Smart ring resonator–based sensor for multicomponent chemical analysis via machine learning  Download: 734次
Download: 734次
1 National Key Laboratory of Science and Technology on Micro/Nano Fabrication, Institute of Microelectronics, Peking University, Beijing 100871, China
2 Quantum Science and Engineering Centre, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 639798, Singapore
3 Institute of Microelectronics, A*STAR (Agency for Science, Technology and Research), Singapore 138634, Singapore
4 School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 639798, Singapore
5 e-mail: haoyl@pku.edu.cn
6 e-mail: yi_zhang@ntu.edu.sg
7 e-mail: eaqliu@ntu.edu.sg
Figures & Tables
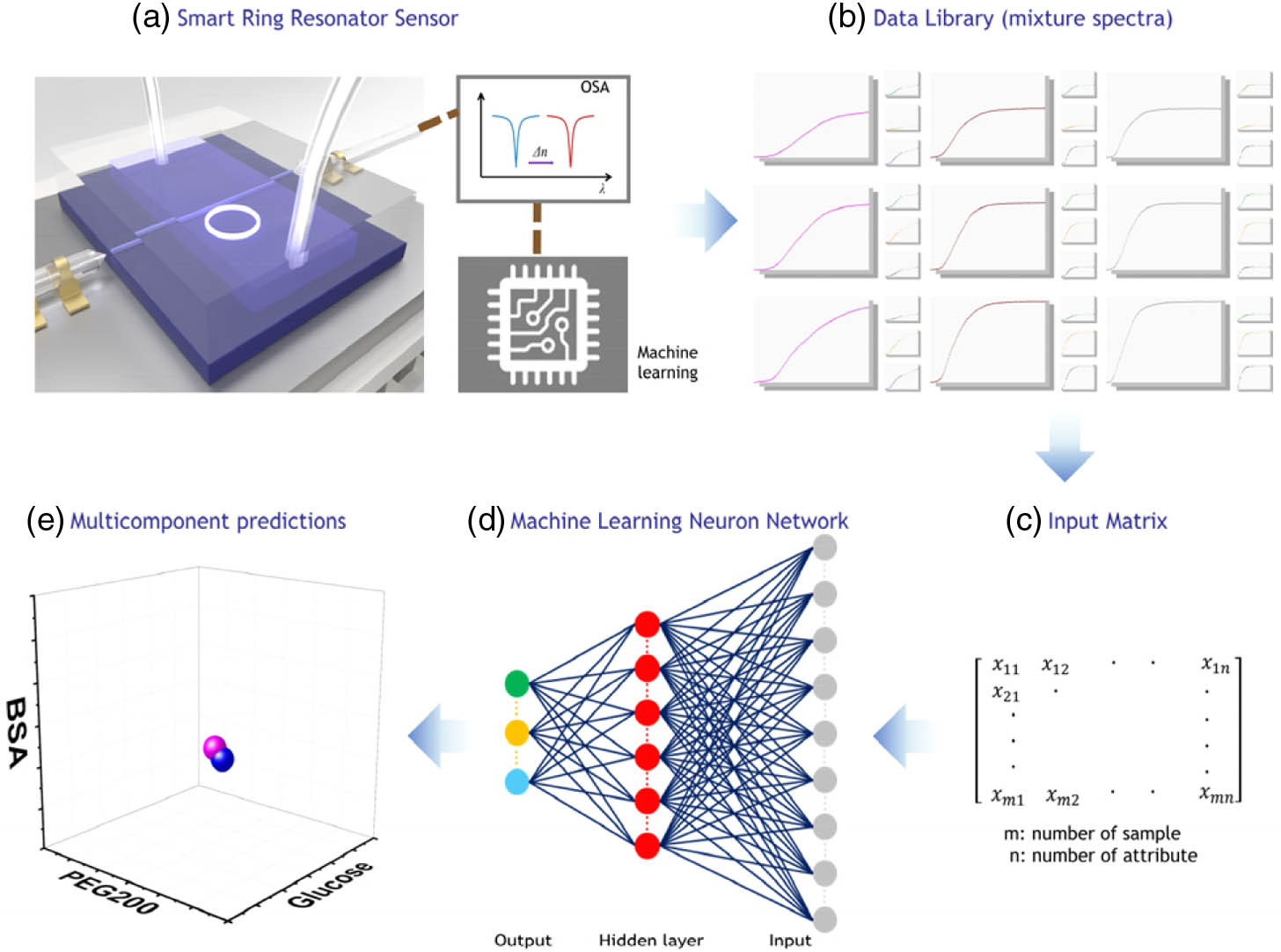
Fig. 1. Schematic illustration of smart sensor framework. (a) Acquisition of resonant spectrum using ring resonator–based smart sensor. (b) Resonant spectra are collected into a data library. (c) Transformation of resonant spectra to matrices. (d) Neural network training with transformed resonant spectra. (e) Composition prediction with neural network model.
