics Express, 2014, 5(7): 2376-2389.
[273] Sun J S, Chen Q, Zhang Y Z, et al. Sampling criteria for Fourier ptychographic microscopy in object space and frequency space[J]. Optics Express, 2016, 24(14): 15765-15781.
[274] Katz B, Rosen J. Could safe concept be applied for designing a new synthetic aperture telescope?[J]. Optics Express, 2011, 19(6): 4924-4936.
[276] Kashter Y, Vijayakumar A, Miyamoto Y, et al. Enhanced resolution using Fresnel incoherent correlation holography with structured illumination[J]. Optics Letters, 2016, 41(7): 1558-1561.
[277] Su T H, Liu G Y, Badham K E, et al. Interferometric imaging using Si3N4 photonic integrated circuits for a spider imager[J]. Optics Express, 2018, 26(10): 12801-12812.
[279] Shimano T, Nakamura Y, Tajima K, et al. Lensless light-field imaging with Fresnel zone aperture: quasi-coherent coding[J]. Applied Optics, 2018, 57(11): 2841-2850.
[280] TajimaK, ShimanoT, NakamuraY, et al.Lensless light-field imaging with multi-phased Fresnel zone aperture[C] //2017 IEEE International Conference on Computational Photography (ICCP), May 12-14, 2017, Stanford, CA, USA.New York: IEEE Press, 2017: 1- 7.
[281] Sao M Y, Nakamura Y, Tajima K, et al. Lensless close-up imaging with Fresnel zone aperture[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2018, 57(9S1): 09SB05.
[282] Wu J C, Zhang H, Zhang W H, et al. Single-shot lensless imaging with Fresnel zone aperture and incoherent illumination[J]. Light, Science & Applications, 2020, 9: 53.
[283] Wolf E. Invariance of the spectrum of light on propagation[J]. Physical Review Letters, 1986, 56(13): 1370-1372.
[284] 饶连周, 渠彪, 陈子阳, 等. 部分相干光经单缝衍射后的光谱变化[J]. 光子学报, 2007, 36(3): 467-470.
[285] Siegman A E. New developments in laser resonators[J]. Proceedings of SPIE, 1990, 1224: 2-14.
[286] Rydberg C, Bengtsson J. Numerical algorithm for the retrieval of spatial coherence properties of partially coherent beams from transverse intensity measurements[J]. Optics Express, 2007, 15(21): 13613-13623.
张润南, 蔡泽伟, 孙佳嵩, 卢林芃, 管海涛, 胡岩, 王博文, 周宁, 陈钱, 左超. 光场相干测量及其在计算成像中的应用[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2021, 58(18): 1811003. Runnan Zhang, Zewei Cai, Jiasong Sun, Linpeng Lu, Haitao Guan, Yan Hu, Bowen Wang, Ning Zhou, Qian Chen, Chao Zuo. Optical-Field Coherence Measurement and Its Applications in Computational Imaging[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2021, 58(18): 1811003.