Advanced Photonics, 2019, 1 (5): 055001, Published Online: Sep. 25, 2019
Robust and rapidly tunable light source for SRS/CARS microscopy with low-intensity noise  Download: 759次
Download: 759次
Figures & Tables
Fig. 1. (a) Schematic experimental setup. An Yb-solid-state oscillator allows synchronous generation of the Raman Stokes and pump beams. Using an etalon, the narrowband Stokes beam with picosecond pulse duration is obtained, whereas the Raman pump beam is generated by pumping an OPO, which is subsequently frequency doubled in a periodically poled crystal employing the effect of spectral compression. Using this system, CARS and SRS spectroscopies are both feasible, as depicted in (b) and (c).
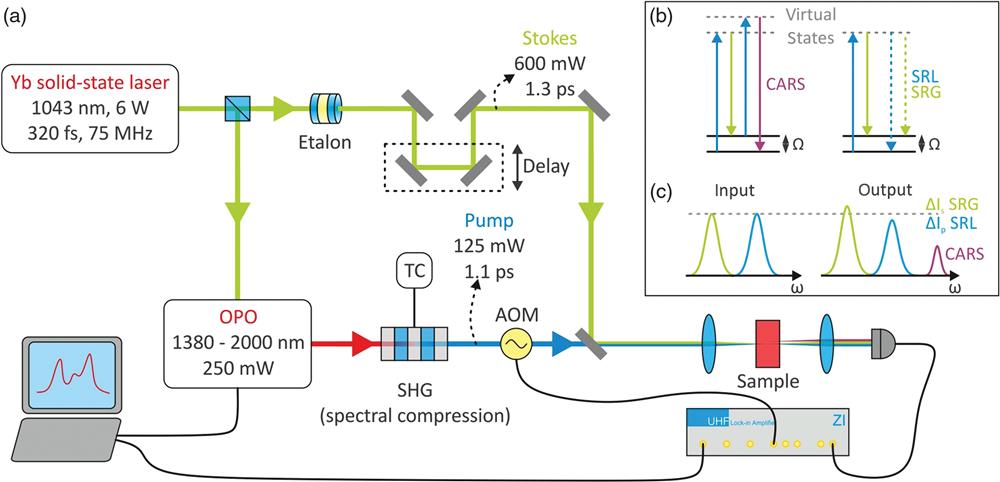
Fig. 2. (a), (b) Spectral range and typical output power of the broadband Raman laser system. (c) By employing an etalon, the Stokes beam reaches a bandwidth of 0.71 nm at 1043.1 nm. The original solid-state oscillator spectrum is indicated in gray. (d) Typical spectrum within the Raman pump spectral range. Due to spectral compression during the SHG, the spectrum typically reaches a bandwidth between 0.5 and 1.2 nm.

Fig. 3. (a) Autocorrelation traces of the Raman pump beam between 750 and 940 nm. Nearly Fourier-limited pulses are observed over the entire Raman pump tuning range, exhibiting typical pulse durations of about 1.1 ps. (b) Autocorrelation of the Stokes beam. (c) Long-term power stability of the Stokes, OPO, and Raman pump (SHG) beams. Fluctuations below 0.5% rms are observed within the Raman pump spectral range, achieving excellent long-term stability. (d) Corresponding relative intensity noise measurements. The Stokes beam reaches the shot-noise limit at a photocurrent of 1.5 mA at about 150 kHz, whereas the OPO and the SHG (Raman pump) exhibit slightly higher noise. All beams are shot-noise limited above 1 MHz, enabling low-noise coherent Raman spectroscopy.

Fig. 4. (a) SRS spectrum of a 1:1 volume mixture of

Fig. 5. (a)

Heiko Linnenbank, Tobias Steinle, Florian Mörz, Moritz Flöss, Han Cui, Andrew Glidle, Harald Giessen. Robust and rapidly tunable light source for SRS/CARS microscopy with low-intensity noise[J]. Advanced Photonics, 2019, 1(5): 055001.