下载图片 查看原文
Fig. 2. Neural network of the smart sensor. (a) The resonant spectrum of an unknown sample mixture is acquired with the ring resonator and fed into the trained neural network. The number of neurons in the input, hidden, and output layers is 160, 64, 36, respectively. The 36 attributes of the output are divided into three groups, each with 12 attributes. Each group of 12 attributes is used to predict the concentration of one component in the mixture. The composition of the unknown sample is determined by the predicted concentrations of all three components. (b) Cost function versus training interactions for samples at 10 μL/min as an example.
下载图片 查看原文
Fig. 3. Resonant spectra measured by the ring resonator under various conditions. (a)–(c) Resonator spectra for PEG200, glucose, and BSA solution under a constant flow rate of 30 μL/min. The concentration ranges from 0 to 30 mg/mL with an increment of 5 mg/mL. (d)–(f) Resonator spectra for PEG200, glucose, and BSA solution under a constant concentration of 20 mg/mL. The flow rate ranges from 10 to 90 μL/min with an increment of 20 μL/min. (g) For the resonant spectrum of the mixture with 15 mg/mL PEG200, 5 mg/mL glucose, and 15 mg/mL BSA at 50 μL/min flow rate; (h) for the resonant spectrum of the mixture with 25 mg/mL PEG200, 5 mg/mL glucose, and 5 mg/mL BSA at 50 μL/min flow rate; and (i) for the resonant spectrum of the mixture with 20 mg/mL PEG200, 10 mg/mL glucose, and 5 mg/mL BSA at 50 μL/min flow rate.
下载图片 查看原文
Fig. 4. Composition predicted by the neural network model. (a) 3D distribution of the prediction composition and the ground truth (10 representative points). (b) Histogram of prediction error (RMSE) for all 114 samples in the testing dataset.
下载图片 查看原文
Fig. 5. Predicted concentration versus expected concentration (ground truth) for (a) PEG200, (b) glucose, and (c) BSA.
下载图片 查看原文
Fig. 6. SEM of the fabricated microring resonator.
下载图片 查看原文
Table1. Representative Sample 1 Composition Prediction under Different Experiment Conditionsa
| Flow Rate (μL/min) | PEG200 (mg/mL) | Glucose (mg/mL) | BSA (mg/mL) | Prediction Error RMSE (mg/mL) | | 10 | 15.4 | 5.9 | 14.8 | 0.58 | | 30 | 15.7 | 4.6 | 15.3 | 0.50 | | 50 | 15.0 | 6.0 | 14.3 | 0.70 | | 70 | 14.6 | 4.9 | 14.6 | 0.33 | | 90 | 14.3 | 5.1 | 14.8 | 0.42 | | Average | 15.0 | 5.3 | 14.8 | 0.21 |
|
查看原文
Table2. Representative Sample 2 Composition Prediction under Different Experiment Conditionsa
| Flow Rate (μL/min) | PEG200 (mg/mL) | Glucose (mg/mL) | BSA (mg/mL) | Prediction Error RMSE (mg/mL) | | 10 | 20.7 | 25.7 | 15.8 | 0.73 | | 30 | 21.5 | 24.6 | 15.8 | 1.01 | | 50 | 20.4 | 25.5 | 14.6 | 0.44 | | 70 | 19.9 | 25.2 | 13.9 | 0.65 | | 90 | 19.5 | 25.0 | 14.2 | 0.54 | | Average | 20.4 | 25.3 | 14.9 | 0.29 |
|
查看原文
Table3. Representative Sample 3 Composition Prediction under Different Experiment Conditionsa
| Flow Rate (μL/min) | PEG200 (mg/mL) | Glucose (mg/mL) | BSA (mg/mL) | Prediction Error RMSE (mg/mL) | | 10 | 21.1 | 10.4 | 4.1 | 0.85 | | 30 | 20.6 | 10.1 | 5.3 | 0.39 | | 50 | 19.6 | 11.4 | 4.8 | 0.85 | | 70 | 19.4 | 10.3 | 5.4 | 0.45 | | 90 | 19.4 | 9.7 | 5.3 | 0.42 | | Average | 20.0 | 10.4 | 5.0 | 0.23 |
|
查看原文
Zhenyu Li, Hui Zhang, Binh Thi Thanh Nguyen, Shaobo Luo, Patricia Yang Liu, Jun Zou, Yuzhi Shi, Hong Cai, Zhenchuan Yang, Yufeng Jin, Yilong Hao, Yi Zhang, Ai-Qun Liu. Smart ring resonator–based sensor for multicomponent chemical analysis via machine learning[J]. Photonics Research, 2021, 9(2): 02000B38.
 Download: 734次
Download: 734次